lucene
【搜索客社区日报】第2193期 (2026-03-06)
社区日报 • Fred2000 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 2778 次浏览 • 5 天前
搜索百科(3):Elasticsearch — 搜索界的“流量明星”
Elasticsearch • liaosy 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 17358 次浏览 • 2025-09-16 11:20
大家好,我是 INFINI Labs 的石阳。
欢迎关注 《搜索百科》 专栏!每天 5 分钟,带你速览一款搜索相关的技术或产品,同时还会带你探索它们背后的技术原理、发展故事及上手体验等。
前两篇我们探讨了搜索技术的基石 Apache Lucene 和企业级搜索解决方案 Apache Solr。今天,我们来聊聊一个真正改变搜索游戏规则,但也充满争议的产品 — Elasticsearch。

引言
如果说 Lucene 是幕后英雄,那么 Elasticsearch 就是舞台中央的明星。借助 REST API、分布式架构、强大的生态系统,它让搜索 + 分析成为“马上可用”的服务形式。
在日志平台、可观察性、安全监控、AI 与语义检索等领域,Elasticsearch 的名字几乎成了默认选项。
Elasticsearch 概述
Elasticsearch 是一个开源的分布式搜索和分析引擎,构建于 Apache Lucene 之上。作为一个检索平台,它可以实时存储结构化、非结构化和向量数据,提供快速的混合和向量搜索,支持可观测性与安全分析,并以高性能、高准确性和高相关性实现 AI 驱动的应用。
- 首次发布:2010 年 2 月
- 最新版本:9.1.3(截止 2025 年 9 月)
- 核心依赖:Apache Lucene
- 开源协议:AGPL v3
- 官方网址:https://www.elastic.co/elasticsearch/
- GitHub 仓库:https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch
起源:从食谱搜索到全球“流量明星”
Elasticsearch 的故事始于以色列开发者 Shay Banon。2010 年,当时他在学习厨师课程的妻子需要一款能够快速搜索食谱的工具。虽然当时已经有 Solr 这样的搜索解决方案,但 Shay 认为它们对于分布式场景的支持不够完善。
基于之前开发 Compass(一个基于 Lucene 的搜索库)的经验,Shay 开始构建一个完全分布式的、基于 JSON 的搜索引擎。2010 年 2 月,Elasticsearch 的第一个版本发布。
随着用户日益增多、企业级需求增强,Shay 在 2012 年创立了 Elastic 公司,把 Elasticsearch 不仅作为开源项目,也逐渐商业化运营起来,包括提供托管服务、企业支持,加入 Logstash 日志处理、Kibana 可视化工具等,Elastic 公司也逐渐从一个纯搜索引擎项目演变为一个更广泛的“数据搜索与分析”平台。
协议变更:开源和商业化的博弈
Elasticsearch 的发展并非一帆风顺。其历史上最具转折性的事件当属与 AWS 的冲突及随之而来的开源协议变更。
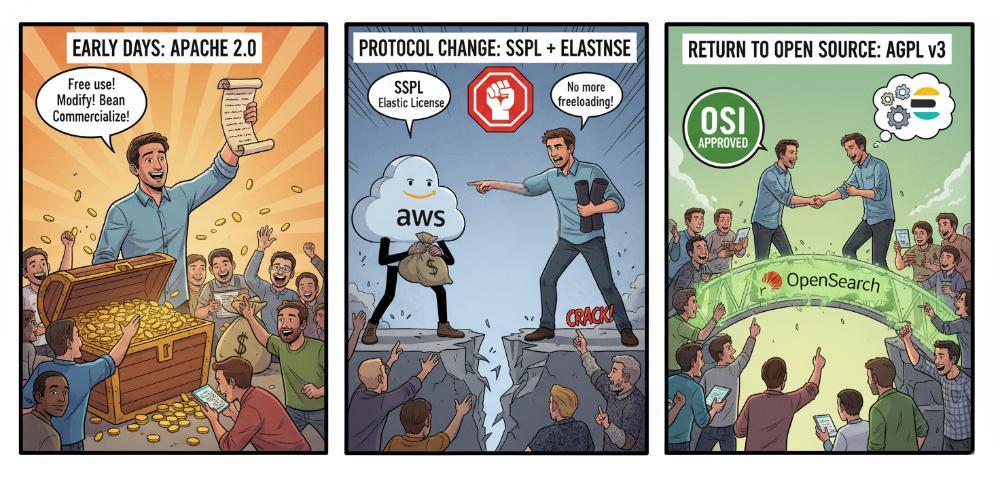
- 早期:Apache 2.0 协议
2010 年 Shay Banon 开源 Elasticsearch 时,最初采用的是 Apache 2.0 协议。Apache 2.0 属于宽松的自由协议,允许任何人免费使用、修改和商用(包括 SaaS 模式)。这帮助 Elasticsearch 快速壮大,成为事实上的“搜索引擎标准”。
- 协议变更:应对云厂商“白嫖”
随着 Elasticsearch 的流行,像 AWS(Amazon Web Services) 等云厂商直接将 Elasticsearch 做成托管服务,并从中获利。Elastic 公司认为这损害了他们的商业利益,因为云厂商“用开源赚钱,却没有回馈社区”。2021 年 1 月,Elastic 宣布 Elasticsearch 和 Kibana 不再采用 Apache 2.0,改为 双重协议:SSPL + Elastic License。这一步导致社区巨大分裂,AWS 带头将 Elasticsearch 分叉为 OpenSearch,并继续以 Apache 2.0 协议维护。
- 再次转向开源:AGPL v3
2024 年 3 月,Elastic 宣布新的版本(Elasticsearch 8.13 起)又新增 AGPL v3 作为一个开源许可选项。AGPL v3 既符合 OSI 真正开源标准,又能约束云厂商闭源托管服务,同时修复社区关系,Elastic 希望通过重新拥抱开源,减少分裂,吸引开发者回归。
Elasticsearch 从宽松到收紧,再到回归开源,是在社区生态与商业利益间寻找平衡的过程。
基本概念
要学习 Elasticsearch,得先了解其五大基本概览:集群、节点、分片、索引和文档。
- 集群(Cluster)
由一个或多个节点组成的整体,提供统一的搜索与存储服务。对外看起来像一个单一系统。
- 节点(Node)
集群中的一台服务器实例。节点有不同角色:
- Master 节点:负责集群管理(分片分配、元数据维护)。
- Data 节点:存储数据、处理搜索和聚合。
- Coordinating 节点:接收请求并调度任务。
- Ingest 节点:负责数据写入前的预处理。
- 索引(Index)
类似于传统数据库的“库”,按逻辑组织数据。一个索引往往对应一个业务场景(如日志、商品信息)。
- 分片(Shard)
为了让索引能水平扩展,Elasticsearch 会把索引拆分为多个 主分片,并为每个主分片创建 副本分片,提升高可用和查询性能。
- 文档(Document)
Elasticsearch 存储和检索的最小数据单元,通常是 JSON 格式。多个文档组成一个索引。
集群架构
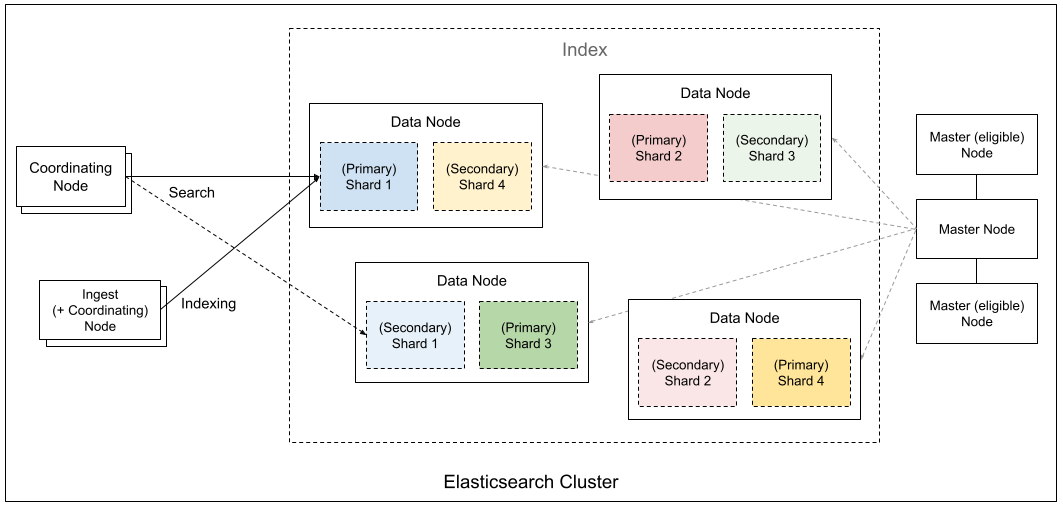
Elasticsearch 通过 Master、Data、Coordinating、Ingest 等不同角色节点的协作,将数据切分成分片并分布式存储,实现了高可用、可扩展的搜索与分析引擎架构。
快速开始:5 分钟体验 Elasticsearch
1. 使用 Docker 启动
# 拉取最新镜像
docker pull docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:9.1.3
# 启动单节点集群
docker run -d --name elasticsearch \
-p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 \
-e "discovery.type=single-node" \
-e "xpack.security.enabled=false" \
docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:9.1.32. 验证安装
# 检查集群状态
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/"
3. 索引文档
# 索引文档
curl -X POST "http://localhost:9200/myindex/_doc" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"title": "Hello Elasticsearch",
"description": "An example document"
}'
3. 搜索文档
# 搜索文档
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/myindex/_search" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "Hello"
}
}
}'
结语
Elasticsearch 是搜索与分析领域标杆性的产品。它将 Lucene 的能力包装起来,加上分布式、易用以及与数据可视化、安全监控等功能的整合,使搜索引擎从专业技术逐渐变为“随手可用”的基础设施。
虽然协议变动、与 OpenSearch 的分叉引发争议,但它在企业与开发者群体中的实际应用价值依然难以替代。
🚀 下期预告
下一篇我们将介绍 OpenSearch,探讨这个 Elasticsearch 分支项目的发展现状、技术特点以及与 Elasticsearch 的详细对比。如果您有特别关注的问题,欢迎提前提出!
💬 三连互动
- 你或公司最近在用 Elasticsearch 吗?拿来做了什么场景?
- 在 Elasticsearch 和 OpenSearch 之间做过技术选型?
- 对 Elasticsearch 的许可证变化有什么看法?
对搜索技术感兴趣的朋友,也欢迎加我微信(ID:lsy965145175)备注“搜索百科”,拉你进 搜索技术交流群,一起探讨与学习!
✨ 推荐阅读
🔗 参考
原文:https://infinilabs.cn/blog/2025/search-wiki-3-elasticsearch/
搜索百科(2):Apache Solr — 企业级搜索的开源先锋
开源项目 • liaosy 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 5765 次浏览 • 2025-09-15 18:12
大家好,我是 INFINI Labs 的石阳。
欢迎回到 《搜索百科》 专栏!每天 5 分钟,带你速览一款搜索相关的技术或产品,同时还会带你探索它们背后的技术原理、发展故事及上手体验等。
上一篇我们认识了搜索技术的基石 Apache Lucene,今天我们将继续这个旅程,了解基于 Lucene 构建的第一个成功商业级搜索平台 —— Apache Solr。

