Part4:如何解决ES的性能问题
本文是对一篇外文博客的翻译
This post is the final part of a 4-part series on monitoring Elasticsearch performance. Part 1 provides an overview of Elasticsearch and its key performance metrics, Part 2 explains how to collect these metrics, and Part 3describes how to monitor Elasticsearch with Datadog.
这篇文章是监控ES性能系列文章的最后一部分。第1部分概述了ES及其关键性能指标,第2部分解释了如何收集这些指标,第3部分描述了如何使用Datadog监视ES。
Like a car, Elasticsearch was designed to allow its users to get up and running quickly, without having to understand all of its inner workings. However, it’s only a matter of time before you run into engine trouble here or there. This article will walk through five common Elasticsearch challenges, and how to deal with them.
就像汽车一样,用户可以在无需了解其所有内部工作原理的情况下,快速地站起来并运行。然而,在这里或那里遇到引擎故障只是时间问题。本文将介绍五种常见的ES的挑战,以及如何处理它们。
Problem #1: My cluster status is red or yellow. What should I do?
问题#1:我的集群状态是红色或黄色。我应该做什么?
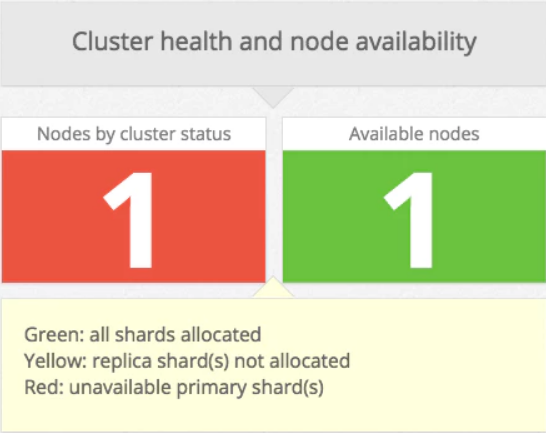
If you recall from Part 1, cluster status is reported as red if one or more primary shards (and its replicas) is missing, and yellow if one or more replica shards is missing. Normally, this happens when a node drops off the cluster for whatever reason (hardware failure, long garbage collection time, etc.). Once the node recovers, its shards will remain in an initializing state before they transition back to active status.
回顾第1部分,如果丢失一个或多个主分片(及其副本),集群状态将报告为红色;如果丢失一个或多个副本分片,则报告为黄色。通常,这种情况发生在节点出于某些原因(硬件故障、长时间的垃圾收集时间等)退出集群时。一旦节点恢复,它的分片在转换会活跃状态之前将保持初始化状态。
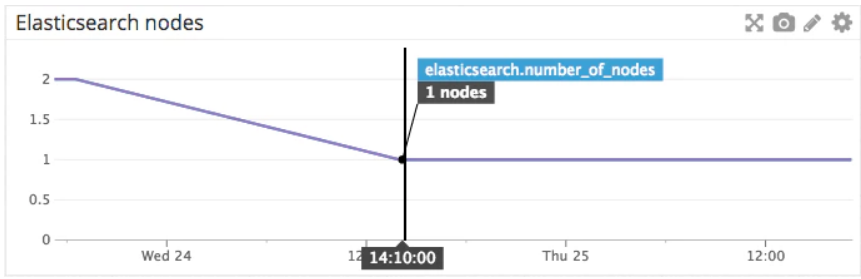
The number of initializing shards typically peaks when a node rejoins the cluster, and then drops back down as the shards transition into an active state, as shown in the graph below.
初始化碎片的数量通常在节点重新加入集群时达到峰值,然后随着分片转换为活跃状态而下降,如下图所示。
During this initialization period, your cluster state may transition from green to yellow or red until the shards on the recovering node regain active status. In many cases, a brief status change to yellow or red may not require any action on your part.
在此初始化期间,集群状态可能从绿色转变为黄色或红色,直到恢复节点上的分片重新恢复到活跃状态。在很多情况下,一个简短的状态变化为黄色或红色可能不需要你的任何行动。
However, if you notice that your cluster status is lingering in red or yellow state for an extended period of time, verify that the cluster is recognizing the correct number of Elasticsearch nodes, either by consulting Datadog’s dashboard or by querying the Cluster Health API detailed in Part 2.
但是,如果您注意到您的集群状态在红色或黄色状态中徘徊了很长一段时间,请通过查阅Datadog的仪表板或查询第2部分中详细介绍的集群健康API来验证集群是否识别了正确的ES节点数量。
If the number of active nodes is lower than expected, it means that at least one of your nodes lost its connection and hasn’t been able to rejoin the cluster. To find out which node(s) left the cluster, check the logs (located by default in the logs folder of your Elasticsearch home directory) for a line similar to the following:
如果活动节点的数量低于预期,则意味着至少有一个节点失去了连接,无法重新加入集群。要找出离开集群的节点,请检查日志(默认位于您的Elasticsearch home目录的logs文件夹中),查找与以下内容类似的行::
Reasons for node failure can vary, ranging from hardware or hypervisor failures, to out-of-memory errors. Check any of the monitoring tools outlined here for unusual changes in performance metrics that may have occurred around the same time the node failed, such as a sudden spike in the current rate of search or indexing requests. Once you have an idea of what may have happened, if it is a temporary failure, you can try to get the disconnected node(s) to recover and rejoin the cluster. If it is a permanent failure, and you are not able to recover the node, you can add new nodes and let Elasticsearch take care of recovering from any available replica shards; replica shards can be promoted to primary shards and redistributed on the new nodes you just added.
