【携程旅行网 吴晓刚】
上周有用户在社区发了一例Kibana读取超时的问题:question#2319 。周末找时间帮其调查了下,发现某些较新的ES版本和Kibana搭配,会产生意想不到的缓慢问题。 考虑到这个问题比较普遍,因此在这里总结一下问题的根源和解决办法,希望用到问题版本的用户不要踩到坑。
首先问题的现象在上面的问题链接里有描述,简而言之就是对于一个硬件配置比较高的集群,每天写入一个20亿左右数据的索引,通过kibana的discovery面板查看数据会一直超时。即使时间范围放到最近半小时,超时依旧,有些蹊跷。
周末拿到用户给的测试账号,登陆集群看了下状态。 从机器的硬件配置,集群和索引的配置看,没找到什么特别不对劲的地方。然而点击到Discovery面板,的确数据显示不出来。 集群监控数据看,并没有其他用户在做查询,cpu利用率和集群负载都比较低。因此初步可以判定,就是查询本身比较缓慢所致。
对于诊断查询缓慢问题,我通常的做法,就是将对应面板下的查询拷贝出来,在Kibana Dev Console里手动执行,然后再加上"profile":true选项,看看查询是如何解析和执行的。对应的查询形如下面这样:
{
"profile": true,
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"query_string": {
"analyze_wildcard": true,
"query": "*"
}
},
{
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "now-1h",
"lte": "now",
"format": "epoch_millis"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}因为用户query框什么都没有输入,因此默认查询串被Kibana设置为*, 然后根据选择的时间范围加了一个range查询。 profile的输出让我稍微有些吃惊,其中 query_string的里的*居然被解析成非常复杂的DisjunctionMaxQuery,主要查询耗时都在这里了。
{
"type": "DisjunctionMaxQuery",
"description": "(ConstantScore(_field_names:remote_addr.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.country_isocode) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.country_name.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:via) | ConstantScore(_field_names:domain.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:request_method.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:protocol) | ConstantScore(_field_names:xff.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:host) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.city_name.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:client_ip) | ConstantScore(_field_names:host.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.longitude) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.subdivision_name.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.country_code) | ConstantScore(_field_names:upstream_addr.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:@version.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:request_uri) | ConstantScore(_field_names:tags) | ConstantScore(_field_names:idc_tag) | ConstantScore(_field_names:size) | ConstantScore(_field_names:http_referer) | ConstantScore(_field_names:message.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:domain) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.latitude) | ConstantScore(_field_names:xff) | ConstantScore(_field_names:protocol.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.country_code.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:status) | ConstantScore(_field_names:upstream_addr) | ConstantScore(_field_names:http_referer.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:tags.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:client_ip.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:request_method) | ConstantScore(_field_names:upstream_status) | ConstantScore(_field_names:request_time) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.location) | ConstantScore(_field_names:@version) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.country_name) | ConstantScore(_field_names:user_agent) | ConstantScore(_field_names:idc_tag.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:remote_addr) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.country_isocode.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.city_name) | ConstantScore(_field_names:via.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:message) | ConstantScore(_field_names:user_agent.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:request_uri.keyword) | ConstantScore(_field_names:@timestamp) | ConstantScore(_field_names:upstream_response_time) | ConstantScore(_field_names:geoip.subdivision_name))",
"time": "5535.127008ms",
"time_in_nanos": 5535127008也就是说, ES将只含一个*的query_string query解析成了针对mapping里能找到的所有字段的field:*查询,然后合并所有的查询结果。 可想而知,对于比较大,字段比较多的索引这个查询是非常耗时的。而我对于*的认知,是其应该被rewrite成一个match_all query即可,这样几乎没有什么开销。
为什么会这样? 查询了一下ES官方关于Query String Query的文档,其中的default_field和all_fields起到了一定作用: elasticsearch/reference/5.5/query-dsl-query-string-query.html
default_field
The default field for query terms if no prefix field is specified. Defaults to the index.query.default_field index settings, which in turn defaults to _all.
all_fields
Perform the query on all fields detected in the mapping that can be queried. Will be used by default when the _all field is disabled and no default_field is specified (either in the index settings or in the request body) and no fields are specified.
根据解释,查询的时候可以带一个default_field选项,其默认值为索引级别设置index.query.default_field,如果这个设置没有设置,则默认为_all。 但一般用户索引日志的时候,都会关掉_all字段,用于节省磁盘空间,提升索引速率。那么这时候default_field是什么呢? 答案是all_fields,也就是ES会将查询转换为对所有字段的查询。
为了验证这个是问题所在,我在索引里加了一个default_field的设置,随意挑选了一个字段。 果然问题就解决了,discovery面板渲染速度快了差不多有10倍。
但仔细想想,这也只是绕过了问题。 问题的根源,为什么*不被rewrite成match_all呢?
