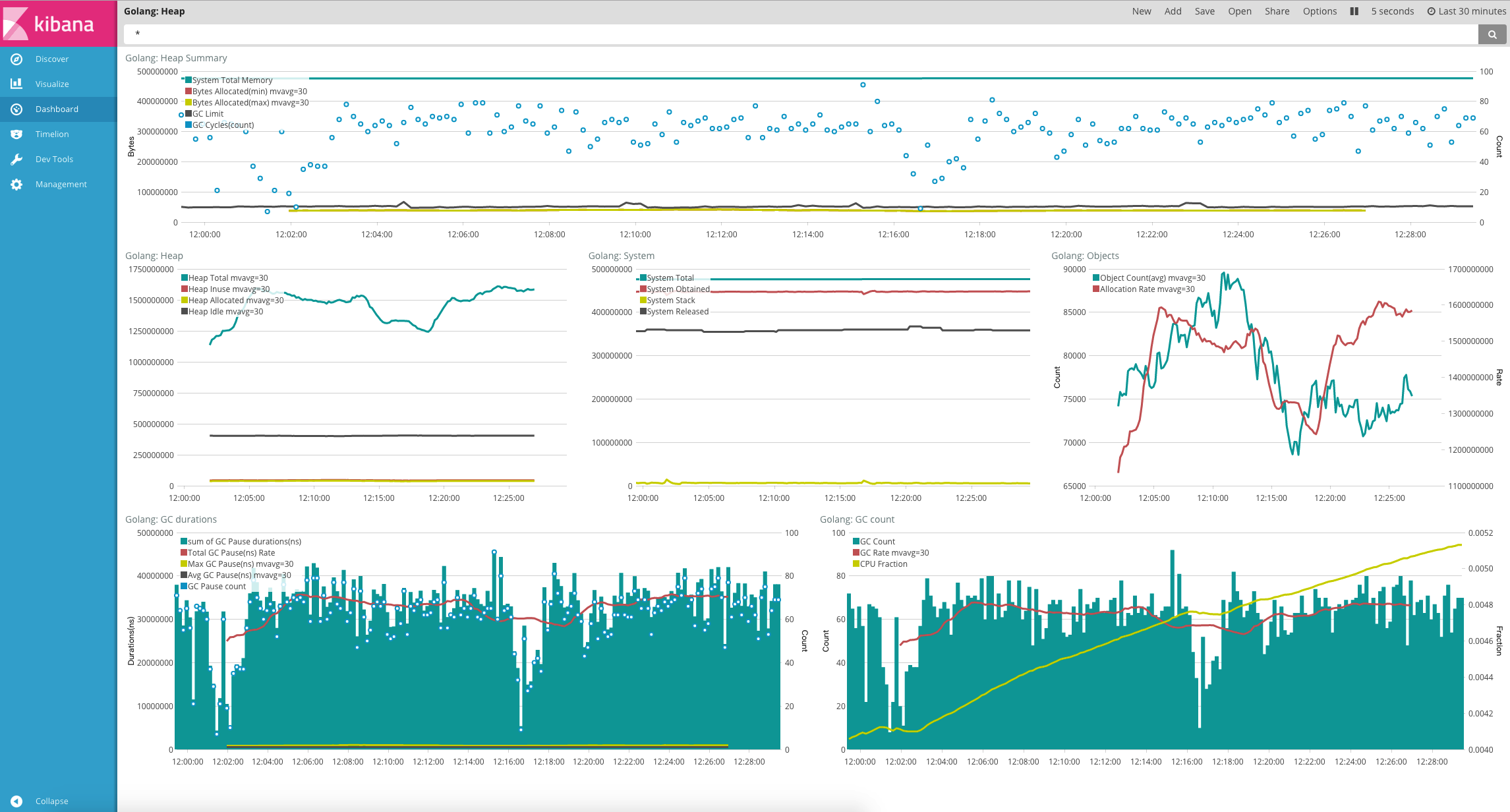
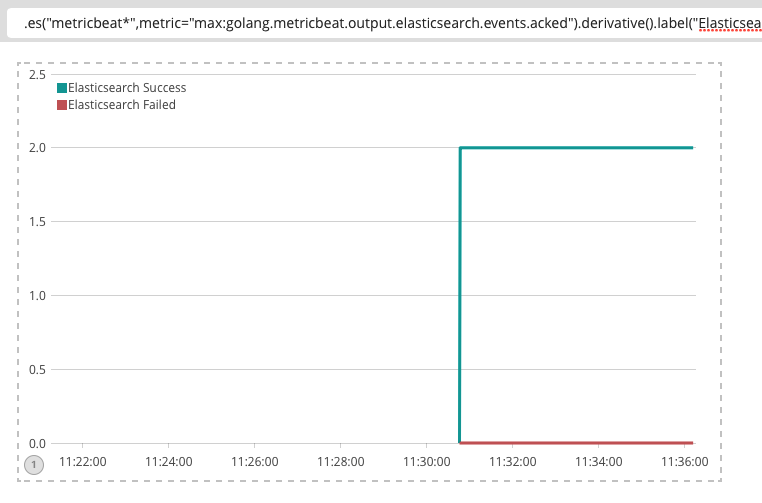
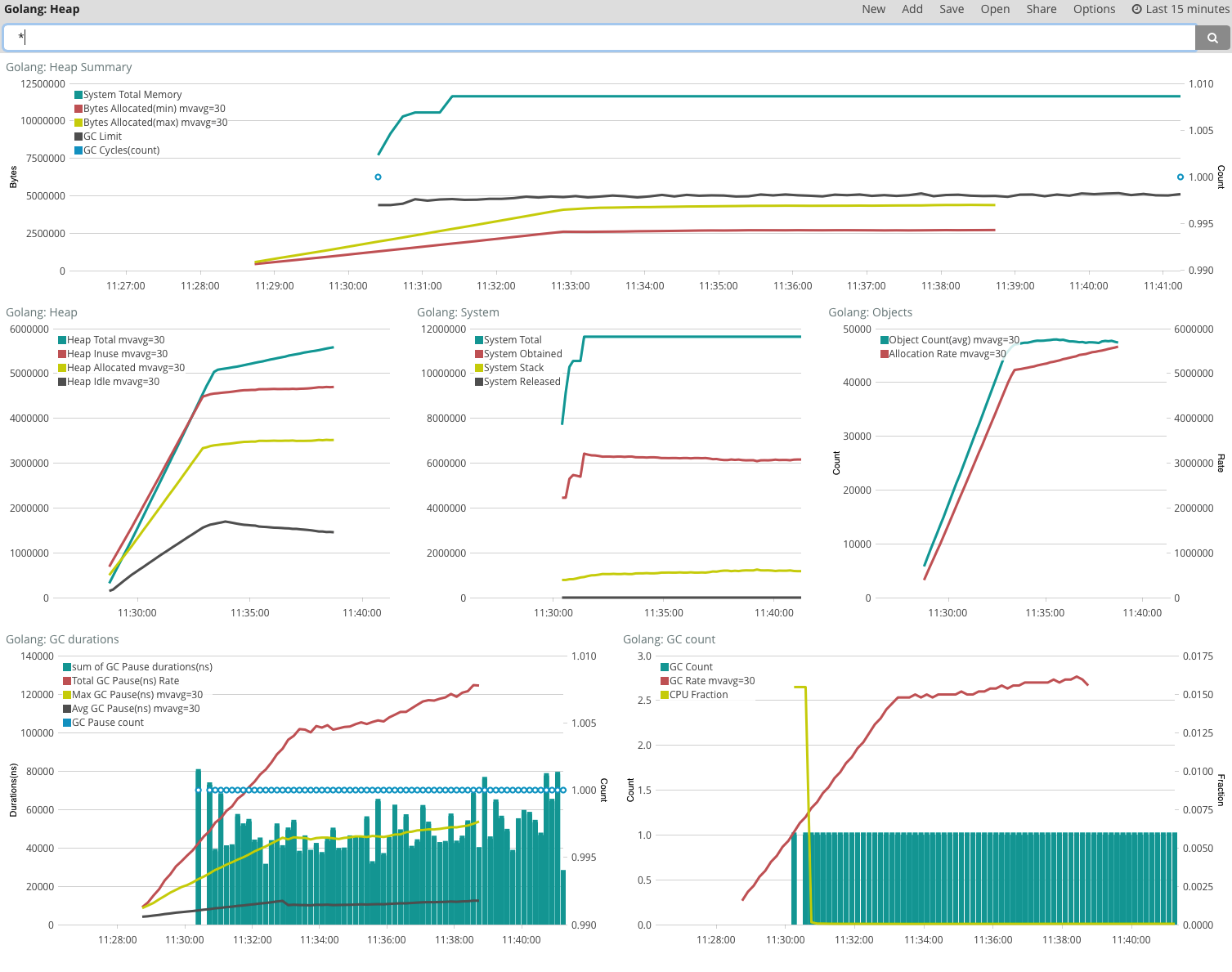
Heap
老生常谈ES heap问题;
Elasticsearch • HelloClyde 回复了问题 • 3 人关注 • 2 个回复 • 4157 次浏览 • 2018-12-18 17:14
Elasticsearch 内存泄漏 oom 没有bulk输入
回复Elasticsearch • caomaocao 发起了问题 • 1 人关注 • 0 个回复 • 6999 次浏览 • 2017-12-22 18:15
请问一下 集群的 heap总是不平均 这是不是有问题呢
Elasticsearch • liuyt123 发表了文章 • 8 个评论 • 2802 次浏览 • 2017-11-20 11:05
使用 Elastic Stack 来监控和调优 Golang 应用程序
Beats • medcl 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 13396 次浏览 • 2017-03-03 11:16
- Apache Module
- Couchbase Module
- Docker Module
- HAProxy Module
- kafka Module
- MongoDB Module
- MySQL Module
- Nginx Module
- PostgreSQL Module
- Prometheus Module
- Redis Module
- System Module
- ZooKeeper Module
import _ "expvar"func metricsHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=utf-8")
first := true
report := func(key string, value interface{}) {
if !first {
fmt.Fprintf(w, ",\n")
}
first = false
if str, ok := value.(string); ok {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%q: %q", key, str)
} else {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%q: %v", key, value)
}
}
fmt.Fprintf(w, "{\n")
expvar.Do(func(kv expvar.KeyValue) {
report(kv.Key, kv.Value)
})
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\n}\n")
}
func main() {
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/vars", metricsHandler)
endpoint := http.ListenAndServe("localhost:6060", mux)
}metricbeat.modules:
- module: golang
metricsets: ["heap"]
enabled: true
period: 10s
hosts: ["localhost:6060"]
heap.path: "/debug/vars"output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]./metricbeat -e -vvar inerInt int64 = 1024
pubInt := expvar.NewInt("your_metric_key")
pubInt.Set(inerInt)
pubInt.Add(2)./metricbeat -httpprof="127.0.0.1:6060" -e -v{
"output.events.acked": 1088,
"output.write.bytes": 1027455,
"output.write.errors": 0,
"output.messages.dropped": 0,
"output.elasticsearch.publishEvents.call.count": 24,
"output.elasticsearch.read.bytes": 12215,
"output.elasticsearch.read.errors": 0,
"output.elasticsearch.write.bytes": 1027455,
"output.elasticsearch.write.errors": 0,
"output.elasticsearch.events.acked": 1088,
"output.elasticsearch.events.not_acked": 0,
"output.kafka.events.acked": 0,
"output.kafka.events.not_acked": 0,
"output.kafka.publishEvents.call.count": 0,