Solr 是什么?
Solr 是一款极速的开源多模态搜索平台,基于 Apache Lucene 的全文、向量和地理空间搜索能力构建而成。Solr 具备高可靠性、可扩展性和容错性,支持分布式索引、复制与负载均衡查询,提供自动故障转移与恢复、集中化配置等功能。如今,Solr 为全球众多大型互联网网站提供搜索和导航功能。
- 首次发布:2004 年,2006 年进入 Apache
- 最新版本:截至 2025 年,已更新至 9.x 系列
- 核心依赖:Apache Lucene
- 开源协议:Apache License 2.0
- 官方网址:https://solr.apache.org
- GitHub 仓库:https://github.com/apache/solr
它的定位是:把 Lucene 打造成独立的企业级搜索服务。相比 Lucene 需要写代码调用,Solr 提供了 Web 管理界面、REST API 和配置文件,让开发者更容易上手。
起源:从网站搜索到 Apache 顶级项目
Solr(读作"solar")的故事始于 2004 年,当时 CNET 公司的开发人员 Yonik Seeley 需要为其新闻网站构建一个搜索功能。虽然 Lucene 提供了强大的核心搜索能力,但直接使用 Lucene 需要编写大量 Java 代码,缺乏开箱即用的功能。
Seeley 决定在 Lucene 之上构建一个更易用的搜索服务器,于是 Solr 诞生了。最初的目标很明确:通过 HTTP/XML 接口提供搜索服务,让任何编程语言都能轻松集成搜索功能。
2006 年,Solr 捐赠给 Apache 基金会,2007 年成为顶级项目。2010 年,Solr 与 Lucene 项目合并,形成了今天我们所知的 Apache Lucene/Solr 项目。
技术架构
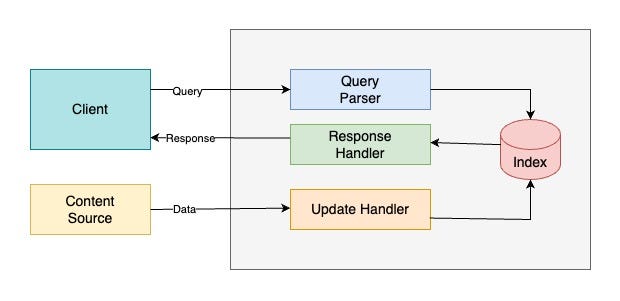
Index(索引)
Apache Solr 的索引就像是用于管理结构化 / 非结构化数据的“数据库”。它以便于分析和全文检索的方式存储数据。
Query Parser(查询解析器)
所有由客户端提交的查询都会由查询解析器处理。
Response Handler(响应处理器)
响应处理器负责为客户端生成合适格式的响应(如 JSON/XML/CSV)。
Update Handler(更新处理器)
更新处理器用于索引操作,即对索引中的数据进行插入、更新和删除。例如,如果我们希望 MySQL 数据与 Apache Solr 保持同步,就需要创建一个负责同步的更新处理器。
功能亮点
- 全文检索:高效支持关键词搜索、布尔查询、短语匹配等。
- 分面搜索(Faceted Search):可以对搜索结果进行分类和聚合统计。
- 分布式架构(SolrCloud):支持集群部署、自动分片、副本和容错。
- 丰富的数据接口:提供 RESTful API,支持 JSON、XML、CSV 等多种格式的数据交互。
- 扩展性与可定制性:通过插件机制支持多语言分词、排序、评分模型等个性化定制。
- 地理位置搜索:内置空间搜索能力,支持基于经纬度的范围查询和排序。
对比: Solr vs Elasticsearch 如何选择?
虽然两者都基于 Lucene,但在设计哲学上有所不同:
| 特性 | Apache Solr | Elasticsearch |
|---|---|---|
| 定位 | 企业级搜索服务器 | 分布式搜索和分析引擎 |
| API | 更标准化,遵循传统 REST | 更灵活,JSON 原生 |
| 分布式 | 需要 ZooKeeper 协调 | 内置分布式协调 |
| 上手难度 | 相对简单,开箱即用 | 学习曲线较陡峭 |
| 生态系统 | 搜索功能更丰富 | 分析和可视化更强 |
| 适用场景 | 传统企业搜索、电商 | 日志分析、实时监控 |
简单来说:Solr 更像"精装房",开箱即用;Elasticsearch 更像"毛坯房",需要更多自定义但更灵活。
快速开始:5 分钟搭建 Solr 服务
1. 下载和安装
# 下载 8.x 版 Solr
wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/solr/solr/8.11.4/solr-8.11.4.tgz
# 解压
tar -xzf solr-8.11.4.tgz
# 启动 Solr(单机模式)
cd solr-8.11.4
bin/solr start2. 创建 Core
# 创建测试 Core
bin/solr create -c test_core
# 查看 Core 状态
bin/solr status3. 索引文档
# 使用 curl 索引 JSON 文档
curl http://localhost:8983/solr/test_core/update -d '
[
{"id": "1", "title": "Solr 入门指南", "content": "Apache Solr 是企业级搜索平台"},
{"id": "2", "title": "搜索技术演进", "content": "从 Lucene 到 Solr 的技术发展"}
]' -H 'Content-type:application/json'
# 提交更改
curl http://localhost:8983/solr/test_core/update -d '<commit/>' -H 'Content-type:application/xml'4. 执行搜索
# 搜索"Solr"
curl "http://localhost:8983/solr/test_core/select?q=content:Solr"
# 使用 JSON 格式返回
curl "http://localhost:8983/solr/test_core/select?q=content:Solr&wt=json"执行搜索返回结果:
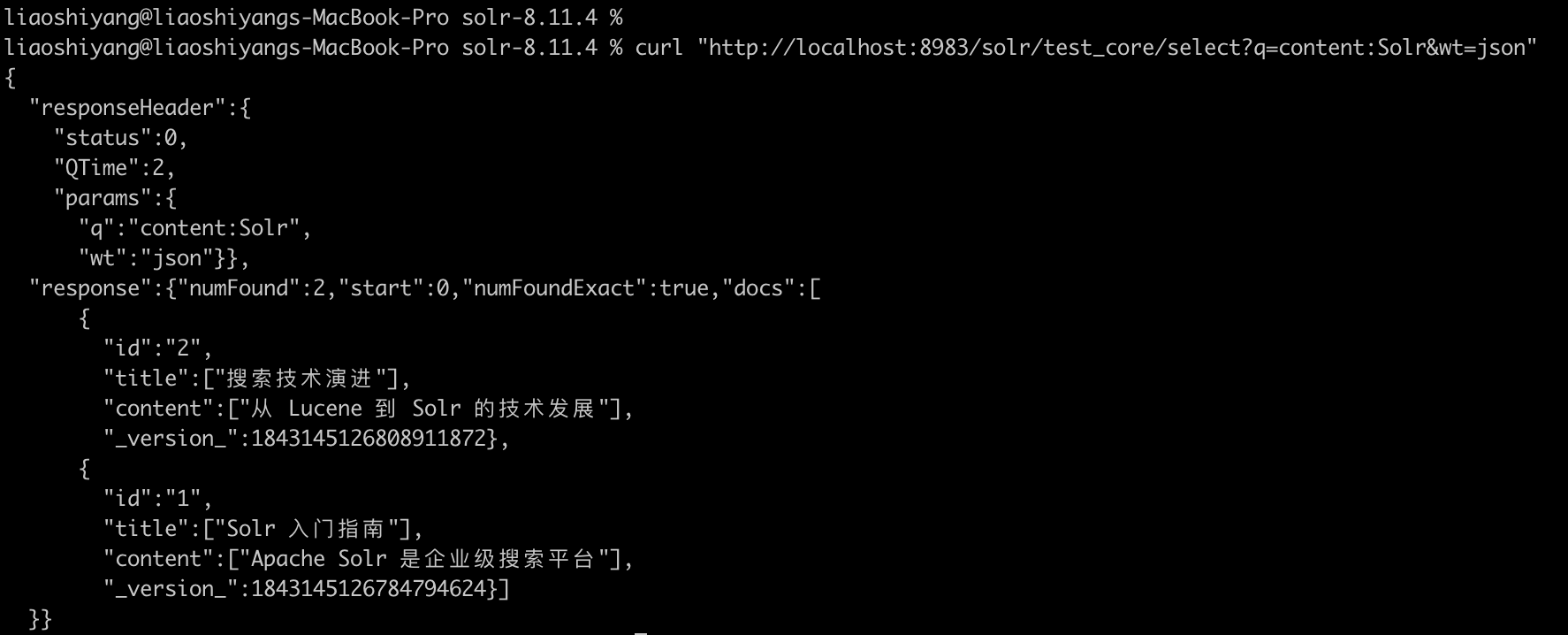
访问 http://localhost:8983/solr 即可使用 Solr 的管理界面。
Dashboard:
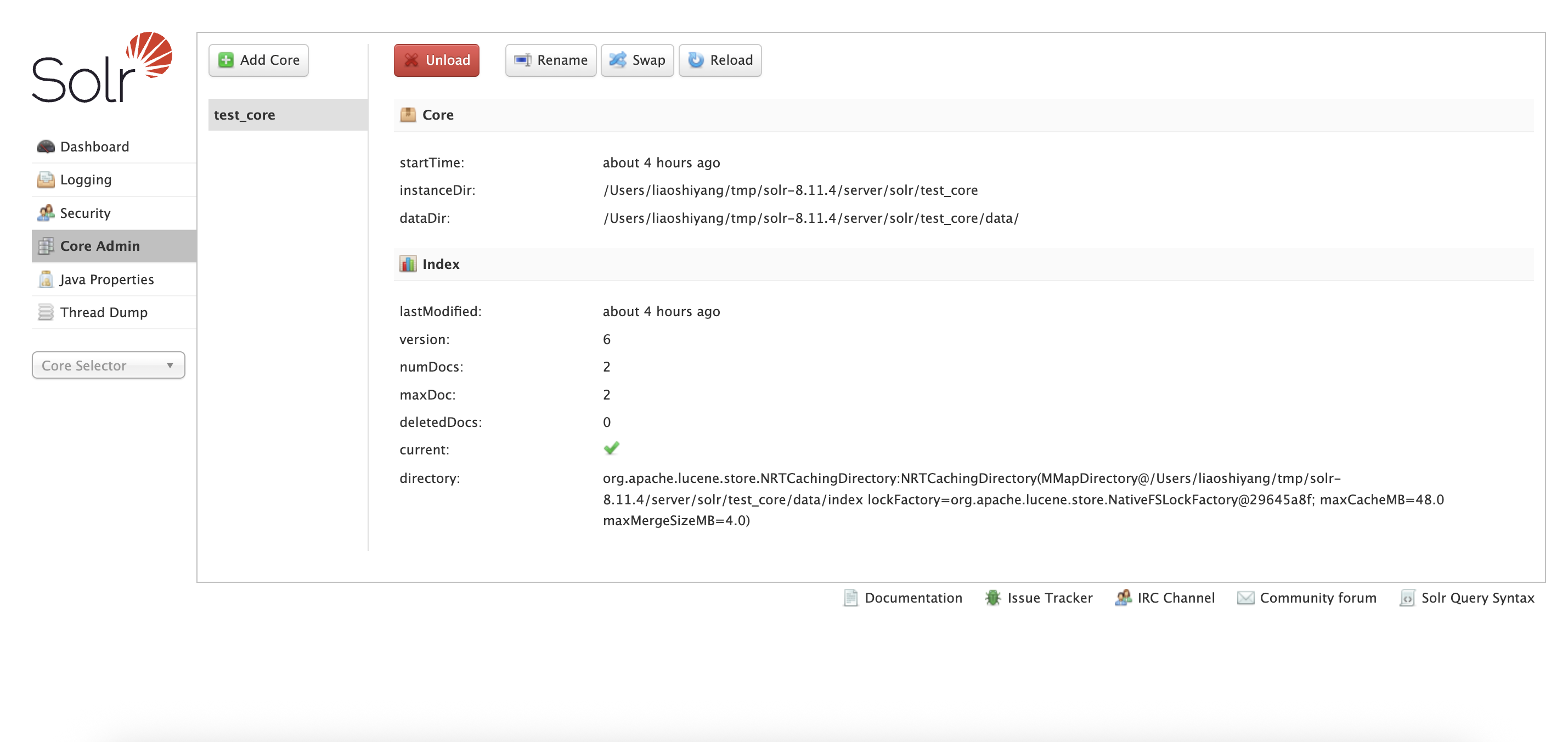
Core Admin:
结语
从最初的公司内部工具,到成为全球范围内广泛使用的开源搜索引擎,Apache Solr 见证并推动了搜索技术的进化。尽管近年来 Elasticsearch、向量数据库和 AI 驱动的搜索技术逐渐崛起,但 Solr 依然是许多企业可靠且成熟的选择。它的故事不仅属于开源社区,也代表了搜索技术发展的一个重要阶段。
🚀 下期预告
在下一篇「搜索百科」中,我们将介绍它的明星兄弟 —— Elasticsearch。
💬 三连互动
- 你现在还在用 Solr 吗?
- 在 Solr 和 Elasticsearch 之间做过技术选型?
- 遇到过有趣的 Solr 使用案例或挑战?
对搜索技术感兴趣的朋友,也欢迎加我微信(ID:lsy965145175)备注“搜索百科”,拉你进 搜索技术交流群,一起探讨与学习!
✨ 推荐阅读
🔗 参考
搜索百科(1):Lucene —— 打开现代搜索世界的第一扇门
Lucene • liaosy 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 5389 次浏览 • 2025-09-10 14:52
大家好,我是 INFINI Labs 的石阳。
这是《搜索百科》系列文章,每天 5 分钟,带你速览一款搜索相关的技术或产品,同时还会带你探索它们背后的技术原理、发展故事及上手体验等。
搜索技术看似专业,但它早已深度融入我们的日常生活。无论是电商搜索、知识检索,还是 AI 语义搜索、RAG、向量检索,背后都有经典与新兴技术的结合。希望这个系列能帮大家建立更清晰的认知,也欢迎留言交流。
引言:为什么先写 Lucene?

如果你曾用 GitHub 搜代码、用电商网站搜商品,或者在日志平台里“捞”报错,你就已经享受了 Lucene 的红利——只是自己还不知道。今天,让我们认识下这位“幕后大佬”,看看它如何以一己之力,孵化了整个现代搜索江湖。没有它,就没有 Elasticsearch 的锋芒,也没有 Solr 的稳健。讲搜索,不从 Lucene 开始,就像讲武侠不提《易筋经》——根基都丢了。
诞生故事:一个程序员的“副业”成果
Lucene 的诞生颇具传奇色彩。它的创造者 Doug Cutting(后来也是 Hadoop 的创始人之一)在 1997 年开始开发 Lucene,最初是为了给他的个人项目——一个网络爬虫和搜索引擎——提供搜索能力。