节点失败的原因可能不同,从硬件失败,管理程序失败到内存不足的错误。检查监视工具,这些工具可能是在节点失败的同时出现的性能指标的异常变化,比如当前搜索或索引请求的速度突然激增。一旦您知道可能发生了什么,如果是临时故障,您可以尝试让断开连接的节点恢复并重新加入集群。如果是永久性故障,您无法恢复节点,您可以添加新节点,并让Elasticsearch负责从任何可用的副本分片中恢复,副本分片可以提升到主分片,并在刚刚添加的新节点上重新分布。
However, if you lost both the primary and replica copy of a shard, you can try to recover as much of the missing data as possible by using Elasticsearch’s snapshot and restore module. If you’re not already familiar with this module, it can be used to store snapshots of indices over time in a remote repository for backup purposes.
但是,如果您同时丢失了分片的主分片和副本,那么您可以使用ES的快照和恢复模块尽可能多地恢复丢失的数据。如果您还不熟悉这个模块,那么可以使用它在远程存储库中存储索引的快照,以便进行备份。
Problem #2: Help! Data nodes are running out of disk space
问题#2:数据节点空间将要耗尽
If all of your data nodes are running low on disk space, you will need to add more data nodes to your cluster. You will also need to make sure that your indices have enough primary shards to be able to balance their data across all those nodes.
如果所有数据节点的磁盘空间都很低,那么将需要向集群添加更多的数据节点。你还需要确保您的索引拥有足够的主分片,以便能够跨所有这些节点能够平衡它的数据。
However, if only certain nodes are running out of disk space, this is usually a sign that you initialized an index with too few shards. If an index is composed of a few very large shards, it’s hard for Elasticsearch to distribute these shards across nodes in a balanced manner.
但是,如果只有特定的节点耗尽了磁盘空间,这通常是你用了太多的分片在初始化索引的时候。如果一个索引是由一些非常大的分片组成的,那么用ES很难以一种平衡的方式在节点之间分布这些分片。
Elasticsearch takes available disk space into account when allocating shards to nodes. By default, it will not assign shards to nodes that have over 85 percent disk in use. In Datadog, you can set up a threshold alert to notify you when any individual data node’s disk space usage approaches 80 percent, which should give you enough time to take action.
当master将分片分配给节点时,ES会考虑到节点可用的磁盘空间。默认情况下,它不会将分片分配给使用超过85%磁盘的节点。在Datadog中,您可以设置一个阈值警报,当任何单个数据节点的磁盘空间使用量接近80%时通知您,这应该会给您足够的时间采取行动。
There are two remedies for low disk space. One is to remove outdated data and store it off the cluster. This may not be a viable option for all users, but, if you’re storing time-based data, you can store a snapshot of older indices’ data off-cluster for backup, and update the index settings to turn off replication for those indices.
对于低磁盘空间有两种补救方法。一种是删除过时的数据并将其存储在集群之外。对于所有用户来说,这可能不是一个可行的选择,但是,如果您正在存储基于时间的数据,您可以将旧索引的数据快照存储到集群之外进行备份,并更新索引设置,以关闭对这些索引的复制。
The second approach is the only option for you if you need to continue storing all of your data on the cluster: scaling vertically or horizontally. If you choose to scale vertically, that means upgrading your hardware. However, to avoid having to upgrade again down the line, you should take advantage of the fact that Elasticsearch was designed to scale horizontally. To better accommodate future growth, you may be better off reindexing the data and specifying more primary shards in the newly created index (making sure that you have enough nodes to evenly distribute the shards).
如果需要继续将所有数据存储在集群上,那么第二种方法是惟一的选择:垂直或横向地伸缩集群。如果选择垂直伸缩,就意味着升级硬件。然而,为了避免再次升级,最好使用ES的横向伸缩。为了更好地适应未来的增长,你最好对数据进行索引重建,并在新创建的索引中指定更多的主碎片(确保您有足够的节点来均匀分布碎片)。
Another way to scale horizontally is to roll over the index by creating a new index, and using an alias to join the two indices together under one namespace. Though there is technically no limit to how much data you can store on a single shard, Elasticsearch recommends a soft upper limit of 50 GB per shard, which you can use as a general guideline that signals when it’s time to start a new index.
横向扩展的另一种方法是创建一个新索引,并使用别名滚动改变索引。虽然从技术上讲,您可以在一个分片上存储多少数据没有限制,但Elasticsearch建议在每个碎片上设置一个50 GB的软上限,您可以将其作为一个通用指南,在开始创建新索引时发出信号。
Problem #3: My searches are taking too long to execute
问题#3:我的搜索执行时间太长了
Search performance varies widely according to what type of data is being searched and how each query is structured. Depending on the way your data is organized, you may need to experiment with a few different methods before finding one that will help speed up search performance. We’ll cover two of them here: custom routing and force merging.