"output.logstash.write.errors": 0,
"output.logstash.write.bytes": 0,
"output.logstash.events.acked": 0,
"output.logstash.events.not_acked": 0,
"output.logstash.publishEvents.call.count": 0,
"output.logstash.read.bytes": 0,
"output.logstash.read.errors": 0,
"output.redis.events.acked": 0,
"output.redis.events.not_acked": 0,
"output.redis.read.bytes": 0,
"output.redis.read.errors": 0,
"output.redis.write.bytes": 0,
"output.redis.write.errors": 0,
"beat.memstats.memory_total": 155721720,
"beat.memstats.memory_alloc": 3632728,
"beat.memstats.gc_next": 6052800,
"cmdline": ["./metricbeat","-httpprof=127.0.0.1:6060","-e","-v"],
"fetches": {"system-cpu": {"events": 4, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-filesystem": {"events": 20, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-fsstat": {"events": 4, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-load": {"events": 4, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-memory": {"events": 4, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-network": {"events": 44, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-process": {"events": 1008, "failures": 0, "success": 4}},
"libbeat.config.module.running": 0,
"libbeat.config.module.starts": 0,
"libbeat.config.module.stops": 0,
"libbeat.config.reloads": 0,
"memstats": {"Alloc":3637704,"TotalAlloc":155
... ...- module: golang
metricsets: ["heap","expvar"]
enabled: true
period: 1s
hosts: ["localhost:6060"]
heap.path: "/debug/vars"
expvar:
namespace: "metricbeat"
path: "/debug/vars".es("metricbeat*",metric="max:golang.metricbeat.output.elasticsearch.events.acked").derivative().label("Elasticsearch Success"),.es("metricbeat*",metric="max:golang.metricbeat.output.elasticsearch.events.not_acked").derivative().label("Elasticsearch Failed")使用 Elastic Stack 来监控和调优 Golang 应用程序
Beats • medcl 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 13396 次浏览 • 2017-03-03 11:16
- Apache Module
- Couchbase Module
- Docker Module
- HAProxy Module
- kafka Module
- MongoDB Module
- MySQL Module
- Nginx Module
- PostgreSQL Module
- Prometheus Module
- Redis Module
- System Module
- ZooKeeper Module
import _ "expvar"func metricsHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=utf-8")
first := true
report := func(key string, value interface{}) {
if !first {
fmt.Fprintf(w, ",\n")
}
first = false