当时,市面上并没有成熟的开源搜索库可用,Doug 决定自己写一个。他在业余时间一点点打磨,最终在 1999 年发布了第一个版本。2001 年,Lucene 加入了 Apache 软件基金会,成为 Apache 的第一个开源搜索项目。
有趣的是,Lucene 的名字并不是来自什么技术术语,而是取自 Doug Cutting 妻子的中间名——Lucene。这也让这个项目多了一丝浪漫的色彩。
Lucene 概述
Apache Lucene,是一个用 Java 编写的高性能、全文搜索引擎库。它不是那种你下载下来就能直接用的“搜索软件”,而是一个底层库,就像乐高积木里的基础砖块,虽然不起眼,但没有它,很多搜索产品根本搭不起来。
Lucene 提供了强大的索引和查询能力,支持分词、倒排索引、相关性评分、模糊查询、布尔查询等一系列功能。它是 Elasticsearch、Solr、Easysearch、OpenSearch 等现代搜索引擎的核心引擎。
- 首次发布:1999 年
- 最新版本:截至 2025 年 9 月,Lucene 已更新至
10.2.x系列 - 开源协议:Apache License 2.0(商业友好)
- 官网:https://lucene.apache.org/
- GitHub:https://github.com/apache/lucene
社区生态
虽然已经 25 岁"高龄",Lucene 的社区却依然活力满满。作为 Apache 软件基金会的顶级项目,它拥有:
- 100+ 活跃贡献者
- 每月都有新的 commit 和 issue 处理
- 每年发布 2-4 个主要版本
- 完善的文档和活跃的邮件列表
虽然不像 Elasticsearch 那样“出圈”,但在开发者和企业内部系统中仍有广泛使用。
功能亮点:为什么大家都爱它?
- 高性能全文检索内核:倒排索引、短语/布尔/通配符/模糊查询、相关性打分。
- 面向工程的可扩展分析链:分词器、过滤器、同义词、停用词、高亮、排序等。
- 近邻向量检索(KNN):原生支持高维向量的最近邻搜索,为语义检索/RAG 奠基。 
- 嵌入式 & 纯 Java:作为库嵌入任意 Java 应用,掌控细粒度行为与性能。
- 成熟稳定的版本线:9.x 与 10.x 并行演进,兼顾稳定与新特性。
对比优势:Lucene vs 世界
| 产品 | 类型 | 与 Lucene 的关系 |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticsearch | 分布式引擎 | 基于 Lucene,提供分布式、RESTful 接口 |
| Apache Solr | 搜索平台 | 基于 Lucene,提供 Web 管理界面和更多功能 |
| Meilisearch | 轻量引擎 | 不基于 Lucene,用 Rust 编写,主打易用性 |
Lucene 是底层引擎,而其他产品是在它之上构建的完整解决方案。如果你想要完全控制搜索逻辑,Lucene 是最佳选择;如果你想要开箱即用的搜索服务,可以考虑 Elasticsearch 或 Solr。
快速上手:10 分钟体验 Lucene
虽然 Lucene 需要写一些 Java 代码,但其实入门并不复杂。
1. 环境准备
// Maven 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId>
<artifactId>lucene-core</artifactId>
<version>10.xx.xx</version>
</dependency>2. 创建你的第一个索引
// 创建分析器(支持中文)
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();
// 创建索引
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(Paths.get("index"));
IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter(directory, config);
Document doc = new Document();
doc.add(new TextField("content", "欢迎来到 Lucene 的世界", Field.Store.YES));
writer.addDocument(doc);
writer.close();3. 执行搜索
// 搜索 "Lucene"
Query query = new TermQuery(new Term("content", "lucene"));
IndexReader reader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(reader);
TopDocs results = searcher.search(query, 10);
System.out.println("找到 " + results.totalHits + " 条结果");几行 Java 代码,就能完成一个迷你搜索引擎。
结语
Apache Lucene 虽然不是面向最终用户的产品,但它是搜索技术的基石。几乎所有现代搜索引擎都离不开它。如果你对搜索技术有兴趣,学习 Lucene 是理解搜索引擎工作原理的最佳途径。
🚀 下期预告
下一篇,我将介绍 Lucene 的第一个"孩子"—— Apache Solr,看看这个基于 Lucene 的企业级搜索平台如何让搜索变得更简单。
💬 三连互动
- 你或公司最近在用 Lucene 吗?拿来做了什么场景?
- 你觉得 Lucene 最香 / 最坑的点是什么?
- 下一期想先看 Solr 还是 Elasticsearch ?留言告诉我,我来插队!
对搜索技术感兴趣的朋友,也欢迎加我微信(ID:lsy965145175)备注“搜索百科”,拉你进 搜索技术交流群,一起探讨与学习!
elasticsearcg索引配置不变,doc数量不变却越写越慢
Elasticsearch • kin122 回复了问题 • 2 人关注 • 3 个回复 • 12984 次浏览 • 2025-07-30 08:47
Lucene如何实现SpanAndQuery,即SpanTermQuery与逻辑?
Lucene • Charele 回复了问题 • 2 人关注 • 1 个回复 • 4455 次浏览 • 2024-05-15 05:14
Lucene源码和历史版本的问题
默认分类 • pzw9696 回复了问题 • 2 人关注 • 1 个回复 • 2571 次浏览 • 2022-03-13 17:46
社区日报 第1247期 (2021-11-12)
社区日报 • kin122 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 1762 次浏览 • 2021-11-13 23:20
社区日报 第1245期 (2021-11-10)
社区日报 • kin122 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 2099 次浏览 • 2021-11-10 09:41
Lucene索引倒排链数据结构为什么采用单链表,是基于什么考虑的?
Elasticsearch • Ombres 回复了问题 • 4 人关注 • 3 个回复 • 3320 次浏览 • 2021-02-07 14:35
Lucene中如何获取一个字段中所有term的tf最大的那个值
Lucene • suisuimu 回复了问题 • 2 人关注 • 1 个回复 • 6688 次浏览 • 2020-10-27 12:59
lucene 或者 es中不存储原字段的应用场景是什么呢???
Lucene • Charele 回复了问题 • 3 人关注 • 2 个回复 • 3820 次浏览 • 2020-07-22 15:32
关于默认排序的问题。
Elasticsearch • WarrenW 回复了问题 • 3 人关注 • 2 个回复 • 4442 次浏览 • 2020-07-10 14:24
https://www.elastic.co/blog/a-heap-of-trouble
显示全部 »
https://www.elastic.co/blog/a-heap-of-trouble
elasticsearcg索引配置不变,doc数量不变却越写越慢
回复Elasticsearch • kin122 回复了问题 • 2 人关注 • 3 个回复 • 12984 次浏览 • 2025-07-30 08:47
Lucene如何实现SpanAndQuery,即SpanTermQuery与逻辑?
回复Lucene • Charele 回复了问题 • 2 人关注 • 1 个回复 • 4455 次浏览 • 2024-05-15 05:14
Lucene索引倒排链数据结构为什么采用单链表,是基于什么考虑的?
回复Elasticsearch • Ombres 回复了问题 • 4 人关注 • 3 个回复 • 3320 次浏览 • 2021-02-07 14:35
Lucene中如何获取一个字段中所有term的tf最大的那个值
回复Lucene • suisuimu 回复了问题 • 2 人关注 • 1 个回复 • 6688 次浏览 • 2020-10-27 12:59
lucene 或者 es中不存储原字段的应用场景是什么呢???
回复Lucene • Charele 回复了问题 • 3 人关注 • 2 个回复 • 3820 次浏览 • 2020-07-22 15:32
修改Lucene源码,重新打包,替换elasticsearch中原有的Lucene-core.jar包,出现问题
回复Elasticsearch • Kalasearch 回复了问题 • 2 人关注 • 1 个回复 • 9274 次浏览 • 2019-12-29 04:06
es是构建在lucene之上,中国目前有lucene的社区吗?国外的也行
回复Elasticsearch • medcl 回复了问题 • 2 人关注 • 1 个回复 • 3304 次浏览 • 2019-11-15 09:18
Lucene doc value结构自己的一点理解
回复Elasticsearch • code4j 回复了问题 • 5 人关注 • 3 个回复 • 6013 次浏览 • 2019-07-31 14:57
Lucene用LongPoint或者StringField或者IntPoint做主键,哪个效率更高?
回复Lucene • codepub 发起了问题 • 1 人关注 • 0 个回复 • 4428 次浏览 • 2018-04-23 17:00
【搜索客社区日报】第2193期 (2026-03-06)
社区日报 • Fred2000 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 2778 次浏览 • 5 天前
搜索百科(3):Elasticsearch — 搜索界的“流量明星”
Elasticsearch • liaosy 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 17358 次浏览 • 2025-09-16 11:20
大家好,我是 INFINI Labs 的石阳。
欢迎关注 《搜索百科》 专栏!每天 5 分钟,带你速览一款搜索相关的技术或产品,同时还会带你探索它们背后的技术原理、发展故事及上手体验等。
前两篇我们探讨了搜索技术的基石 Apache Lucene 和企业级搜索解决方案 Apache Solr。今天,我们来聊聊一个真正改变搜索游戏规则,但也充满争议的产品 — Elasticsearch。

引言
如果说 Lucene 是幕后英雄,那么 Elasticsearch 就是舞台中央的明星。借助 REST API、分布式架构、强大的生态系统,它让搜索 + 分析成为“马上可用”的服务形式。
在日志平台、可观察性、安全监控、AI 与语义检索等领域,Elasticsearch 的名字几乎成了默认选项。
Elasticsearch 概述
Elasticsearch 是一个开源的分布式搜索和分析引擎,构建于 Apache Lucene 之上。作为一个检索平台,它可以实时存储结构化、非结构化和向量数据,提供快速的混合和向量搜索,支持可观测性与安全分析,并以高性能、高准确性和高相关性实现 AI 驱动的应用。
- 首次发布:2010 年 2 月
- 最新版本:9.1.3(截止 2025 年 9 月)
- 核心依赖:Apache Lucene
- 开源协议:AGPL v3
- 官方网址:https://www.elastic.co/elasticsearch/
- GitHub 仓库:https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch
起源:从食谱搜索到全球“流量明星”
Elasticsearch 的故事始于以色列开发者 Shay Banon。2010 年,当时他在学习厨师课程的妻子需要一款能够快速搜索食谱的工具。虽然当时已经有 Solr 这样的搜索解决方案,但 Shay 认为它们对于分布式场景的支持不够完善。

基于之前开发 Compass(一个基于 Lucene 的搜索库)的经验,Shay 开始构建一个完全分布式的、基于 JSON 的搜索引擎。2010 年 2 月,Elasticsearch 的第一个版本发布。
随着用户日益增多、企业级需求增强,Shay 在 2012 年创立了 Elastic 公司,把 Elasticsearch 不仅作为开源项目,也逐渐商业化运营起来,包括提供托管服务、企业支持,加入 Logstash 日志处理、Kibana 可视化工具等,Elastic 公司也逐渐从一个纯搜索引擎项目演变为一个更广泛的“数据搜索与分析”平台。
协议变更:开源和商业化的博弈
Elasticsearch 的发展并非一帆风顺。其历史上最具转折性的事件当属与 AWS 的冲突及随之而来的开源协议变更。

- 早期:Apache 2.0 协议
2010 年 Shay Banon 开源 Elasticsearch 时,最初采用的是 Apache 2.0 协议。Apache 2.0 属于宽松的自由协议,允许任何人免费使用、修改和商用(包括 SaaS 模式)。这帮助 Elasticsearch 快速壮大,成为事实上的“搜索引擎标准”。
- 协议变更:应对云厂商“白嫖”
随着 Elasticsearch 的流行,像 AWS(Amazon Web Services) 等云厂商直接将 Elasticsearch 做成托管服务,并从中获利。Elastic 公司认为这损害了他们的商业利益,因为云厂商“用开源赚钱,却没有回馈社区”。2021 年 1 月,Elastic 宣布 Elasticsearch 和 Kibana 不再采用 Apache 2.0,改为 双重协议:SSPL + Elastic License。这一步导致社区巨大分裂,AWS 带头将 Elasticsearch 分叉为 OpenSearch,并继续以 Apache 2.0 协议维护。
- 再次转向开源:AGPL v3
2024 年 3 月,Elastic 宣布新的版本(Elasticsearch 8.13 起)又新增 AGPL v3 作为一个开源许可选项。AGPL v3 既符合 OSI 真正开源标准,又能约束云厂商闭源托管服务,同时修复社区关系,Elastic 希望通过重新拥抱开源,减少分裂,吸引开发者回归。
Elasticsearch 从宽松到收紧,再到回归开源,是在社区生态与商业利益间寻找平衡的过程。
基本概念
要学习 Elasticsearch,得先了解其五大基本概览:集群、节点、分片、索引和文档。
- 集群(Cluster)
由一个或多个节点组成的整体,提供统一的搜索与存储服务。对外看起来像一个单一系统。
- 节点(Node)
集群中的一台服务器实例。节点有不同角色:
- Master 节点:负责集群管理(分片分配、元数据维护)。
- Data 节点:存储数据、处理搜索和聚合。
- Coordinating 节点:接收请求并调度任务。
- Ingest 节点:负责数据写入前的预处理。
- 索引(Index)
类似于传统数据库的“库”,按逻辑组织数据。一个索引往往对应一个业务场景(如日志、商品信息)。
- 分片(Shard)
为了让索引能水平扩展,Elasticsearch 会把索引拆分为多个 主分片,并为每个主分片创建 副本分片,提升高可用和查询性能。
- 文档(Document)
Elasticsearch 存储和检索的最小数据单元,通常是 JSON 格式。多个文档组成一个索引。
集群架构

Elasticsearch 通过 Master、Data、Coordinating、Ingest 等不同角色节点的协作,将数据切分成分片并分布式存储,实现了高可用、可扩展的搜索与分析引擎架构。
快速开始:5 分钟体验 Elasticsearch
1. 使用 Docker 启动
# 拉取最新镜像
docker pull docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:9.1.3
# 启动单节点集群
docker run -d --name elasticsearch \
-p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 \
-e "discovery.type=single-node" \
-e "xpack.security.enabled=false" \
docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:9.1.32. 验证安装
# 检查集群状态
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/"
3. 索引文档
# 索引文档
curl -X POST "http://localhost:9200/myindex/_doc" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"title": "Hello Elasticsearch",
"description": "An example document"
}'
3. 搜索文档
# 搜索文档
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/myindex/_search" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "Hello"
}
}
}'
结语
Elasticsearch 是搜索与分析领域标杆性的产品。它将 Lucene 的能力包装起来,加上分布式、易用以及与数据可视化、安全监控等功能的整合,使搜索引擎从专业技术逐渐变为“随手可用”的基础设施。
虽然协议变动、与 OpenSearch 的分叉引发争议,但它在企业与开发者群体中的实际应用价值依然难以替代。
🚀 下期预告
下一篇我们将介绍 OpenSearch,探讨这个 Elasticsearch 分支项目的发展现状、技术特点以及与 Elasticsearch 的详细对比。如果您有特别关注的问题,欢迎提前提出!
💬 三连互动
- 你或公司最近在用 Elasticsearch 吗?拿来做了什么场景?
- 在 Elasticsearch 和 OpenSearch 之间做过技术选型?
- 对 Elasticsearch 的许可证变化有什么看法?
对搜索技术感兴趣的朋友,也欢迎加我微信(ID:lsy965145175)备注“搜索百科”,拉你进 搜索技术交流群,一起探讨与学习!
✨ 推荐阅读
🔗 参考
原文:https://infinilabs.cn/blog/2025/search-wiki-3-elasticsearch/
搜索百科(2):Apache Solr — 企业级搜索的开源先锋
开源项目 • liaosy 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 5765 次浏览 • 2025-09-15 18:12
大家好,我是 INFINI Labs 的石阳。
欢迎回到 《搜索百科》 专栏!每天 5 分钟,带你速览一款搜索相关的技术或产品,同时还会带你探索它们背后的技术原理、发展故事及上手体验等。
上一篇我们认识了搜索技术的基石 Apache Lucene,今天我们将继续这个旅程,了解基于 Lucene 构建的第一个成功商业级搜索平台 —— Apache Solr。