根据搜索的数据类型以及每个查询的结构,搜索性能会有很大的不同。根据您的数据的组织方式,您可能需要在找到一个有助于提高搜索性能的方法之前尝试一些不同的方法。我们将介绍其中的两个:自定义路由和强制合并。
Typically, when a node receives a search request, it needs to communicate that request to a copy (either primary or replica) of every shard in the index. Custom routing allows you to store related data on the same shard, so that you only have to search a single shard to satisfy a query.
通常,当一个节点收到一个搜索请求时,它需要将该请求传递给索引中的每个分片的副本(主分片和副本分片)。自定义路由允许你将相关数据存储在同一个shard上,这样您只需要搜索一个分片来满足查询。
For example, you can store all of blogger1’s data on the same shard by specifying a _routing value in the mapping for the blogger type within your index, blog_index.
例如,你可以在索引blog_index中为blogger类型指定一个_routing值,从而将blogger1的所有数据存储在相同的分片上。
First, make sure _routing is required so that you don’t forget to specify a custom routing value whenever you index information of the blogger type.
首先,确保需要_routing,以便在索引blogger类型的信息时不会忘记指定一个定制的路由值。
当您准备索引与blogger1相关的文档时,请指定路由值:
Now, in order to search through blogger1’s comments, you will need to remember to specify the routing value in the query like this:
现在,为了搜索blogger1的评论,您需要记住在查询中指定如下的路由值:
In Elasticsearch, every search request has to check every segment of each shard it hits. So once you have reduced the number of shards you’ll have to search, you can also reduce the number of segments per shard by triggering the Force Merge API on one or more of your indices. The Force Merge API (or Optimize API in versions prior to 2.1.0) prompts the segments in the index to continue merging until each shard’s segment count is reduced to max_num_segments (1, by default). It’s worth experimenting with this feature, as long as you account for the computational cost of triggering a high number of merges.
在ES中,每个搜索请求都必须检查它所命中的每个分片的每一段。一旦你可以减少了搜索的分片数量,你也可以通过在一个或多个索引上触发Force Merge API来减少每个分片的段数量。强制合并API(或在2.1.0之前的版本中优化API)提示索引中的段合并,直到每个分片的段计数减少到max_num_segment(默认为1)。考虑一下这个成本和查询的时间成本,值得对该特性进行试验。
When it comes to shards with a large number of segments, the force merge process becomes much more computationally expensive. For instance, force merging an index of 10,000 segments down to 5,000 segments doesn’t take much time, but merging 10,000 segments all the way down to one segment can take hours. The more merging that must occur, the more resources you take away from fulfilling search requests, which may defeat the purpose of calling a force merge in the first place. In any case, it’s usually a good idea to schedule a force merge during non-peak hours, such as overnight, when you don’t expect many search or indexing requests.
当涉及到索引具有大量的段,段合并过程的计算开销就会大得多。例如,强制合并10000个段的索引到5000个段并不需要花费太多时间,但是将10000个段一直合并到一个段需要花费数小时。合并越多,搜索请求越快,这是调用force merge的目的。在任何情况下,通常最好在非高峰时间(比如在一夜之间)安排一个force merge,这样就不会有太多的搜索或索引请求。
Problem #4: How can I speed up my index-heavy workload?
问题#4:怎样才能加快我的索引沉重的工作量?
Elasticsearch comes pre-configured with many settings that try to ensure that you retain enough resources for searching and indexing data. However, if your usage of Elasticsearch is heavily skewed towards writes, you may find that it makes sense to tweak certain settings to boost indexing performance, even if it means losing some search performance or data replication. Below, we will explore a number of methods to optimize your use case for indexing, rather than searching, data.
ES具有许多预先配置的设置,这些设置试图确保您保留足够的资源用于搜索和索引数据。但是,如果您对ES的使用严重偏向于写操作,可能会发现调整某些设置以提高索引性能是有意义的,即使这意味着丢失一些搜索性能或数据副本。下面,我们将探索一些方法来优化索引而不是优化搜索性能。
Shard allocation: As a high-level strategy, if you are creating an index that you plan to update frequently, make sure you designate enough primary shards so that you can spread the indexing load evenly across all of your nodes. The general recommendation is to allocate one primary shard per node in your cluster, and possibly two or more primary shards per node, but only if you have a lot of CPU and disk bandwidth on those nodes. However, keep in mind that shard overallocation adds overhead and may negatively impact search, since search requests need to hit every shard in the index. On the other hand, if you assign fewer primary shards than the number of nodes, you may create hotspots, as the nodes that contain those shards will need to handle more indexing requests than nodes that don’t contain any of the index’s shards.
分片分配:作为一种高级策略,如果你正在创建频繁更新索引的集群,请确保指定了足够的主分片,这样你就可以将索引负载均匀地分布到所有节点上。一般的建议是为集群中的每个节点分配一个主分片,可能为每个节点分配两个或多个主分片,但前提是这些节点上有大量的CPU和磁盘带宽。但是,请记住,分片过度分配会增加开销,并可能对搜索产生负面影响,因为搜索请求需要命中索引中的每个分片。另一方面,如果你分配的主碎片数量少于节点数量,那么您可能会创建热点(热节点),因为包含这些分片的节点将需要处理更多的索引请求,而不包含索引分片的节点将不做什么操作。
Disable merge throttling: Merge throttling is Elasticsearch’s automatic tendency to throttle indexing requests when it detects that merging is falling behind indexing. It makes sense to update your cluster settings to disable merge throttling (by setting indices.store.throttle.type to “none”) if you want to optimize indexing performance, not search. You can make this change persistent (meaning it will persist after a cluster restart) or transient (resets back to default upon restart), based on your use case.