if str, ok := value.(string); ok {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%q: %q", key, str)
} else {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%q: %v", key, value)
}
}
fmt.Fprintf(w, "{\n")
expvar.Do(func(kv expvar.KeyValue) {
report(kv.Key, kv.Value)
})
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\n}\n")
}
func main() {
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/vars", metricsHandler)
endpoint := http.ListenAndServe("localhost:6060", mux)
}metricbeat.modules:
- module: golang
metricsets: ["heap"]
enabled: true
period: 10s
hosts: ["localhost:6060"]
heap.path: "/debug/vars"output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]./metricbeat -e -vvar inerInt int64 = 1024
pubInt := expvar.NewInt("your_metric_key")
pubInt.Set(inerInt)
pubInt.Add(2)./metricbeat -httpprof="127.0.0.1:6060" -e -v{
"output.events.acked": 1088,
"output.write.bytes": 1027455,
"output.write.errors": 0,
"output.messages.dropped": 0,
"output.elasticsearch.publishEvents.call.count": 24,
"output.elasticsearch.read.bytes": 12215,
"output.elasticsearch.read.errors": 0,
"output.elasticsearch.write.bytes": 1027455,
"output.elasticsearch.write.errors": 0,
"output.elasticsearch.events.acked": 1088,
"output.elasticsearch.events.not_acked": 0,
"output.kafka.events.acked": 0,
"output.kafka.events.not_acked": 0,
"output.kafka.publishEvents.call.count": 0,
"output.logstash.write.errors": 0,
"output.logstash.write.bytes": 0,
"output.logstash.events.acked": 0,
"output.logstash.events.not_acked": 0,
"output.logstash.publishEvents.call.count": 0,
"output.logstash.read.bytes": 0,
"output.logstash.read.errors": 0,
"output.redis.events.acked": 0,
"output.redis.events.not_acked": 0,
"output.redis.read.bytes": 0,
"output.redis.read.errors": 0,
"output.redis.write.bytes": 0,
"output.redis.write.errors": 0,
"beat.memstats.memory_total": 155721720,
"beat.memstats.memory_alloc": 3632728,
"beat.memstats.gc_next": 6052800,
"cmdline": ["./metricbeat","-httpprof=127.0.0.1:6060","-e","-v"],
"fetches": {"system-cpu": {"events": 4, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-filesystem": {"events": 20, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-fsstat": {"events": 4, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-load": {"events": 4, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-memory": {"events": 4, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-network": {"events": 44, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-process": {"events": 1008, "failures": 0, "success": 4}},