Solr 是什么?
Solr 是一款极速的开源多模态搜索平台,基于 Apache Lucene 的全文、向量和地理空间搜索能力构建而成。Solr 具备高可靠性、可扩展性和容错性,支持分布式索引、复制与负载均衡查询,提供自动故障转移与恢复、集中化配置等功能。如今,Solr 为全球众多大型互联网网站提供搜索和导航功能。
- 首次发布:2004 年,2006 年进入 Apache
- 最新版本:截至 2025 年,已更新至 9.x 系列
- 核心依赖:Apache Lucene
- 开源协议:Apache License 2.0
- 官方网址:https://solr.apache.org
- GitHub 仓库:https://github.com/apache/solr
它的定位是:把 Lucene 打造成独立的企业级搜索服务。相比 Lucene 需要写代码调用,Solr 提供了 Web 管理界面、REST API 和配置文件,让开发者更容易上手。
起源:从网站搜索到 Apache 顶级项目
Solr(读作"solar")的故事始于 2004 年,当时 CNET 公司的开发人员 Yonik Seeley 需要为其新闻网站构建一个搜索功能。虽然 Lucene 提供了强大的核心搜索能力,但直接使用 Lucene 需要编写大量 Java 代码,缺乏开箱即用的功能。
Seeley 决定在 Lucene 之上构建一个更易用的搜索服务器,于是 Solr 诞生了。最初的目标很明确:通过 HTTP/XML 接口提供搜索服务,让任何编程语言都能轻松集成搜索功能。
2006 年,Solr 捐赠给 Apache 基金会,2007 年成为顶级项目。2010 年,Solr 与 Lucene 项目合并,形成了今天我们所知的 Apache Lucene/Solr 项目。
技术架构

Index(索引)
Apache Solr 的索引就像是用于管理结构化 / 非结构化数据的“数据库”。它以便于分析和全文检索的方式存储数据。
Query Parser(查询解析器)
所有由客户端提交的查询都会由查询解析器处理。
Response Handler(响应处理器)
响应处理器负责为客户端生成合适格式的响应(如 JSON/XML/CSV)。
Update Handler(更新处理器)
更新处理器用于索引操作,即对索引中的数据进行插入、更新和删除。例如,如果我们希望 MySQL 数据与 Apache Solr 保持同步,就需要创建一个负责同步的更新处理器。
功能亮点
- 全文检索:高效支持关键词搜索、布尔查询、短语匹配等。
- 分面搜索(Faceted Search):可以对搜索结果进行分类和聚合统计。
- 分布式架构(SolrCloud):支持集群部署、自动分片、副本和容错。
- 丰富的数据接口:提供 RESTful API,支持 JSON、XML、CSV 等多种格式的数据交互。
- 扩展性与可定制性:通过插件机制支持多语言分词、排序、评分模型等个性化定制。
- 地理位置搜索:内置空间搜索能力,支持基于经纬度的范围查询和排序。
对比: Solr vs Elasticsearch 如何选择?
虽然两者都基于 Lucene,但在设计哲学上有所不同:
| 特性 | Apache Solr | Elasticsearch |
|---|---|---|
| 定位 | 企业级搜索服务器 | 分布式搜索和分析引擎 |
| API | 更标准化,遵循传统 REST | 更灵活,JSON 原生 |
| 分布式 | 需要 ZooKeeper 协调 | 内置分布式协调 |
| 上手难度 | 相对简单,开箱即用 | 学习曲线较陡峭 |
| 生态系统 | 搜索功能更丰富 | 分析和可视化更强 |
| 适用场景 | 传统企业搜索、电商 | 日志分析、实时监控 |
简单来说:Solr 更像"精装房",开箱即用;Elasticsearch 更像"毛坯房",需要更多自定义但更灵活。
快速开始:5 分钟搭建 Solr 服务
1. 下载和安装
# 下载 8.x 版 Solr
wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/solr/solr/8.11.4/solr-8.11.4.tgz
# 解压
tar -xzf solr-8.11.4.tgz
# 启动 Solr(单机模式)
cd solr-8.11.4
bin/solr start2. 创建 Core
# 创建测试 Core
bin/solr create -c test_core
# 查看 Core 状态
bin/solr status3. 索引文档
# 使用 curl 索引 JSON 文档
curl http://localhost:8983/solr/test_core/update -d '
[
{"id": "1", "title": "Solr 入门指南", "content": "Apache Solr 是企业级搜索平台"},
{"id": "2", "title": "搜索技术演进", "content": "从 Lucene 到 Solr 的技术发展"}
]' -H 'Content-type:application/json'
# 提交更改
curl http://localhost:8983/solr/test_core/update -d '<commit/>' -H 'Content-type:application/xml'4. 执行搜索
# 搜索"Solr"
curl "http://localhost:8983/solr/test_core/select?q=content:Solr"
# 使用 JSON 格式返回
curl "http://localhost:8983/solr/test_core/select?q=content:Solr&wt=json"执行搜索返回结果:

访问 http://localhost:8983/solr 即可使用 Solr 的管理界面。
Dashboard:

Core Admin:

结语
从最初的公司内部工具,到成为全球范围内广泛使用的开源搜索引擎,Apache Solr 见证并推动了搜索技术的进化。尽管近年来 Elasticsearch、向量数据库和 AI 驱动的搜索技术逐渐崛起,但 Solr 依然是许多企业可靠且成熟的选择。它的故事不仅属于开源社区,也代表了搜索技术发展的一个重要阶段。
🚀 下期预告
在下一篇「搜索百科」中,我们将介绍它的明星兄弟 —— Elasticsearch。
💬 三连互动
- 你现在还在用 Solr 吗?
- 在 Solr 和 Elasticsearch 之间做过技术选型?
- 遇到过有趣的 Solr 使用案例或挑战?
对搜索技术感兴趣的朋友,也欢迎加我微信(ID:lsy965145175)备注“搜索百科”,拉你进 搜索技术交流群,一起探讨与学习!
✨ 推荐阅读
🔗 参考
搜索百科(1):Lucene —— 打开现代搜索世界的第一扇门
Lucene • liaosy 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 5389 次浏览 • 2025-09-10 14:52
大家好,我是 INFINI Labs 的石阳。
这是《搜索百科》系列文章,每天 5 分钟,带你速览一款搜索相关的技术或产品,同时还会带你探索它们背后的技术原理、发展故事及上手体验等。
搜索技术看似专业,但它早已深度融入我们的日常生活。无论是电商搜索、知识检索,还是 AI 语义搜索、RAG、向量检索,背后都有经典与新兴技术的结合。希望这个系列能帮大家建立更清晰的认知,也欢迎留言交流。
引言:为什么先写 Lucene?

如果你曾用 GitHub 搜代码、用电商网站搜商品,或者在日志平台里“捞”报错,你就已经享受了 Lucene 的红利——只是自己还不知道。今天,让我们认识下这位“幕后大佬”,看看它如何以一己之力,孵化了整个现代搜索江湖。没有它,就没有 Elasticsearch 的锋芒,也没有 Solr 的稳健。讲搜索,不从 Lucene 开始,就像讲武侠不提《易筋经》——根基都丢了。
诞生故事:一个程序员的“副业”成果
Lucene 的诞生颇具传奇色彩。它的创造者 Doug Cutting(后来也是 Hadoop 的创始人之一)在 1997 年开始开发 Lucene,最初是为了给他的个人项目——一个网络爬虫和搜索引擎——提供搜索能力。