禁用合并节流:合并节流是ES在检测到合并落后于索引时自动抑制索引请求的趋势。更新集群设置以禁用合并节流是有意义的(设置index .store.throttle.type为none)。这样做可以优化索引性能,而不是搜索。根据你的用例,你可以使这个设置为persist(意味着在集群重新启动之后它将持续)或transient(在重新启动时重新设置为默认)。
Increase the size of the indexing buffer: This setting (indices.memory.index_buffer_size) determines how full the buffer can get before its documents are written to a segment on disk. The default setting limits this value to 10 percent of the total heap in order to reserve more of the heap for serving search requests, which doesn’t help you if you’re using Elasticsearch primarily for indexing.
增加索引缓冲区的大小:此设置(indices.memory.index_buffer_size)确定将文档写到磁盘上的段之前缓冲区的容量。默认设置限制为总堆的10%,以便为服务搜索请求保留更多的堆,如果您主要是在使用Elasticsearch进行索引,这对你是没有帮助。
Index first, replicate later: When you initialize an index, specify zero replica shards in the index settings, and add replicas after you’re done indexing. This will boost indexing performance, but it can be a bit risky if the node holding the only copy of the data crashes before you have a chance to replicate it.
*先索引,后复制:初始化索引时,在索引设置中指定0个复制碎片,索引完成后添加副本。这将提高索引性能,但如果拥有数据惟一副本的节点在您有机会复制数据之前崩溃,则可能存在一些风险。
Refresh less frequently: Increase the refresh interval in the Index Settings API. By default, the index refresh process occurs every second, but during heavy indexing periods, reducing the refresh frequency can help alleviate some of the workload.
不经常刷新:增加索引设置API中的刷新间隔。默认情况下,索引refresh过程每秒钟发生一次,但是在索引不断更新的时期,减少刷新频率可以帮助减轻一些工作负载。
Tweak your translog settings: As of version 2.0, Elasticsearch will flush translog data to disk after every request, reducing the risk of data loss in the event of hardware failure. If you want to prioritize indexing performance over potential data loss, you can change index.translog.durability to async in the index settings. With this in place, the index will only commit writes to disk upon every sync_interval, rather than after each request, leaving more of its resources free to serve indexing requests.
调整您的translog设置:在2.0版本中,弹性搜索将在每次请求之后将translog数据刷新到磁盘,从而在硬件故障时降低数据丢失的风险。如果希望将索引性能优先于潜在的数据丢失,可以更改index.translog.durability为async。有了这一点,索引将在sync_interval上提交对磁盘的写操作,而不是在每个请求之后,从而使更多的资源可以用于索引请求。
For more suggestions on boosting indexing performance, check out this guide from Elastic.
有关提高索引性能的更多建议,请参阅《ES》。
Problem #5: What should I do about all these bulk thread pool rejections?
问题#5:对于所有这些大容量线程池拒绝,我应该怎么做?
Thread pool rejections are typically a sign that you are sending too many requests to your nodes, too quickly. If this is a temporary situation (for instance, you have to index an unusually large amount of data this week, and you anticipate that it will return to normal soon), you can try to slow down the rate of your requests. However, if you want your cluster to be able to sustain the current rate of requests, you will probably need to scale out your cluster by adding more data nodes. In order to utilize the processing power of the increased number of nodes, you should also make sure that your indices contain enough shards to be able to spread the load evenly across all of your nodes.
线程池的拒绝通常表明向节点发送了过多的请求或者请求速度太快。如果这是一个临时的情况(例如,本周必须索引超大量的数据,并且预期它将很快恢复正常),可以尝试降低请求的速度。但是,如果您希望集群能够维持当前的请求速率,您可能需要通过添加更多的数据节点来扩展集群。为了利用增加的节点数量的处理能力,还应该确保索引包含足够的分片,以便能够在所有节点上均匀地分配负载。
Go forth and optimize!
优化
Even more performance tips are available in Elasticsearch’s learning resources and documentation. Since results will vary depending on your particular use case and setup, you can test out different settings and indexing/querying strategies to determine which approaches work best for your clusters.
在ES的学习资源和文档中可以找到更多的性能技巧。由于结果将根据您的特定用例和设置而变化,您可以测试不同的设置和索引/查询策略,以确定哪种方法最适合您的集群。
As you experiment with these and other optimizations, make sure to watch your Elasticsearch dashboards closely to monitor the resulting impact on your clusters’ key Elasticsearch performance metrics.
当您尝试这些优化和其他优化时,请确保密切关注您的ES仪表盘,以监视由此对集群的关键ES性能指标的影响。
With a built-in Elasticsearch dashboard that highlights key cluster metrics, Datadog enables you to effectively monitor Elasticsearch in real-time. If you already have a Datadog account, you can set up the Elasticsearch integrationin minutes. If you don’t yet have a Datadog account, sign up for a free trialtoday.