"libbeat.config.module.running": 0,
"libbeat.config.module.starts": 0,
"libbeat.config.module.stops": 0,
"libbeat.config.reloads": 0,
"memstats": {"Alloc":3637704,"TotalAlloc":155
... ...- module: golang
metricsets: ["heap","expvar"]
enabled: true
period: 1s
hosts: ["localhost:6060"]
heap.path: "/debug/vars"
expvar:
namespace: "metricbeat"
path: "/debug/vars".es("metricbeat*",metric="max:golang.metricbeat.output.elasticsearch.events.acked").derivative().label("Elasticsearch Success"),.es("metricbeat*",metric="max:golang.metricbeat.output.elasticsearch.events.not_acked").derivative().label("Elasticsearch Failed")Elasticsearch 内存泄漏 oom 没有bulk输入
回复Elasticsearch • caomaocao 发起了问题 • 1 人关注 • 0 个回复 • 6999 次浏览 • 2017-12-22 18:15
请问一下 集群的 heap总是不平均 这是不是有问题呢
Elasticsearch • liuyt123 发表了文章 • 8 个评论 • 2802 次浏览 • 2017-11-20 11:05
使用 Elastic Stack 来监控和调优 Golang 应用程序
Beats • medcl 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 13396 次浏览 • 2017-03-03 11:16
- Apache Module
- Couchbase Module
- Docker Module
- HAProxy Module
- kafka Module
- MongoDB Module
- MySQL Module
- Nginx Module
- PostgreSQL Module
- Prometheus Module
- Redis Module
- System Module
- ZooKeeper Module
import _ "expvar"func metricsHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=utf-8")
first := true
report := func(key string, value interface{}) {
if !first {
fmt.Fprintf(w, ",\n")
}
first = false
if str, ok := value.(string); ok {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%q: %q", key, str)
} else {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%q: %v", key, value)
}
}
fmt.Fprintf(w, "{\n")
expvar.Do(func(kv expvar.KeyValue) {
report(kv.Key, kv.Value)
})
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\n}\n")
}
func main() {
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/vars", metricsHandler)
endpoint := http.ListenAndServe("localhost:6060", mux)
}metricbeat.modules:
- module: golang
metricsets: ["heap"]
enabled: true
period: 10s
hosts: ["localhost:6060"]
heap.path: "/debug/vars"output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]./metricbeat -e -vvar inerInt int64 = 1024
pubInt := expvar.NewInt("your_metric_key")
pubInt.Set(inerInt)