当时,市面上并没有成熟的开源搜索库可用,Doug 决定自己写一个。他在业余时间一点点打磨,最终在 1999 年发布了第一个版本。2001 年,Lucene 加入了 Apache 软件基金会,成为 Apache 的第一个开源搜索项目。
有趣的是,Lucene 的名字并不是来自什么技术术语,而是取自 Doug Cutting 妻子的中间名——Lucene。这也让这个项目多了一丝浪漫的色彩。
Lucene 概述
Apache Lucene,是一个用 Java 编写的高性能、全文搜索引擎库。它不是那种你下载下来就能直接用的“搜索软件”,而是一个底层库,就像乐高积木里的基础砖块,虽然不起眼,但没有它,很多搜索产品根本搭不起来。
Lucene 提供了强大的索引和查询能力,支持分词、倒排索引、相关性评分、模糊查询、布尔查询等一系列功能。它是 Elasticsearch、Solr、Easysearch、OpenSearch 等现代搜索引擎的核心引擎。
- 首次发布:1999 年
- 最新版本:截至 2025 年 9 月,Lucene 已更新至
10.2.x系列 - 开源协议:Apache License 2.0(商业友好)
- 官网:https://lucene.apache.org/
- GitHub:https://github.com/apache/lucene
社区生态
虽然已经 25 岁"高龄",Lucene 的社区却依然活力满满。作为 Apache 软件基金会的顶级项目,它拥有:
- 100+ 活跃贡献者
- 每月都有新的 commit 和 issue 处理
- 每年发布 2-4 个主要版本
- 完善的文档和活跃的邮件列表
虽然不像 Elasticsearch 那样“出圈”,但在开发者和企业内部系统中仍有广泛使用。
功能亮点:为什么大家都爱它?
- 高性能全文检索内核:倒排索引、短语/布尔/通配符/模糊查询、相关性打分。
- 面向工程的可扩展分析链:分词器、过滤器、同义词、停用词、高亮、排序等。
- 近邻向量检索(KNN):原生支持高维向量的最近邻搜索,为语义检索/RAG 奠基。 
- 嵌入式 & 纯 Java:作为库嵌入任意 Java 应用,掌控细粒度行为与性能。
- 成熟稳定的版本线:9.x 与 10.x 并行演进,兼顾稳定与新特性。
对比优势:Lucene vs 世界
| 产品 | 类型 | 与 Lucene 的关系 |
|---|---|---|
| Elasticsearch | 分布式引擎 | 基于 Lucene,提供分布式、RESTful 接口 |
| Apache Solr | 搜索平台 | 基于 Lucene,提供 Web 管理界面和更多功能 |
| Meilisearch | 轻量引擎 | 不基于 Lucene,用 Rust 编写,主打易用性 |
Lucene 是底层引擎,而其他产品是在它之上构建的完整解决方案。如果你想要完全控制搜索逻辑,Lucene 是最佳选择;如果你想要开箱即用的搜索服务,可以考虑 Elasticsearch 或 Solr。
快速上手:10 分钟体验 Lucene
虽然 Lucene 需要写一些 Java 代码,但其实入门并不复杂。
1. 环境准备
// Maven 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId>
<artifactId>lucene-core</artifactId>
<version>10.xx.xx</version>
</dependency>2. 创建你的第一个索引
// 创建分析器(支持中文)
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();
// 创建索引
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(Paths.get("index"));
IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter(directory, config);
Document doc = new Document();
doc.add(new TextField("content", "欢迎来到 Lucene 的世界", Field.Store.YES));
writer.addDocument(doc);
writer.close();3. 执行搜索
// 搜索 "Lucene"
Query query = new TermQuery(new Term("content", "lucene"));
IndexReader reader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(reader);
TopDocs results = searcher.search(query, 10);
System.out.println("找到 " + results.totalHits + " 条结果");几行 Java 代码,就能完成一个迷你搜索引擎。
结语
Apache Lucene 虽然不是面向最终用户的产品,但它是搜索技术的基石。几乎所有现代搜索引擎都离不开它。如果你对搜索技术有兴趣,学习 Lucene 是理解搜索引擎工作原理的最佳途径。
🚀 下期预告
下一篇,我将介绍 Lucene 的第一个"孩子"—— Apache Solr,看看这个基于 Lucene 的企业级搜索平台如何让搜索变得更简单。
💬 三连互动
- 你或公司最近在用 Lucene 吗?拿来做了什么场景?
- 你觉得 Lucene 最香 / 最坑的点是什么?
- 下一期想先看 Solr 还是 Elasticsearch ?留言告诉我,我来插队!
对搜索技术感兴趣的朋友,也欢迎加我微信(ID:lsy965145175)备注“搜索百科”,拉你进 搜索技术交流群,一起探讨与学习!
社区日报 第1247期 (2021-11-12)
社区日报 • kin122 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 1762 次浏览 • 2021-11-13 23:20
社区日报 第1245期 (2021-11-10)
社区日报 • kin122 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 2099 次浏览 • 2021-11-10 09:41
Day 7 - Elasticsearch中数据是如何存储的
Advent • weizijun 发表了文章 • 7 个评论 • 78098 次浏览 • 2018-12-07 13:55
前言
很多使用Elasticsearch的同学会关心数据存储在ES中的存储容量,会有这样的疑问:xxTB的数据入到ES会使用多少存储空间。这个问题其实很难直接回答的,只有数据写入ES后,才能观察到实际的存储空间。比如同样是1TB的数据,写入ES的存储空间可能差距会非常大,可能小到只有300~400GB,也可能多到6-7TB,为什么会造成这么大的差距呢?究其原因,我们来探究下Elasticsearch中的数据是如何存储。文章中我以Elasticsearch 2.3版本为示例,对应的lucene版本是5.5,Elasticsearch现在已经来到了6.5版本,数字类型、列存等存储结构有些变化,但基本的概念变化不多,文章中的内容依然适用。
Elasticsearch索引结构
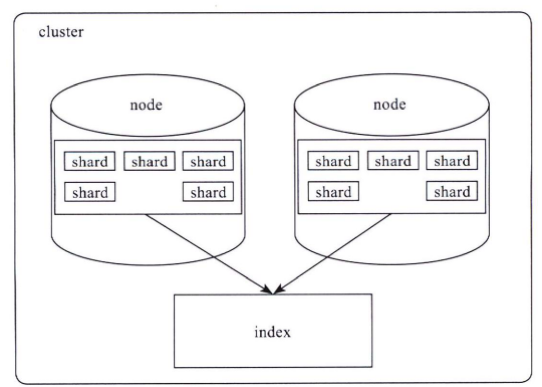
Elasticsearch对外提供的是index的概念,可以类比为DB,用户查询是在index上完成的,每个index由若干个shard组成,以此来达到分布式可扩展的能力。比如下图是一个由10个shard组成的index。
shard是Elasticsearch数据存储的最小单位,index的存储容量为所有shard的存储容量之和。Elasticsearch集群的存储容量则为所有index存储容量之和。
一个shard就对应了一个lucene的library。对于一个shard,Elasticsearch增加了translog的功能,类似于HBase WAL,是数据写入过程中的中间数据,其余的数据都在lucene库中管理的。
所以Elasticsearch索引使用的存储内容主要取决于lucene中的数据存储。
lucene数据存储
下面我们主要看下lucene的文件内容,在了解lucene文件内容前,大家先了解些lucene的基本概念。
lucene基本概念
- segment : lucene内部的数据是由一个个segment组成的,写入lucene的数据并不直接落盘,而是先写在内存中,经过了refresh间隔,lucene才将该时间段写入的全部数据refresh成一个segment,segment多了之后会进行merge成更大的segment。lucene查询时会遍历每个segment完成。由于lucene* 写入的数据是在内存中完成,所以写入效率非常高。但是也存在丢失数据的风险,所以Elasticsearch基于此现象实现了translog,只有在segment数据落盘后,Elasticsearch才会删除对应的translog。
- doc : doc表示lucene中的一条记录
- field :field表示记录中的字段概念,一个doc由若干个field组成。
- term :term是lucene中索引的最小单位,某个field对应的内容如果是全文检索类型,会将内容进行分词,分词的结果就是由term组成的。如果是不分词的字段,那么该字段的内容就是一个term。
- 倒排索引(inverted index): lucene索引的通用叫法,即实现了term到doc list的映射。
- 正排数据:搜索引擎的通用叫法,即原始数据,可以理解为一个doc list。
- docvalues :Elasticsearch中的列式存储的名称,Elasticsearch除了存储原始存储、倒排索引,还存储了一份docvalues,用作分析和排序。
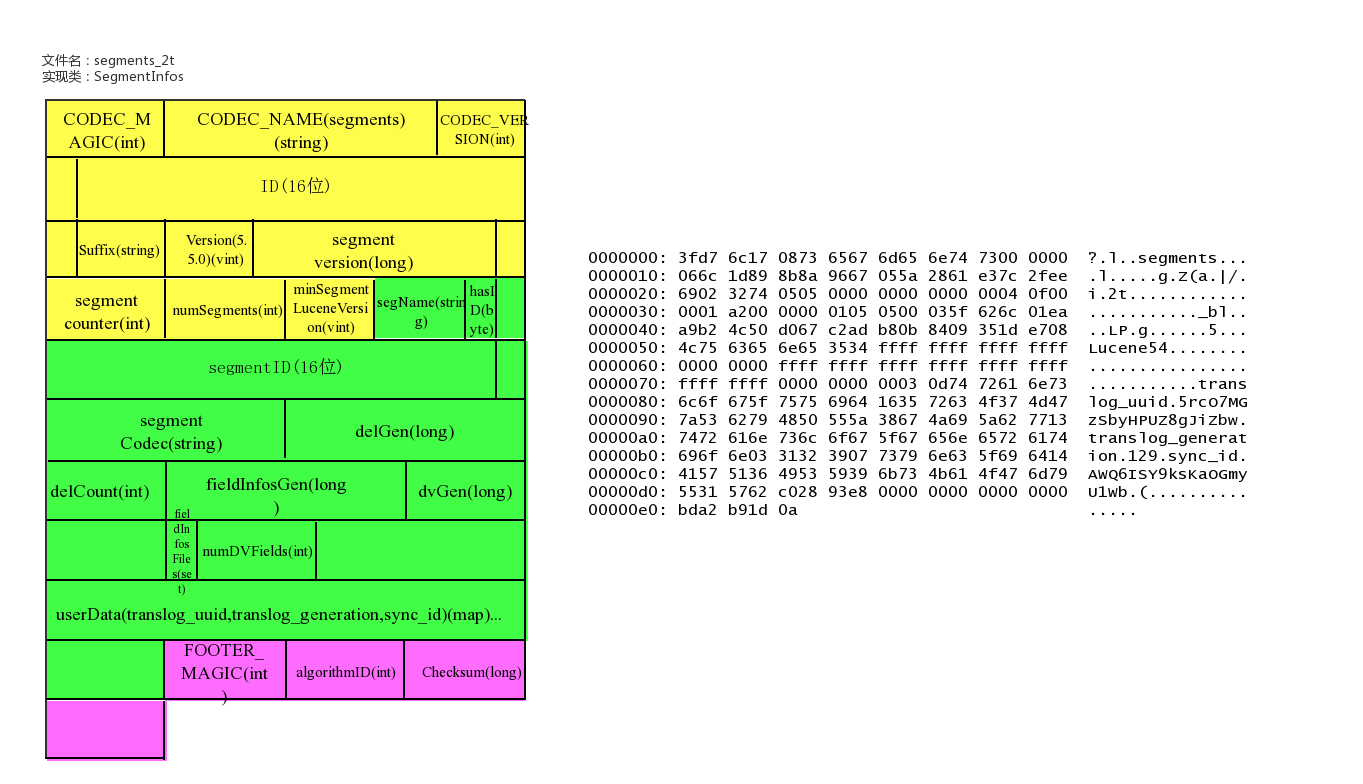
lucene文件内容
lucene包的文件是由很多segment文件组成的,segments_xxx文件记录了lucene包下面的segment文件数量。每个segment会包含如下的文件。
| Name | Extension | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|
| Segment Info | .si | segment的元数据文件 |
| Compound File | .cfs, .cfe | 一个segment包含了如下表的各个文件,为减少打开文件的数量,在segment小的时候,segment的所有文件内容都保存在cfs文件中,cfe文件保存了lucene各文件在cfs文件的位置信息 |
| Fields | .fnm | 保存了fields的相关信息 |
| Field Index | .fdx | 正排存储文件的元数据信息 |
| Field Data | .fdt | 存储了正排存储数据,写入的原文存储在这 |
| Term Dictionary | .tim | 倒排索引的元数据信息 |
| Term Index | .tip | 倒排索引文件,存储了所有的倒排索引数据 |
| Frequencies | .doc | 保存了每个term的doc id列表和term在doc中的词频 |
| Positions | .pos | Stores position information about where a term occurs in the index 全文索引的字段,会有该文件,保存了term在doc中的位置 |
| Payloads | .pay | Stores additional per-position metadata information such as character offsets and user payloads 全文索引的字段,使用了一些像payloads的高级特性会有该文件,保存了term在doc中的一些高级特性 |
| Norms | .nvd, .nvm | 文件保存索引字段加权数据 |
| Per-Document Values | .dvd, .dvm | lucene的docvalues文件,即数据的列式存储,用作聚合和排序 |
| Term Vector Data | .tvx, .tvd, .tvf | Stores offset into the document data file 保存索引字段的矢量信息,用在对term进行高亮,计算文本相关性中使用 |
| Live Documents | .liv | 记录了segment中删除的doc |
测试数据示例
下面我们以真实的数据作为示例,看看lucene中各类型数据的容量占比。
写100w数据,有一个uuid字段,写入的是长度为36位的uuid,字符串总为3600w字节,约为35M。
数据使用一个shard,不带副本,使用默认的压缩算法,写入完成后merge成一个segment方便观察。
使用线上默认的配置,uuid存为不分词的字符串类型。创建如下索引:
PUT test_field
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": "1",
"number_of_replicas": "0",
"refresh_interval": "30s"
}
},
"mappings": {
"type": {
"_all": {
"enabled": false
},
"properties": {
"uuid": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
}
}
}
}
}首先写入100w不同的uuid,使用磁盘容量细节如下:
health status index pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
green open test_field 1 0 1000000 0 122.7mb 122.7mb
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 41M Aug 19 21:23 _8.fdt
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 17K Aug 19 21:23 _8.fdx
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 688B Aug 19 21:23 _8.fnm
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 494B Aug 19 21:23 _8.si
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 265K Aug 19 21:23 _8_Lucene50_0.doc
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 44M Aug 19 21:23 _8_Lucene50_0.tim
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 340K Aug 19 21:23 _8_Lucene50_0.tip
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 37M Aug 19 21:23 _8_Lucene54_0.dvd
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 254B Aug 19 21:23 _8_Lucene54_0.dvm
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 195B Aug 19 21:23 segments_2
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 0B Aug 19 21:20 write.lock可以看到正排数据、倒排索引数据,列存数据容量占比几乎相同,正排数据和倒排数据还会存储Elasticsearch的唯一id字段,所以容量会比列存多一些。
35M的uuid存入Elasticsearch后,数据膨胀了3倍,达到了122.7mb。Elasticsearch竟然这么消耗资源,不要着急下结论,接下来看另一个测试结果。
我们写入100w一样的uuid,然后看看Elasticsearch使用的容量。
health status index pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
green open test_field 1 0 1000000 0 13.2mb 13.2mb
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 5.5M Aug 19 21:29 _6.fdt
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 15K Aug 19 21:29 _6.fdx
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 688B Aug 19 21:29 _6.fnm
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 494B Aug 19 21:29 _6.si
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 309K Aug 19 21:29 _6_Lucene50_0.doc
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 7.0M Aug 19 21:29 _6_Lucene50_0.tim
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 195K Aug 19 21:29 _6_Lucene50_0.tip
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 244K Aug 19 21:29 _6_Lucene54_0.dvd
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 252B Aug 19 21:29 _6_Lucene54_0.dvm
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 195B Aug 19 21:29 segments_2
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 0B Aug 19 21:26 write.lock这回35M的数据Elasticsearch容量只有13.2mb,其中还有主要的占比还是Elasticsearch的唯一id,100w的uuid几乎不占存储容积。
所以在Elasticsearch中建立索引的字段如果基数越大(count distinct),越占用磁盘空间。
我们再看看存100w个不一样的整型会是如何。
health status index pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
green open test_field 1 0 1000000 0 13.6mb 13.6mb
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 6.1M Aug 28 10:19 _42.fdt
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 22K Aug 28 10:19 _42.fdx
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 688B Aug 28 10:19 _42.fnm
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 503B Aug 28 10:19 _42.si
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 2.8M Aug 28 10:19 _42_Lucene50_0.doc
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 2.2M Aug 28 10:19 _42_Lucene50_0.tim
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 83K Aug 28 10:19 _42_Lucene50_0.tip
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 2.5M Aug 28 10:19 _42_Lucene54_0.dvd
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 228B Aug 28 10:19 _42_Lucene54_0.dvm
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 196B Aug 28 10:19 segments_2
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 0B Aug 28 10:16 write.lock从结果可以看到,100w整型数据,Elasticsearch的存储开销为13.6mb。如果以int型计算100w数据的长度的话,为400w字节,大概是3.8mb数据。忽略Elasticsearch唯一id字段的影响,Elasticsearch实际存储容量跟整型数据长度差不多。
我们再看一下开启最佳压缩参数对存储空间的影响:
health status index pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
green open test_field 1 0 1000000 0 107.2mb 107.2mb
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 25M Aug 20 12:30 _5.fdt
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 6.0K Aug 20 12:30 _5.fdx
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 688B Aug 20 12:31 _5.fnm
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 500B Aug 20 12:31 _5.si
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 265K Aug 20 12:31 _5_Lucene50_0.doc
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 44M Aug 20 12:31 _5_Lucene50_0.tim
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 322K Aug 20 12:31 _5_Lucene50_0.tip
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 37M Aug 20 12:31 _5_Lucene54_0.dvd