有了一个内置的ES仪表盘,它突出关键的集群指标,Datadog使您能够实时监控弹性搜索。如果您已经有了一个Datadog帐户,那么您可以在几分钟内设置Elasticsearch集成。如果你还没有一个Datadog帐户,那么今天就注册一个免费试用。
Source Markdown for this post is available on GitHub. Questions, corrections, additions, etc.? Please let us know.
本文是对一篇外文博客的翻译
This post is the final part of a 4-part series on monitoring Elasticsearch performance. Part 1 provides an overview of Elasticsearch and its key performance metrics, Part 2 explains how to collect these metrics, and Part 3describes how to monitor Elasticsearch with Datadog.
这篇文章是监控ES性能系列文章的最后一部分。第1部分概述了ES及其关键性能指标,第2部分解释了如何收集这些指标,第3部分描述了如何使用Datadog监视ES。
Like a car, Elasticsearch was designed to allow its users to get up and running quickly, without having to understand all of its inner workings. However, it’s only a matter of time before you run into engine trouble here or there. This article will walk through five common Elasticsearch challenges, and how to deal with them.
就像汽车一样,用户可以在无需了解其所有内部工作原理的情况下,快速地站起来并运行。然而,在这里或那里遇到引擎故障只是时间问题。本文将介绍五种常见的ES的挑战,以及如何处理它们。
Problem #1: My cluster status is red or yellow. What should I do?
问题#1:我的集群状态是红色或黄色。我应该做什么?
If you recall from Part 1, cluster status is reported as red if one or more primary shards (and its replicas) is missing, and yellow if one or more replica shards is missing. Normally, this happens when a node drops off the cluster for whatever reason (hardware failure, long garbage collection time, etc.). Once the node recovers, its shards will remain in an initializing state before they transition back to active status.
回顾第1部分,如果丢失一个或多个主分片(及其副本),集群状态将报告为红色;如果丢失一个或多个副本分片,则报告为黄色。通常,这种情况发生在节点出于某些原因(硬件故障、长时间的垃圾收集时间等)退出集群时。一旦节点恢复,它的分片在转换会活跃状态之前将保持初始化状态。
The number of initializing shards typically peaks when a node rejoins the cluster, and then drops back down as the shards transition into an active state, as shown in the graph below.
初始化碎片的数量通常在节点重新加入集群时达到峰值,然后随着分片转换为活跃状态而下降,如下图所示。
During this initialization period, your cluster state may transition from green to yellow or red until the shards on the recovering node regain active status. In many cases, a brief status change to yellow or red may not require any action on your part.
在此初始化期间,集群状态可能从绿色转变为黄色或红色,直到恢复节点上的分片重新恢复到活跃状态。在很多情况下,一个简短的状态变化为黄色或红色可能不需要你的任何行动。
However, if you notice that your cluster status is lingering in red or yellow state for an extended period of time, verify that the cluster is recognizing the correct number of Elasticsearch nodes, either by consulting Datadog’s dashboard or by querying the Cluster Health API detailed in Part 2.
但是,如果您注意到您的集群状态在红色或黄色状态中徘徊了很长一段时间,请通过查阅Datadog的仪表板或查询第2部分中详细介绍的集群健康API来验证集群是否识别了正确的ES节点数量。
If the number of active nodes is lower than expected, it means that at least one of your nodes lost its connection and hasn’t been able to rejoin the cluster. To find out which node(s) left the cluster, check the logs (located by default in the logs folder of your Elasticsearch home directory) for a line similar to the following:
如果活动节点的数量低于预期,则意味着至少有一个节点失去了连接,无法重新加入集群。要找出离开集群的节点,请检查日志(默认位于您的Elasticsearch home目录的logs文件夹中),查找与以下内容类似的行::
[TIMESTAMP] ... Cluster health status changed from [GREEN] to [RED]Reasons for node failure can vary, ranging from hardware or hypervisor failures, to out-of-memory errors. Check any of the monitoring tools outlined here for unusual changes in performance metrics that may have occurred around the same time the node failed, such as a sudden spike in the current rate of search or indexing requests. Once you have an idea of what may have happened, if it is a temporary failure, you can try to get the disconnected node(s) to recover and rejoin the cluster. If it is a permanent failure, and you are not able to recover the node, you can add new nodes and let Elasticsearch take care of recovering from any available replica shards; replica shards can be promoted to primary shards and redistributed on the new nodes you just added.
节点失败的原因可能不同,从硬件失败,管理程序失败到内存不足的错误。检查监视工具,这些工具可能是在节点失败的同时出现的性能指标的异常变化,比如当前搜索或索引请求的速度突然激增。一旦您知道可能发生了什么,如果是临时故障,您可以尝试让断开连接的节点恢复并重新加入集群。如果是永久性故障,您无法恢复节点,您可以添加新节点,并让Elasticsearch负责从任何可用的副本分片中恢复,副本分片可以提升到主分片,并在刚刚添加的新节点上重新分布。
However, if you lost both the primary and replica copy of a shard, you can try to recover as much of the missing data as possible by using Elasticsearch’s snapshot and restore module. If you’re not already familiar with this module, it can be used to store snapshots of indices over time in a remote repository for backup purposes.