这时候想到我们自己生产的集群似乎没有这个问题,于是用我们自己的集群测试了一下,*果然是正常解析成match_all了。 于是对比了一下集群ES的版本,我们正常工作的是5.3.2,用户的集群是5.5.0。
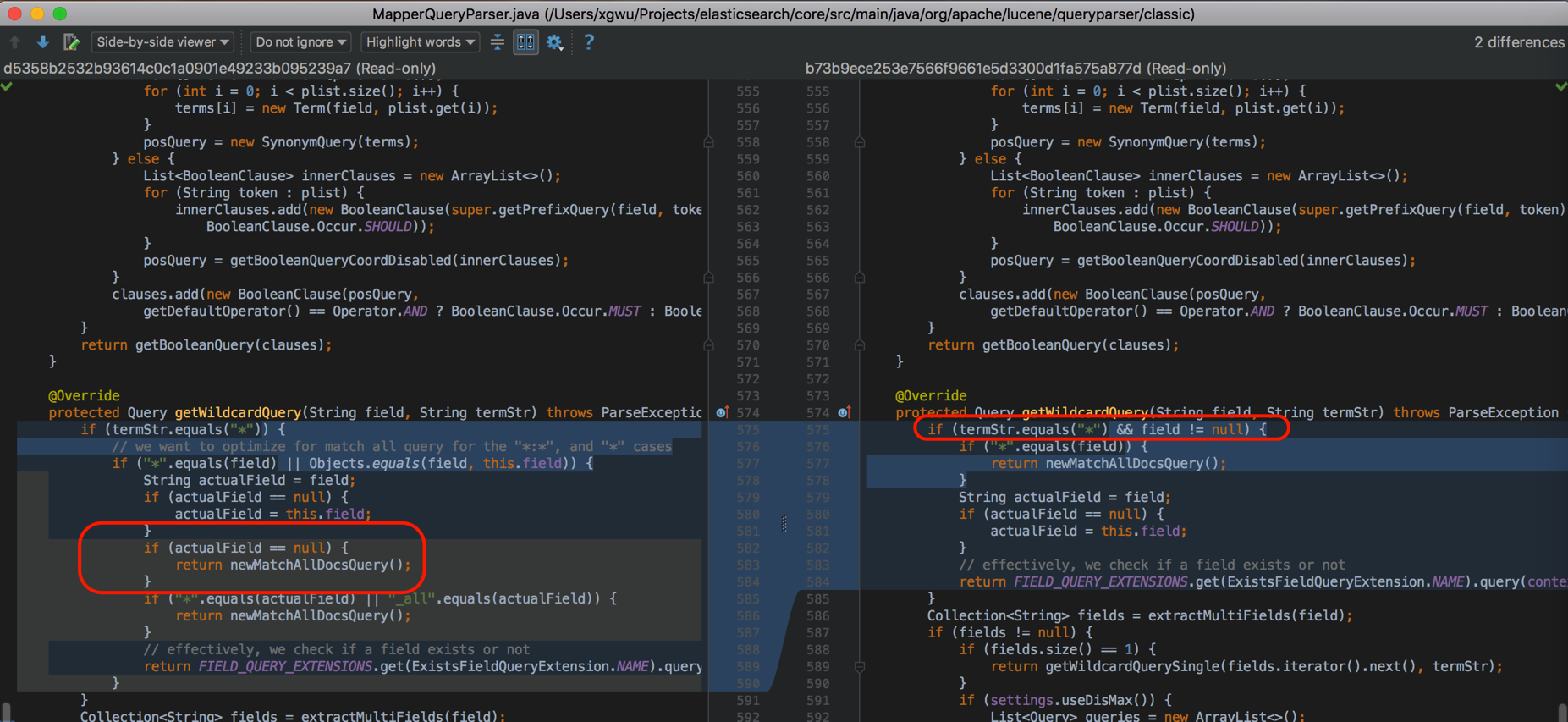
接下来,我想找到这些版本之间,ES对于query string的解析源码层面做了什么改动。经过一番探查,找到了下面这个变更历史:
可以看到,在pull/23433里,为了修复一个foo:*解析歧义的问题,对于field为空,类似光一个*的Query string查询,不再被解析成match_all了,而是扩展成全部字段的DisjunctionMaxQuery查询。 由此Kibana默认的*,会引起非常严重的性能问题。
这个问题会影响5.4和5.5两个小版本的ES/Kibana。
顺着这个issue里的链接摸下去,找到了对应Kibana相关问题讨论:issues#12097,以及对应的修复: pull/13047,修复版本默认发出的查询串是match all。
修复的版本则是5.5.2及5.6.0, 因此有用到5.4.0到5.5.1之间版本的ELK用户一定要安排升级!
本文地址:http://elasticsearch.cn/article/269