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 254B Aug 20 12:31 _5_Lucene54_0.dvm
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 224B Aug 20 12:31 segments_4
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 0B Aug 20 12:00 write.lock结果中可以发现,只有正排数据会启动压缩,压缩能力确实强劲,不考虑唯一id字段,存储容量大概压缩到接近50%。
我们还做了一些实验,Elasticsearch默认是开启_all参数的,_all可以让用户传入的整体json数据作为全文检索的字段,可以更方便的检索,但在现实场景中已经使用的不多,相反会增加很多存储容量的开销,可以看下开启_all的磁盘空间使用情况:
health status index pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
green open test_field 1 0 1000000 0 162.4mb 162.4mb
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 41M Aug 18 22:59 _20.fdt
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 18K Aug 18 22:59 _20.fdx
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 777B Aug 18 22:59 _20.fnm
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 59B Aug 18 22:59 _20.nvd
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 78B Aug 18 22:59 _20.nvm
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 539B Aug 18 22:59 _20.si
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 7.2M Aug 18 22:59 _20_Lucene50_0.doc
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 4.2M Aug 18 22:59 _20_Lucene50_0.pos
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 73M Aug 18 22:59 _20_Lucene50_0.tim
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 832K Aug 18 22:59 _20_Lucene50_0.tip
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 37M Aug 18 22:59 _20_Lucene54_0.dvd
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 254B Aug 18 22:59 _20_Lucene54_0.dvm
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 196B Aug 18 22:59 segments_2
-rw-r--r-- 1 weizijun staff 0B Aug 18 22:53 write.lock
开启_all比不开启多了40mb的存储空间,多的数据都在倒排索引上,大约会增加30%多的存储开销。所以线上都直接禁用。
然后我还做了其他几个尝试,为了验证存储容量是否和数据量成正比,写入1000w数据的uuid,发现存储容量基本为100w数据的10倍。我还验证了数据长度是否和数据量成正比,发现把uuid增长2倍、4倍,存储容量也响应的增加了2倍和4倍。在此就不一一列出数据了。
lucene各文件具体内容和实现
lucene数据元信息文件
文件名为:segments_xxx
该文件为lucene数据文件的元信息文件,记录所有segment的元数据信息。
该文件主要记录了目前有多少segment,每个segment有一些基本信息,更新这些信息定位到每个segment的元信息文件。
lucene元信息文件还支持记录userData,Elasticsearch可以在此记录translog的一些相关信息。
文件示例
具体实现类
public final class SegmentInfos implements Cloneable, Iterable<SegmentCommitInfo> {
// generation是segment的版本的概念,从文件名中提取出来,实例中为:2t/101
private long generation; // generation of the "segments_N" for the next commit
private long lastGeneration; // generation of the "segments_N" file we last successfully read
// or wrote; this is normally the same as generation except if
// there was an IOException that had interrupted a commit
/** Id for this commit; only written starting with Lucene 5.0 */
private byte[] id;
/** Which Lucene version wrote this commit, or null if this commit is pre-5.3. */
private Version luceneVersion;
/** Counts how often the index has been changed. */
public long version;
/** Used to name new segments. */
// TODO: should this be a long ...?
public int counter;
/** Version of the oldest segment in the index, or null if there are no segments. */
private Version minSegmentLuceneVersion;
private List<SegmentCommitInfo> segments = new ArrayList<>();
/** Opaque Map<String, String> that user can specify during IndexWriter.commit */
public Map<String,String> userData = Collections.emptyMap();
}
/** Embeds a [read-only] SegmentInfo and adds per-commit
* fields.
*
* @lucene.experimental */
public class SegmentCommitInfo {
/** The {@link SegmentInfo} that we wrap. */
public final SegmentInfo info;
// How many deleted docs in the segment:
private int delCount;
// Generation number of the live docs file (-1 if there
// are no deletes yet):
private long delGen;
// Normally 1+delGen, unless an exception was hit on last
// attempt to write:
private long nextWriteDelGen;
// Generation number of the FieldInfos (-1 if there are no updates)
private long fieldInfosGen;
// Normally 1+fieldInfosGen, unless an exception was hit on last attempt to
// write
private long nextWriteFieldInfosGen; //fieldInfosGen == -1 ? 1 : fieldInfosGen + 1;
// Generation number of the DocValues (-1 if there are no updates)
private long docValuesGen;
// Normally 1+dvGen, unless an exception was hit on last attempt to
// write
private long nextWriteDocValuesGen; //docValuesGen == -1 ? 1 : docValuesGen + 1;
// TODO should we add .files() to FieldInfosFormat, like we have on
// LiveDocsFormat?
// track the fieldInfos update files
private final Set<String> fieldInfosFiles = new HashSet<>();
// Track the per-field DocValues update files
private final Map<Integer,Set<String>> dvUpdatesFiles = new HashMap<>();
// Track the per-generation updates files
@Deprecated
private final Map<Long,Set<String>> genUpdatesFiles = new HashMap<>();
private volatile long sizeInBytes = -1;
}
segment的元信息文件
文件后缀:.si
每个segment都有一个.si文件,记录了该segment的元信息。
segment元信息文件中记录了segment的文档数量,segment对应的文件列表等信息。
文件示例
具体实现类
/**
* Information about a segment such as its name, directory, and files related
* to the segment.
*
* @lucene.experimental
*/
public final class SegmentInfo {
// _bl
public final String name;
/** Where this segment resides. */
public final Directory dir;
/** Id that uniquely identifies this segment. */
private final byte[] id;
private Codec codec;
// Tracks the Lucene version this segment was created with, since 3.1. Null
// indicates an older than 3.0 index, and it's used to detect a too old index.
// The format expected is "x.y" - "2.x" for pre-3.0 indexes (or null), and
// specific versions afterwards ("3.0.0", "3.1.0" etc.).
// see o.a.l.util.Version.
private Version version;
private int maxDoc; // number of docs in seg
private boolean isCompoundFile;
private Map<String,String> diagnostics;
private Set<String> setFiles;
private final Map<String,String> attributes;
}fields信息文件
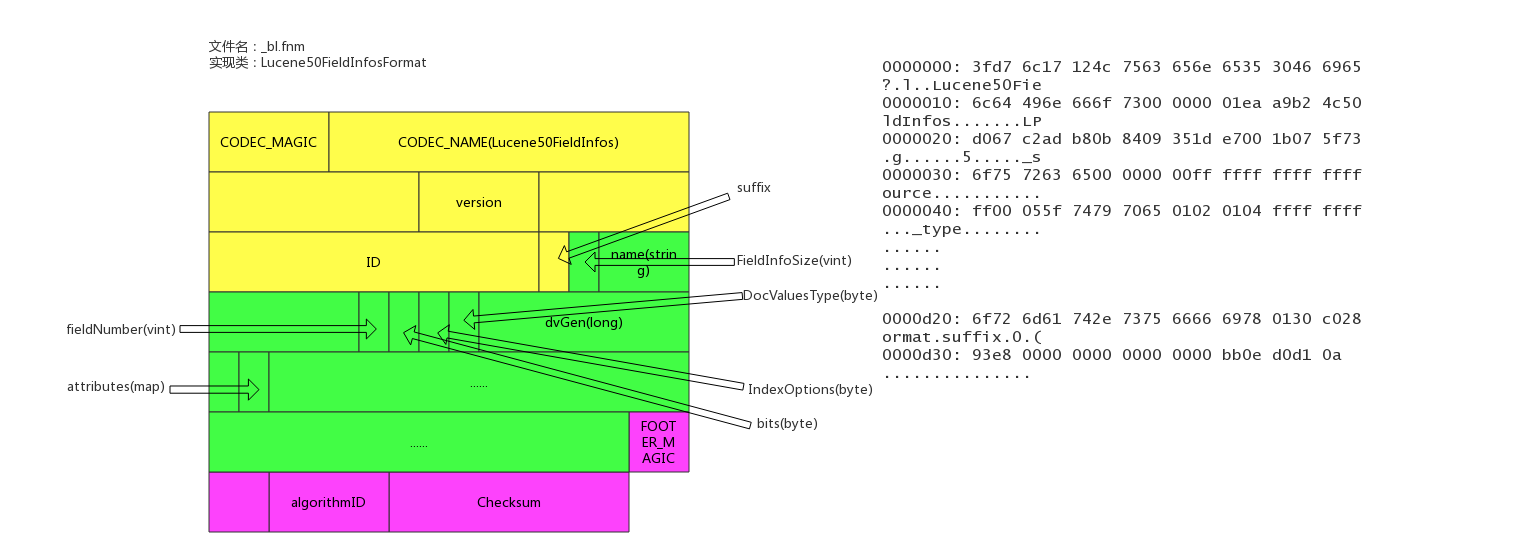
文件后缀:.fnm
该文件存储了fields的基本信息。
fields信息中包括field的数量,field的类型,以及IndexOpetions,包括是否存储、是否索引,是否分词,是否需要列存等等。
文件示例
具体实现类
/**
* Access to the Field Info file that describes document fields and whether or
* not they are indexed. Each segment has a separate Field Info file. Objects
* of this class are thread-safe for multiple readers, but only one thread can
* be adding documents at a time, with no other reader or writer threads
* accessing this object.
**/
public final class FieldInfo {
/** Field's name */
public final String name;
/** Internal field number */
//field在内部的编号
public final int number;
//field docvalues的类型
private DocValuesType docValuesType = DocValuesType.NONE;
// True if any document indexed term vectors
private boolean storeTermVector;
private boolean omitNorms; // omit norms associated with indexed fields
//index的配置项
private IndexOptions indexOptions = IndexOptions.NONE;
private boolean storePayloads; // whether this field stores payloads together with term positions
private final Map<String,String> attributes;
// docvalues的generation
private long dvGen;
}数据存储文件
文件后缀:.fdx, .fdt
索引文件为.fdx,数据文件为.fdt,数据存储文件功能为根据自动的文档id,得到文档的内容,搜索引擎的术语习惯称之为正排数据,即doc_id -> content,es的_source数据就存在这
索引文件记录了快速定位文档数据的索引信息,数据文件记录了所有文档id的具体内容。
文件示例
具体实现类
/**
* Random-access reader for {@link CompressingStoredFieldsIndexWriter}.
* @lucene.internal
*/
public final class CompressingStoredFieldsIndexReader implements Cloneable, Accountable {
private static final long BASE_RAM_BYTES_USED = RamUsageEstimator.shallowSizeOfInstance(CompressingStoredFieldsIndexReader.class);
final int maxDoc;
//docid索引,快速定位某个docid的数组坐标
final int[] docBases;
//快速定位某个docid所在的文件offset的startPointer
final long[] startPointers;
//平均一个chunk的文档数
final int[] avgChunkDocs;
//平均一个chunk的size
final long[] avgChunkSizes;
final PackedInts.Reader[] docBasesDeltas; // delta from the avg
final PackedInts.Reader[] startPointersDeltas; // delta from the avg
}
/**
* {@link StoredFieldsReader} impl for {@link CompressingStoredFieldsFormat}.
* @lucene.experimental
*/
public final class CompressingStoredFieldsReader extends StoredFieldsReader {
//从fdt正排索引文件中获得
private final int version;
// field的基本信息
private final FieldInfos fieldInfos;
//fdt正排索引文件reader
private final CompressingStoredFieldsIndexReader indexReader;
//从fdt正排索引文件中获得,用于指向fdx数据文件的末端,指向numChunks地址4
private final long maxPointer;
//fdx正排数据文件句柄
private final IndexInput fieldsStream;
//块大小
private final int chunkSize;
private final int packedIntsVersion;
//压缩类型
private final CompressionMode compressionMode;
//解压缩处理对象
private final Decompressor decompressor;
//文档数量,从segment元数据中获得
private final int numDocs;
//是否正在merge,默认为false
private final boolean merging;
//初始化时new了一个BlockState,BlockState记录下当前正排文件读取的状态信息
private final BlockState state;
//chunk的数量
private final long numChunks; // number of compressed blocks written
//dirty chunk的数量
private final long numDirtyChunks; // number of incomplete compressed blocks written
//是否close,默认为false
private boolean closed;
}倒排索引文件
索引后缀:.tip,.tim
倒排索引也包含索引文件和数据文件,.tip为索引文件,.tim为数据文件,索引文件包含了每个字段的索引元信息,数据文件有具体的索引内容。
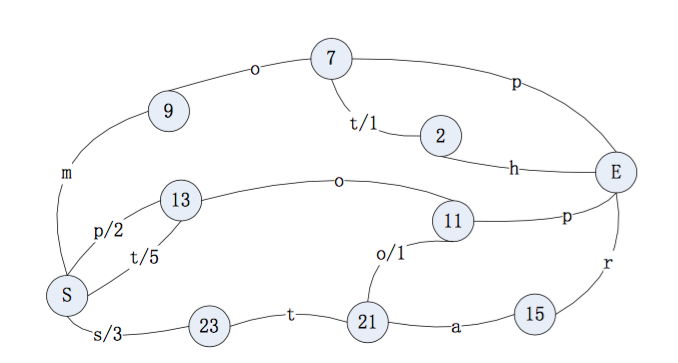
5.5.0版本的倒排索引实现为FST tree,FST tree的最大优势就是内存空间占用非常低 ,具体可以参看下这篇文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/bonelee/p/6226185.html
http://examples.mikemccandless.com/fst.py?terms=&cmd=Build+it 为FST图实例,可以根据输入的数据构造出FST图
输入到 FST 中的数据为:
String inputValues[] = {"mop","moth","pop","star","stop","top"};
long outputValues[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5};生成的 FST 图为:
文件示例
具体实现类
public final class BlockTreeTermsReader extends FieldsProducer {
// Open input to the main terms dict file (_X.tib)
final IndexInput termsIn;
// Reads the terms dict entries, to gather state to
// produce DocsEnum on demand
final PostingsReaderBase postingsReader;
private final TreeMap<String,FieldReader> fields = new TreeMap<>();
/** File offset where the directory starts in the terms file. */
/索引数据文件tim的数据的尾部的元数据的地址
private long dirOffset;
/** File offset where the directory starts in the index file. */
//索引文件tip的数据的尾部的元数据的地址
private long indexDirOffset;
//semgent的名称
final String segment;
//版本号
final int version;
//5.3.x index, we record up front if we may have written any auto-prefix terms,示例中记录的是false
final boolean anyAutoPrefixTerms;
}
/**
* BlockTree's implementation of {@link Terms}.
* @lucene.internal
*/
public final class FieldReader extends Terms implements Accountable {
//term的数量
final long numTerms;
//field信息
final FieldInfo fieldInfo;
final long sumTotalTermFreq;
//总的文档频率
final long sumDocFreq;
//文档数量
final int docCount;
//字段在索引文件tip中的起始位置
final long indexStartFP;
final long rootBlockFP;
final BytesRef rootCode;
final BytesRef minTerm;