但是,如果您同时丢失了分片的主分片和副本,那么您可以使用ES的快照和恢复模块尽可能多地恢复丢失的数据。如果您还不熟悉这个模块,那么可以使用它在远程存储库中存储索引的快照,以便进行备份。
Problem #2: Help! Data nodes are running out of disk space
问题#2:数据节点空间将要耗尽
If all of your data nodes are running low on disk space, you will need to add more data nodes to your cluster. You will also need to make sure that your indices have enough primary shards to be able to balance their data across all those nodes.
如果所有数据节点的磁盘空间都很低,那么将需要向集群添加更多的数据节点。你还需要确保您的索引拥有足够的主分片,以便能够跨所有这些节点能够平衡它的数据。
However, if only certain nodes are running out of disk space, this is usually a sign that you initialized an index with too few shards. If an index is composed of a few very large shards, it’s hard for Elasticsearch to distribute these shards across nodes in a balanced manner.
但是,如果只有特定的节点耗尽了磁盘空间,这通常是你用了太多的分片在初始化索引的时候。如果一个索引是由一些非常大的分片组成的,那么用ES很难以一种平衡的方式在节点之间分布这些分片。
Elasticsearch takes available disk space into account when allocating shards to nodes. By default, it will not assign shards to nodes that have over 85 percent disk in use. In Datadog, you can set up a threshold alert to notify you when any individual data node’s disk space usage approaches 80 percent, which should give you enough time to take action.
当master将分片分配给节点时,ES会考虑到节点可用的磁盘空间。默认情况下,它不会将分片分配给使用超过85%磁盘的节点。在Datadog中,您可以设置一个阈值警报,当任何单个数据节点的磁盘空间使用量接近80%时通知您,这应该会给您足够的时间采取行动。
There are two remedies for low disk space. One is to remove outdated data and store it off the cluster. This may not be a viable option for all users, but, if you’re storing time-based data, you can store a snapshot of older indices’ data off-cluster for backup, and update the index settings to turn off replication for those indices.
对于低磁盘空间有两种补救方法。一种是删除过时的数据并将其存储在集群之外。对于所有用户来说,这可能不是一个可行的选择,但是,如果您正在存储基于时间的数据,您可以将旧索引的数据快照存储到集群之外进行备份,并更新索引设置,以关闭对这些索引的复制。
The second approach is the only option for you if you need to continue storing all of your data on the cluster: scaling vertically or horizontally. If you choose to scale vertically, that means upgrading your hardware. However, to avoid having to upgrade again down the line, you should take advantage of the fact that Elasticsearch was designed to scale horizontally. To better accommodate future growth, you may be better off reindexing the data and specifying more primary shards in the newly created index (making sure that you have enough nodes to evenly distribute the shards).
如果需要继续将所有数据存储在集群上,那么第二种方法是惟一的选择:垂直或横向地伸缩集群。如果选择垂直伸缩,就意味着升级硬件。然而,为了避免再次升级,最好使用ES的横向伸缩。为了更好地适应未来的增长,你最好对数据进行索引重建,并在新创建的索引中指定更多的主碎片(确保您有足够的节点来均匀分布碎片)。
Another way to scale horizontally is to roll over the index by creating a new index, and using an alias to join the two indices together under one namespace. Though there is technically no limit to how much data you can store on a single shard, Elasticsearch recommends a soft upper limit of 50 GB per shard, which you can use as a general guideline that signals when it’s time to start a new index.
横向扩展的另一种方法是创建一个新索引,并使用别名滚动改变索引。虽然从技术上讲,您可以在一个分片上存储多少数据没有限制,但Elasticsearch建议在每个碎片上设置一个50 GB的软上限,您可以将其作为一个通用指南,在开始创建新索引时发出信号。
Problem #3: My searches are taking too long to execute
问题#3:我的搜索执行时间太长了
Search performance varies widely according to what type of data is being searched and how each query is structured. Depending on the way your data is organized, you may need to experiment with a few different methods before finding one that will help speed up search performance. We’ll cover two of them here: custom routing and force merging.
根据搜索的数据类型以及每个查询的结构,搜索性能会有很大的不同。根据您的数据的组织方式,您可能需要在找到一个有助于提高搜索性能的方法之前尝试一些不同的方法。我们将介绍其中的两个:自定义路由和强制合并。
Typically, when a node receives a search request, it needs to communicate that request to a copy (either primary or replica) of every shard in the index. Custom routing allows you to store related data on the same shard, so that you only have to search a single shard to satisfy a query.
通常,当一个节点收到一个搜索请求时,它需要将该请求传递给索引中的每个分片的副本(主分片和副本分片)。自定义路由允许你将相关数据存储在同一个shard上,这样您只需要搜索一个分片来满足查询。
For example, you can store all of blogger1’s data on the same shard by specifying a _routing value in the mapping for the blogger type within your index, blog_index.
例如,你可以在索引blog_index中为blogger类型指定一个_routing值,从而将blogger1的所有数据存储在相同的分片上。
First, make sure _routing is required so that you don’t forget to specify a custom routing value whenever you index information of the blogger type.