pubInt.Add(2)./metricbeat -httpprof="127.0.0.1:6060" -e -v{
"output.events.acked": 1088,
"output.write.bytes": 1027455,
"output.write.errors": 0,
"output.messages.dropped": 0,
"output.elasticsearch.publishEvents.call.count": 24,
"output.elasticsearch.read.bytes": 12215,
"output.elasticsearch.read.errors": 0,
"output.elasticsearch.write.bytes": 1027455,
"output.elasticsearch.write.errors": 0,
"output.elasticsearch.events.acked": 1088,
"output.elasticsearch.events.not_acked": 0,
"output.kafka.events.acked": 0,
"output.kafka.events.not_acked": 0,
"output.kafka.publishEvents.call.count": 0,
"output.logstash.write.errors": 0,
"output.logstash.write.bytes": 0,
"output.logstash.events.acked": 0,
"output.logstash.events.not_acked": 0,
"output.logstash.publishEvents.call.count": 0,
"output.logstash.read.bytes": 0,
"output.logstash.read.errors": 0,
"output.redis.events.acked": 0,
"output.redis.events.not_acked": 0,
"output.redis.read.bytes": 0,
"output.redis.read.errors": 0,
"output.redis.write.bytes": 0,
"output.redis.write.errors": 0,
"beat.memstats.memory_total": 155721720,
"beat.memstats.memory_alloc": 3632728,
"beat.memstats.gc_next": 6052800,
"cmdline": ["./metricbeat","-httpprof=127.0.0.1:6060","-e","-v"],
"fetches": {"system-cpu": {"events": 4, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-filesystem": {"events": 20, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-fsstat": {"events": 4, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-load": {"events": 4, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-memory": {"events": 4, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-network": {"events": 44, "failures": 0, "success": 4}, "system-process": {"events": 1008, "failures": 0, "success": 4}},
"libbeat.config.module.running": 0,
"libbeat.config.module.starts": 0,
"libbeat.config.module.stops": 0,
"libbeat.config.reloads": 0,
"memstats": {"Alloc":3637704,"TotalAlloc":155
... ...- module: golang
metricsets: ["heap","expvar"]
enabled: true
period: 1s
hosts: ["localhost:6060"]
heap.path: "/debug/vars"
expvar:
namespace: "metricbeat"
path: "/debug/vars".es("metricbeat*",metric="max:golang.metricbeat.output.elasticsearch.events.acked").derivative().label("Elasticsearch Success"),.es("metricbeat*",metric="max:golang.metricbeat.output.elasticsearch.events.not_acked").derivative().label("Elasticsearch Failed")