final BytesRef maxTerm;
//longs:metadata buffer, holding monotonic values
final int longsSize;
final BlockTreeTermsReader parent;
final FST<BytesRef> index;
}倒排链文件
文件后缀:.doc, .pos, .pay
.doc保存了每个term的doc id列表和term在doc中的词频
全文索引的字段,会有.pos文件,保存了term在doc中的位置
全文索引的字段,使用了一些像payloads的高级特性才会有.pay文件,保存了term在doc中的一些高级特性
文件示例
具体实现类
/**
* Concrete class that reads docId(maybe frq,pos,offset,payloads) list
* with postings format.
*
* @lucene.experimental
*/
public final class Lucene50PostingsReader extends PostingsReaderBase {
private static final long BASE_RAM_BYTES_USED = RamUsageEstimator.shallowSizeOfInstance(Lucene50PostingsReader.class);
private final IndexInput docIn;
private final IndexInput posIn;
private final IndexInput payIn;
final ForUtil forUtil;
private int version;
//不分词的字段使用的是该对象,基于skiplist实现了倒排链
final class BlockDocsEnum extends PostingsEnum {
}
//全文检索字段使用的是该对象
final class BlockPostingsEnum extends PostingsEnum {
}
//包含高级特性的字段使用的是该对象
final class EverythingEnum extends PostingsEnum {
}
}列存文件(docvalues)
文件后缀:.dvm, .dvd
索引文件为.dvm,数据文件为.dvd。
lucene实现的docvalues有如下类型:
- 1、NONE 不开启docvalue时的状态
- 2、NUMERIC 单个数值类型的docvalue主要包括(int,long,float,double)
- 3、BINARY 二进制类型值对应不同的codes最大值可能超过32766字节,
- 4、SORTED 有序增量字节存储,仅仅存储不同部分的值和偏移量指针,值必须小于等于32766字节
- 5、SORTED_NUMERIC 存储数值类型的有序数组列表
- 6、SORTED_SET 可以存储多值域的docvalue值,但返回时,仅仅只能返回多值域的第一个docvalue
- 7、对应not_anaylized的string字段,使用的是SORTED_SET类型,number的类型是SORTED_NUMERIC类型
其中SORTED_SET 的 SORTED_SINGLE_VALUED类型包括了两类数据 : binary + numeric, binary是按ord排序的term的列表,numeric是doc到ord的映射。
文件示例
具体实现类
/** reader for {@link Lucene54DocValuesFormat} */
final class Lucene54DocValuesProducer extends DocValuesProducer implements Closeable {
//number类型的field的列存列表
private final Map<String,NumericEntry> numerics = new HashMap<>();
//字符串类型的field的列存列表
private final Map<String,BinaryEntry> binaries = new HashMap<>();
//有序字符串类型的field的列存列表
private final Map<String,SortedSetEntry> sortedSets = new HashMap<>();
//有序number类型的field的列存列表
private final Map<String,SortedSetEntry> sortedNumerics = new HashMap<>();
//字符串类型的field的ords列表
private final Map<String,NumericEntry> ords = new HashMap<>();
//docId -> address -> ord 中field的ords列表
private final Map<String,NumericEntry> ordIndexes = new HashMap<>();
//field的数量
private final int numFields;
//内存使用量
private final AtomicLong ramBytesUsed;
//数据源的文件句柄
private final IndexInput data;
//文档数
private final int maxDoc;
// memory-resident structures
private final Map<String,MonotonicBlockPackedReader> addressInstances = new HashMap<>();
private final Map<String,ReverseTermsIndex> reverseIndexInstances = new HashMap<>();
private final Map<String,DirectMonotonicReader.Meta> directAddressesMeta = new HashMap<>();
//是否正在merge
private final boolean merging;
}
/** metadata entry for a numeric docvalues field */
static class NumericEntry {
private NumericEntry() {}
/** offset to the bitset representing docsWithField, or -1 if no documents have missing values */
long missingOffset;
/** offset to the actual numeric values */
//field的在数据文件中的起始地址
public long offset;
/** end offset to the actual numeric values */
//field的在数据文件中的结尾地址
public long endOffset;
/** bits per value used to pack the numeric values */
public int bitsPerValue;
//format类型
int format;
/** count of values written */
public long count;
/** monotonic meta */
public DirectMonotonicReader.Meta monotonicMeta;
//最小的value
long minValue;
//Compressed by computing the GCD
long gcd;
//Compressed by giving IDs to unique values.
long table[];
/** for sparse compression */
long numDocsWithValue;
NumericEntry nonMissingValues;
NumberType numberType;
}
/** metadata entry for a binary docvalues field */
static class BinaryEntry {
private BinaryEntry() {}
/** offset to the bitset representing docsWithField, or -1 if no documents have missing values */
long missingOffset;
/** offset to the actual binary values */
//field的在数据文件中的起始地址
long offset;
int format;
/** count of values written */
public long count;
//最短字符串的长度
int minLength;
//最长字符串的长度
int maxLength;
/** offset to the addressing data that maps a value to its slice of the byte[] */
public long addressesOffset, addressesEndOffset;
/** meta data for addresses */
public DirectMonotonicReader.Meta addressesMeta;
/** offset to the reverse index */
public long reverseIndexOffset;
/** packed ints version used to encode addressing information */
public int packedIntsVersion;
/** packed ints blocksize */
public int blockSize;
}参考资料
一个简单的Lucene工具类,通过注释的方式来配置构建索引的字段。提供新建索引、查找、删除、更新方法,支持分页。
Lucene • pengshaojie 发表了文章 • 6 个评论 • 4532 次浏览 • 2018-02-12 10:23
Lucene 6 基于BKD Tree Index 的应用
Elasticsearch • keehang 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 6830 次浏览 • 2017-08-04 10:20
测试集合:模拟一亿条
0," nnrIuS","raet","lnsr","inu ","saia",83.405273,73.302012,3991,24,"N"," usA","airport","rra i"
1,"omlritp","aaVe","y Mu","AaVV","NMc ",15.459643,-20.826241,2627,54,"a","eemo","airport","MaArp"
2,"kyaneMr","iasm","raAA"," tnt","inls",16.606066,38.663728,2761,53,"o","arIi","airport","uiron"2017年学习内容
Lucene • guoshuangjiang 发表了文章 • 4 个评论 • 5623 次浏览 • 2017-01-05 18:05
- 重新看lucene源码
- 看es源码
- 对比lucene和es
- 基于lucene实现自己的搜索框架
- 重新看lucene源码
- 看es源码
- 对比lucene和es
- 基于lucene实现自己的搜索框架
Lucene5.5入门第十篇完结篇——使用Highlighter使关键词高亮
Lucene • kl 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 7429 次浏览 • 2016-06-24 11:27
前言
我们在使用百度和谷歌等搜索引擎的时候,你会发现,搜索引擎会把和我们输入的关键字以红色的字体显示,来突出显示结果的准确性,这就是高亮显示的使用场景
准备
使用Highlighter需要导入相应的jar包,maven项目可以加入如下依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId>
<artifactId>lucene-highlighter</artifactId>
<version>5.5.0</version>
</dependency>
直接看代码
/**
* @author kl by 2016/3/19
* @boke www.kailing.pub
*/
public class FieldSetBoostTest {
//索引目录
String indexDir="E:\\LuceneIndex";
//测试数据
String theme="中国";
String []title={"中国是一个伟大的国家","我爱你的的祖国,美丽的中国","是什么,中国令美日等国虎视眈眈"};
/**
* Lucence5.5返回IndexWriter实例
* @param directory
* @return
*/
public IndexWriter getIndexWriter(Directory directory){
Analyzer analyzer=new CJKAnalyzer();//中日韩二元分词
IndexWriterConfig writerConfig=new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
IndexWriter writer=null;
try {
writer =new IndexWriter(directory,writerConfig);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return writer;
}
public Directory getDirctory(String indexDir){
Directory directory=null;
try {
directory=FSDirectory.open(Paths.get(indexDir));
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return directory;
}
/**
* 创建索引不加权
* @throws Exception
*/
public void Indexer()throws Exception{
IndexWriter writer=getIndexWriter(getDirctory(indexDir));
Document doc=null;
for(String str:title){
doc=new Document();
//Lucence5.5 Fileld有多个实现,StringFIeld不分词 TextField分词
doc.add(new StringField("theme",theme, Field.Store.YES));
Field field=new TextField("title",str, Field.Store.YES);
doc.add(field);
writer.addDocument(doc);
}
writer.close();
}
/**
* 关键命中词高亮输出处理
* @param query
* @param context
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static String getHighlighterString(Query query,String context)throws Exception{
//对促成文档匹配的实际项进行评分
QueryScorer scorer=new QueryScorer(query);
//设置高亮的HTML标签格式
Formatter simpleHTMLFormatter=new SimpleHTMLFormatter("","");
//实例化高亮分析器
Highlighter highlighter=new Highlighter(simpleHTMLFormatter,scorer);
//提供静态方法,支持从数据源中获取TokenStream,进行token处理
TokenStream tokenStream=new CJKAnalyzer().tokenStream("title", new StringReader(context));
return highlighter.getBestFragment(tokenStream, context);
}
@Test
public void searcherTest()throws Exception{
// Indexer();
IndexReader reader= DirectoryReader.open(getDirctory(indexDir));
IndexSearcher is=new IndexSearcher(reader);
System.out.println("总的文档数:"+reader.numDocs());
QueryParser qp=new QueryParser("title",new CJKAnalyzer());
String q="中国";
Query query=qp.parse(q);
TopDocs tDocs=is.search(query,11);
System.out.println("查询-》"+q+"《-总共命中【"+tDocs.totalHits+"】条结果");
for (ScoreDoc scoredoc:tDocs.scoreDocs){
Document doc = is.doc(scoredoc.doc);
String context=doc.get("title");
if(context!=null){
System.out.println(getHighlighterString(query,context));
}
}
}
}
查询效果如下:
Lucene5.5入门第九篇——使用searchafter方法实现分页查询
Lucene • kl 发表了文章 • 2 个评论 • 11524 次浏览 • 2016-06-24 11:25
前言
任何数据量大的情况下,取数据的时候都需要做分页的处理,比如我们百度的时候,结果往往有上千万的结果,而当前呈现在的只有几页的内容,这就是分页的场景,lucene也提供了分页查询的支持
认识searchafter
使用IndexSearcher的searchafter方法可以轻松实现分页查询,如下图
searchafter有多个重载的方法,其中有些searchafter方法Lucene已不推荐使用了,用的多的就searchAfter(final ScoreDoc after, Query query, int numHits)
它有三个形参,分别是
after:上一页最后一个ScoreDoc;
query:query接口实现类的对象,query对象可以通过QueryParser类来创建,也可以自己new Query接口的某一个特定接口实现类;
numHits:每页显示的条数
searchafter官方文档说明地址
重点在下面
/**
* Created by 小陈 on 2016/3/25.
*/
public class IndexerPaging {
//测试数据,模拟数据库表结构
private static String[] ids={"1","2","3","4","5","6"}; //用户ID
private static String [] names={"kl","kl","kl","kl","kl","fds"};
private static String [] describes={"shi yi ge mei nan zi","Don't know","Is an idiot\n","Is an idiot\n","Is an idiot\n","Is an idiot\n"};
//索引存储地址
private static String indexDir="E:\\javaEEworkspace\\LuceneDemo\\LuceneIndex";
/**
* 获取操作索引实体,并添加测试数据
* @param indexDir 索引存储位置
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void getIndexWriter(String indexDir)throws Exception{
IndexWriterConfig writerConfig=new IndexWriterConfig(getAnalyzer());
IndexWriter indexWriter=new IndexWriter(FSDirectory.open(Paths.get(indexDir)),writerConfig);
Document document=new Document();
//Field.Store.YES或者NO(存储域选项)
//设置为YES表示或把这个域中的内容完全存储到文件中,方便进行文本的还原
//设置为NO表示把这个域的内容不存储到文件中,但是可以被索引,此时内容无法完全还原(doc.get)
for(int i=0;i1){
int pageIndexLast=(pageIndex-1)*pageSize-1;
TopDocs hits=searcher.search(query,pageIndexLast);
if(hits.totalHits>=pageIndexLast)
return hits.scoreDocs[pageIndexLast];
}
return null;
}
public static void searcher(String indexDir,String q,int pageIndex,int pageSize)throws Exception{
Directory directory= FSDirectory.open(Paths.get(indexDir));
IndexReader reader= DirectoryReader.open(directory);
IndexSearcher indexSearcher=new IndexSearcher(reader);
QueryParser queryParser=new QueryParser("names",new StandardAnalyzer());
Query query=queryParser.parse(q);
//分页查询
TopDocs hits= indexSearcher.searchAfter(getPageLastScoreDoc(pageIndex,pageSize,query,indexSearcher),query,pageSize);//查询首次的30条
System.out.println("匹配 "+q+"查询到"+hits.totalHits+"个记录");
for (ScoreDoc scoreDoc:hits.scoreDocs){
Document doc=indexSearcher.doc(scoreDoc.doc);
System.out.println(doc.get("describes"));//打印Document的fileName属性
}
reader.close();
directory.close();//关闭连接
}
/**
* 得到默认分词器
* @return
*/
public static Analyzer getAnalyzer(){