首先,确保需要_routing,以便在索引blogger类型的信息时不会忘记指定一个定制的路由值。
curl -XPUT "localhost:9200/blog_index" -d '
{
"mappings": {
"blogger": {
"_routing": {
"required": true
}
}
}
}'当您准备索引与blogger1相关的文档时,请指定路由值:
curl -XPUT "localhost:9200/blog_index/blogger/1?routing=blogger1" -d '
{
"comment": "blogger1 made this cool comment"
}'Now, in order to search through blogger1’s comments, you will need to remember to specify the routing value in the query like this:
现在,为了搜索blogger1的评论,您需要记住在查询中指定如下的路由值:
curl -XGET "localhost:9200/blog_index/_search?routing=blogger1" -d '
{
"query": {
"match": {
"comment": {
"query": "cool comment"
}
}
}
}'In Elasticsearch, every search request has to check every segment of each shard it hits. So once you have reduced the number of shards you’ll have to search, you can also reduce the number of segments per shard by triggering the Force Merge API on one or more of your indices. The Force Merge API (or Optimize API in versions prior to 2.1.0) prompts the segments in the index to continue merging until each shard’s segment count is reduced to max_num_segments (1, by default). It’s worth experimenting with this feature, as long as you account for the computational cost of triggering a high number of merges.
在ES中,每个搜索请求都必须检查它所命中的每个分片的每一段。一旦你可以减少了搜索的分片数量,你也可以通过在一个或多个索引上触发Force Merge API来减少每个分片的段数量。强制合并API(或在2.1.0之前的版本中优化API)提示索引中的段合并,直到每个分片的段计数减少到max_num_segment(默认为1)。考虑一下这个成本和查询的时间成本,值得对该特性进行试验。
When it comes to shards with a large number of segments, the force merge process becomes much more computationally expensive. For instance, force merging an index of 10,000 segments down to 5,000 segments doesn’t take much time, but merging 10,000 segments all the way down to one segment can take hours. The more merging that must occur, the more resources you take away from fulfilling search requests, which may defeat the purpose of calling a force merge in the first place. In any case, it’s usually a good idea to schedule a force merge during non-peak hours, such as overnight, when you don’t expect many search or indexing requests.
当涉及到索引具有大量的段,段合并过程的计算开销就会大得多。例如,强制合并10000个段的索引到5000个段并不需要花费太多时间,但是将10000个段一直合并到一个段需要花费数小时。合并越多,搜索请求越快,这是调用force merge的目的。在任何情况下,通常最好在非高峰时间(比如在一夜之间)安排一个force merge,这样就不会有太多的搜索或索引请求。
Problem #4: How can I speed up my index-heavy workload?
问题#4:怎样才能加快我的索引沉重的工作量?
Elasticsearch comes pre-configured with many settings that try to ensure that you retain enough resources for searching and indexing data. However, if your usage of Elasticsearch is heavily skewed towards writes, you may find that it makes sense to tweak certain settings to boost indexing performance, even if it means losing some search performance or data replication. Below, we will explore a number of methods to optimize your use case for indexing, rather than searching, data.
ES具有许多预先配置的设置,这些设置试图确保您保留足够的资源用于搜索和索引数据。但是,如果您对ES的使用严重偏向于写操作,可能会发现调整某些设置以提高索引性能是有意义的,即使这意味着丢失一些搜索性能或数据副本。下面,我们将探索一些方法来优化索引而不是优化搜索性能。
Shard allocation: As a high-level strategy, if you are creating an index that you plan to update frequently, make sure you designate enough primary shards so that you can spread the indexing load evenly across all of your nodes. The general recommendation is to allocate one primary shard per node in your cluster, and possibly two or more primary shards per node, but only if you have a lot of CPU and disk bandwidth on those nodes. However, keep in mind that shard overallocation adds overhead and may negatively impact search, since search requests need to hit every shard in the index. On the other hand, if you assign fewer primary shards than the number of nodes, you may create hotspots, as the nodes that contain those shards will need to handle more indexing requests than nodes that don’t contain any of the index’s shards.
分片分配:作为一种高级策略,如果你正在创建频繁更新索引的集群,请确保指定了足够的主分片,这样你就可以将索引负载均匀地分布到所有节点上。一般的建议是为集群中的每个节点分配一个主分片,可能为每个节点分配两个或多个主分片,但前提是这些节点上有大量的CPU和磁盘带宽。但是,请记住,分片过度分配会增加开销,并可能对搜索产生负面影响,因为搜索请求需要命中索引中的每个分片。另一方面,如果你分配的主碎片数量少于节点数量,那么您可能会创建热点(热节点),因为包含这些分片的节点将需要处理更多的索引请求,而不包含索引分片的节点将不做什么操作。
Disable merge throttling: Merge throttling is Elasticsearch’s automatic tendency to throttle indexing requests when it detects that merging is falling behind indexing. It makes sense to update your cluster settings to disable merge throttling (by setting indices.store.throttle.type to “none”) if you want to optimize indexing performance, not search. You can make this change persistent (meaning it will persist after a cluster restart) or transient (resets back to default upon restart), based on your use case.
禁用合并节流:合并节流是ES在检测到合并落后于索引时自动抑制索引请求的趋势。更新集群设置以禁用合并节流是有意义的(设置index .store.throttle.type为none)。这样做可以优化索引性能,而不是搜索。根据你的用例,你可以使这个设置为persist(意味着在集群重新启动之后它将持续)或transient(在重新启动时重新设置为默认)。
Increase the size of the indexing buffer: This setting (indices.memory.index_buffer_size) determines how full the buffer can get before its documents are written to a segment on disk. The default setting limits this value to 10 percent of the total heap in order to reserve more of the heap for serving search requests, which doesn’t help you if you’re using Elasticsearch primarily for indexing.
增加索引缓冲区的大小:此设置(indices.memory.index_buffer_size)确定将文档写到磁盘上的段之前缓冲区的容量。默认设置限制为总堆的10%,以便为服务搜索请求保留更多的堆,如果您主要是在使用Elasticsearch进行索引,这对你是没有帮助。
Index first, replicate later: When you initialize an index, specify zero replica shards in the index settings, and add replicas after you’re done indexing. This will boost indexing performance, but it can be a bit risky if the node holding the only copy of the data crashes before you have a chance to replicate it.
*先索引,后复制:初始化索引时,在索引设置中指定0个复制碎片,索引完成后添加副本。这将提高索引性能,但如果拥有数据惟一副本的节点在您有机会复制数据之前崩溃,则可能存在一些风险。
Refresh less frequently: Increase the refresh interval in the Index Settings API. By default, the index refresh process occurs every second, but during heavy indexing periods, reducing the refresh frequency can help alleviate some of the workload.
不经常刷新:增加索引设置API中的刷新间隔。默认情况下,索引refresh过程每秒钟发生一次,但是在索引不断更新的时期,减少刷新频率可以帮助减轻一些工作负载。
Tweak your translog settings: As of version 2.0, Elasticsearch will flush translog data to disk after every request, reducing the risk of data loss in the event of hardware failure. If you want to prioritize indexing performance over potential data loss, you can change index.translog.durability to async in the index settings. With this in place, the index will only commit writes to disk upon every sync_interval, rather than after each request, leaving more of its resources free to serve indexing requests.
调整您的translog设置:在2.0版本中,弹性搜索将在每次请求之后将translog数据刷新到磁盘,从而在硬件故障时降低数据丢失的风险。如果希望将索引性能优先于潜在的数据丢失,可以更改index.translog.durability为async。有了这一点,索引将在sync_interval上提交对磁盘的写操作,而不是在每个请求之后,从而使更多的资源可以用于索引请求。
For more suggestions on boosting indexing performance, check out this guide from Elastic.
有关提高索引性能的更多建议,请参阅《ES》。
Problem #5: What should I do about all these bulk thread pool rejections?
问题#5:对于所有这些大容量线程池拒绝,我应该怎么做?
Thread pool rejections are typically a sign that you are sending too many requests to your nodes, too quickly. If this is a temporary situation (for instance, you have to index an unusually large amount of data this week, and you anticipate that it will return to normal soon), you can try to slow down the rate of your requests. However, if you want your cluster to be able to sustain the current rate of requests, you will probably need to scale out your cluster by adding more data nodes. In order to utilize the processing power of the increased number of nodes, you should also make sure that your indices contain enough shards to be able to spread the load evenly across all of your nodes.
线程池的拒绝通常表明向节点发送了过多的请求或者请求速度太快。如果这是一个临时的情况(例如,本周必须索引超大量的数据,并且预期它将很快恢复正常),可以尝试降低请求的速度。但是,如果您希望集群能够维持当前的请求速率,您可能需要通过添加更多的数据节点来扩展集群。为了利用增加的节点数量的处理能力,还应该确保索引包含足够的分片,以便能够在所有节点上均匀地分配负载。
Go forth and optimize!
优化
Even more performance tips are available in Elasticsearch’s learning resources and documentation. Since results will vary depending on your particular use case and setup, you can test out different settings and indexing/querying strategies to determine which approaches work best for your clusters.
在ES的学习资源和文档中可以找到更多的性能技巧。由于结果将根据您的特定用例和设置而变化,您可以测试不同的设置和索引/查询策略,以确定哪种方法最适合您的集群。
As you experiment with these and other optimizations, make sure to watch your Elasticsearch dashboards closely to monitor the resulting impact on your clusters’ key Elasticsearch performance metrics.
当您尝试这些优化和其他优化时,请确保密切关注您的ES仪表盘,以监视由此对集群的关键ES性能指标的影响。
With a built-in Elasticsearch dashboard that highlights key cluster metrics, Datadog enables you to effectively monitor Elasticsearch in real-time. If you already have a Datadog account, you can set up the Elasticsearch integrationin minutes. If you don’t yet have a Datadog account, sign up for a free trialtoday.
有了一个内置的ES仪表盘,它突出关键的集群指标,Datadog使您能够实时监控弹性搜索。如果您已经有了一个Datadog帐户,那么您可以在几分钟内设置Elasticsearch集成。如果你还没有一个Datadog帐户,那么今天就注册一个免费试用。
Source Markdown for this post is available on GitHub. Questions, corrections, additions, etc.? Please let us know.
[尊重社区原创,转载请保留或注明出处]
本文地址:http://elasticsearch.cn/article/708
本文地址:http://elasticsearch.cn/article/708