return new StandardAnalyzer();
}
@Test
public void Test()throws Exception{
// getIndexWriter(indexDir);
searcher(indexDir,"kl",1,10);//查询测试
}
}Lucene5.5入门第八篇——使用QueryParser实现高级查询
Lucene • kl 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 10728 次浏览 • 2016-06-24 11:23
前言
为了解决复杂的查询业务,Lucene给我们提供了一个查询语义分析器,一套完整的语法规则,能够满足大部分的查询需求,而不用关心底层是使用什么Query实现类,就好比写sql一样。 Lucene推荐我们使用QueryParser,而不是各种Query的实现类。但是,QueryParser不能满足所有的查询有求,比如多文档域联合查询 。有时候还是需要使用到Query的相关实现类,好了,下面我们就来看看QueryParser能够解析什么语法,解决什么问题,以及多文档域的查询
直接上代码
每个语法都可以多测试一遍,看看结果,能够加深你的理解,因为这边测试的实在是多,测试结果我就不贴了;
ps:各个查询语义可以交叉使用的,下面代码有部分也用到了,但是这边因为是写的例子,为了能更好的区分每个语义的作用,所有没有做太多的尝试
/**
* @author kl by 2016/3/20
* @boke www.kailing.pub
*/
public class QueryTest {
//索引目录
String indexDir="E:\\LuceneIndex";
//测试数据目录
String dataDir="E:\\LuceneTestData";
/**
* Lucence5.5返回IndexWriter实例
* @param directory
* @return
*/
public IndexWriter getIndexWriter(Directory directory){
Analyzer analyzer=new StandardAnalyzer();
IndexWriterConfig writerConfig=new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
IndexWriter writer=null;
try {
writer =new IndexWriter(directory,writerConfig);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return writer;
}
public Directory getDirctory(String indexDir){
Directory directory=null;
try {
directory= FSDirectory.open(Paths.get(indexDir));
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return directory;
}
@Test
public void TestIndexer()throws Exception{
File[] files= new File(dataDir).listFiles();
IndexWriter writer=getIndexWriter(getDirctory(indexDir));
for(File file:files){
Document doc=new Document();
doc.add(new TextField("filePath",file.getCanonicalPath(), Field.Store.YES));
doc.add(new TextField("context",new FileReader(file)));
writer.addDocument(doc);
}
System.out.println("总共添加了"+writer.numDocs()+"个文档");
writer.close();
}
@Test
public void testSearcher()throws Exception{
IndexReader reader= DirectoryReader.open(getDirctory(indexDir));
IndexSearcher searcher=new IndexSearcher(reader);
QueryParser queryParser=new QueryParser("context",new StandardAnalyzer());
Query queryw=queryParser.parse("Licensor");//完整匹配分词查询
/**
* 通配符 ?,*的使用
*/
Query queryy=queryParser.parse("Lice?sor");//使用?匹配单个字符查询
Query queryx=queryParser.parse("L*r");//使用*匹配多个字符查询
/**
* 布尔运算AND, OR,NOT,+,-的使用,注意:一定要是大写的AND和OR,NOT
*/
Query queryo=queryParser.parse("Licensor OR ce*");//使用OR联合多关键字查询,也可用空格代替OR
Query queryoo=queryParser.parse(" Licensor ce*");//这个和使用OR一样的效果
Query queryjia=queryParser.parse("+Licensor Wildcard");//+代表必须的条件,搜索文档必须包含Licensor 可能有Wildcard
Query querya=queryParser.parse("Licensor AND ce* AND Licenso?");//使用AND取多个关键字的并集查询
Query queryNot=queryParser.parse("'Lincensor Apache' NOT 'Apache Licensor'");//搜索Lincensor Apache而不是Apache Licensor
Query queryjian=queryParser.parse("'Lincensor Apache' - 'Apache Licensor'");//"-"同NOT的效果一样
/**
* 使用正则表达式查询
*/
Query queryRegular=queryParser.parse("/[Lab]icensor/");//这个匹配Lincensor,aicensor,bicensor分词
Query queryRegularr=queryParser.parse("/[Lab]icenso[a-z]/");//根据需要可以更灵活的使用
/**
* 使用~模糊匹配查询
* 这个要和*号的用法区分下,*号完整通配多个字符查询,而~不是简单的通配,这个模糊匹配和Lucene的评分有关
*/
Query queryFuzzy=queryParser.parse("icensor~");//可以查到Licensor关键字,而queryParser.parse("icensor*")查不到
Query queryFuzzyparam=queryParser.parse("Licens~1");//~后面可加0-2的整数来制定模糊匹配度,默认不加为1
Query queryFuzzyParam=queryParser.parse("Licens cens ~0");//~还可以模糊匹配差异化N字符数的多个关键字
/**
* 范围查询,多用于数字和时间的查询
*/
Query queryRange =queryParser.parse("{abc TO Licens}");//{}abc与Licenszhi间的文件,不包含
Query queryRangex =queryParser.parse("[abc TO Licens]");//{}abc与Licenszhi间的文件,包含本身
/**
* 关键字加权处理查询
*/
//默认为1,可加权可降权,可通过加权处理给匹配的结果排序
Query queryBoosting =queryParser.parse("Licensor Wildcard^4 ");
/**
* Grouping组合查询
*/
Query queryGrouping =queryParser.parse("(+Licensor +Wildcard) AND easier");//可使用()组合多个条件查询
//ps: 查询部分字符需要转义处理,如(+ - && || ! ( ) { } [ ] ^ " ~ * ? : \ /)
/**
* 使用MultiFieldQueryParser进行多个文档域查询
*/
Map boost=new HashMap();
boost.put("filePath",1.5F);//设置文档域的权值
boost.put("context",2F);
QueryParser multiField=new MultiFieldQueryParser(new String[]{"filePath","context"},new StandardAnalyzer(),boost);
Query queryq=multiField.parse("lucenetestdata");
TopDocs topDocs= searcher.search(queryq,10);
System.out.println("查询结果共有"+topDocs.totalHits+"条");
for(ScoreDoc scoreDoc:topDocs.scoreDocs){
Document document=searcher.doc(scoreDoc.doc);
System.out.println(document.get("filePath")+"--评分:"+scoreDoc.score);
}
}
}
ps:代码中有大量注释,有些不一定理解到位了,深入了解 请参考官方说明:
https://lucene.apache.org/core ... rchesLucene5.5入门第七篇——Lucene索引文档域加权
Lucene • kl 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 7313 次浏览 • 2016-06-24 11:22
前言
就拿百度说事吧,使用百度搜索引擎的时候,你会发现,卧槽,这什么玩意,前面的几个结果根本就不是老子要的东西,都是些推广的内容,而结果匹配度高的还排在老后面去了,百度这铲屎的干嘛吃的!这也不能怪百度,毕竟人家靠推广吃饭的,自然把交了钱的结果权值提高了 !这算文档域加权的使用场景吧
说明
所谓索引域加"权",就是根据需求的不同,对不同的关键值或者不同的关键索引分配不同的权值,因为查询的时候Lucene的评分机制和权值的高低是成正比的,这样权值高的内容更容易被用户搜索出来,而且排在前面。在Lucene3.x版本的时候可以给文档加权,到4.x版本后就取消了给文档加权了,就只有给文档域加权了,如果想达到给文档加权的效果,就要该文档的每个域都加权处理
ps:博主前篇博文谈过IKAnalyzer与paoding中文分词,今天我们使用的是可用于中日韩的二元分词器CJKAnalyzer
闲话少说,直接上代码,看结果
package com.kl.luceneDemo;
import org.apache.lucene.analysis.Analyzer;
import org.apache.lucene.analysis.cjk.CJKAnalyzer;
import org.apache.lucene.document.Document;
import org.apache.lucene.document.Field;
import org.apache.lucene.document.StringField;
import org.apache.lucene.document.TextField;
import org.apache.lucene.index.*;
import org.apache.lucene.queryparser.classic.QueryParser;
import org.apache.lucene.search.IndexSearcher;
import org.apache.lucene.search.Query;
import org.apache.lucene.search.ScoreDoc;
import org.apache.lucene.search.TopDocs;
import org.apache.lucene.store.Directory;
import org.apache.lucene.store.FSDirectory;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
/**
* @author kl by 2016/3/19
* @boke www.kailing.pub
*/
public class FieldSetBoostTest {
//索引目录
String indexDir="E:\\LuceneIndex";
//测试数据
String theme="中国";
String []title={"中国是一个伟大的国家","我爱你的的祖国,美丽的中国","是什么,中国令美日等国虎视眈眈"};
/**
* Lucence5.5返回IndexWriter实例
* @param directory
* @return
*/
public IndexWriter getIndexWriter(Directory directory){
Analyzer analyzer=new CJKAnalyzer();//中日韩二元分词
IndexWriterConfig writerConfig=new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer);
IndexWriter writer=null;
try {
writer =new IndexWriter(directory,writerConfig);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return writer;
}
public Directory getDirctory(String indexDir){
Directory directory=null;
try {
directory=FSDirectory.open(Paths.get(indexDir));
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return directory;
}
/**
* 创建索引不加权
* @throws Exception
*/
public void Indexer()throws Exception{
IndexWriter writer=getIndexWriter(getDirctory(indexDir));
Document doc=null;
for(String str:title){
doc=new Document();
//Lucence5.5 Fileld有多个实现,StringFIeld不分词 TextField分词
doc.add(new StringField("theme",theme, Field.Store.YES));
Field field=new TextField("title",str, Field.Store.YES);
doc.add(field);
writer.addDocument(doc);
}
writer.close();
}
/**
* 创建索引,指定文档域加权
* @throws Exception
*/
public void IndexerSetBoot()throws Exception{
IndexWriter writer=getIndexWriter(getDirctory(indexDir));
Document doc=null;
for(String str:title){
doc=new Document();
//Lucence5.5 Fileld有多个实现,StringFIeld不分词 TextField分词
doc.add(new StringField("theme",theme, Field.Store.YES));
Field field=new TextField("title",str, Field.Store.YES);
if(str.indexOf("是什么")!=-1)
field.setBoost(2);//提高权值
doc.add(field);
writer.addDocument(doc);
}
writer.close();
}
@Test
public void searcherTest()throws Exception{
IndexerSetBoot();
// Indexer();
IndexReader reader= DirectoryReader.open(getDirctory(indexDir));
IndexSearcher is=new IndexSearcher(reader);
System.out.println("总的文档数:"+reader.numDocs());
QueryParser qp=new QueryParser("title",new CJKAnalyzer());
Query query=qp.parse("中国");
TopDocs tDocs=is.search(query,11);//一次查询多少个结果
System.out.println("总共有【"+tDocs.totalHits+"】条结果");
for (ScoreDoc scoredoc:tDocs.scoreDocs){
Document doc = is.doc(scoredoc.doc);
System.out.println(doc.getField("title").stringValue());
}
}
}
加权和不加权的结果如下
Lucene5.5入门第六篇——Analyzer中文分词
Lucene • kl 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 12544 次浏览 • 2016-06-24 11:18
前言
对于中文分词这个字眼,百科是这么描述的:
中文分词(Chinese Word Segmentation) 指的是将一个汉字序列切分成一个一个单独的词。分词就是将连续的字序列按照一定的规范重新组合成词序列的过程。我们知道,在英文的行文中,单词之间是以空格作为自然分界符的,而中文只是字、句和段能通过明显的分界符来简单划界,唯独词没有一个形式上的分界符,虽然英文也同样存在短语的划分问题,不过在词这一层上,中文比之英文要复杂的多、困难的多。
简单的说,就是把一个句子拆分成多个词,有废话的赶脚,呵呵
之前几篇博文,笔者都是用的Lucene里的StandardAnalyzer来做的分词处理,虽然在后面的Lucene版本中,
准备工作
这里先把这两个分词器加入到我们的项目中来
IKAnalyzer:IKAnalyzer是一个国人开发的开源的分词工具,下载地址:https://code.google.com/archiv ... e%3D1,GItHub地址:https://github.com/wks/ik-analyzer。推荐到GitHub上下载源码然后自己打包,项目是maven构建的,打成jar,然后在我们的项目中引用。
ps:打包项目的时候记得去掉test
paoding:paoding也是一个开源的i项目,下载地址:https://code.google.com/archiv ... loads,下载下来是一个压缩文件,里面有源码也有打包好可以直接用的jar
ps:下载paoding的时候请自行翻墙吧,这里推荐一个翻墙神器Lantern
进入正文
笔者在测试过程中并不是一番风顺啊,好多坑,下面我们来看看这些坑
IKAnlyzer的问题:
1.最新的项目也是基于Lucene3.0.3版本的,而笔者一直都是使用的最新的Lucene5.5,所以一测试就报了如下的错误
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.VerifyError: class org.wltea.analyzer.lucene.IKAnalyzer overrides final method tokenStream.(Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/io/Reader;)Lorg/apache/lucene/analysis/TokenStream;
解决:笔者有试着将IKAnlyzer项目的Lucene版本换成5.5的重新打包,然后发现行不通,改动的地方太多了,虽然IKAnlyzer项目不大,文件不多。笔者还没达到重写IKAnlyzer项目的能力,有时间可以研究研究源码,最后只有降级自己的Lucene版本了,幸好有maven,降级只要改下pom.xml就行了
paoding的问题
1.项目首先会依赖apache的commons-logging,笔者测试1.1版本通过。
2.然后就是下面的这个了 问题了,其实这个问题paoding自己的使用文档中类似的说明,(Paoding中文分词参考手册.htm)这个文档包含在了下载的压缩包中了
net.paoding.analysis.exception.PaodingAnalysisException: please set a system env PAODING_DIC_HOME or Config paoding.dic.home in paoding-dic-home.properties point to the dictionaries!
解决:就是指定paoding的一个字典文件目录,这个文件在下载下来的压缩包中的dic中,
三种解决方案:
(1).你可以解压缩jar,然后把paoding-dic-home.properties文件中的paoding.dic.home指定你的doc目录,重新压缩,把后缀换成jar就行了。
(2).就是参照官方的说明,把doc目录添加到环境变量中
(3).把doc放在项目目录下
3.paoding还有个问题就是Lucene3.0.3都不兼容了,笔者只好又把Lucene版本降到2.2.0来测试了
越过那些沟沟坎坎终于要见真功夫了,不多说,直接上代码,上图
package com.kl.Lucene;
import net.paoding.analysis.analyzer.PaodingAnalyzer;
import org.apache.lucene.analysis.Analyzer;
import org.apache.lucene.analysis.Token;
import org.apache.lucene.analysis.TokenStream;
import org.apache.lucene.analysis.tokenattributes.TermAttribute;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.wltea.analyzer.lucene.IKAnalyzer;
import java.io.StringReader;
/**
* @author kl by 2016/3/14
* @boke www.kailing.pub
*/
public class AnalyzerTest {
//测试数据
public static String testData="中文分词(Chinese Word Segmentation) 指的是将一个汉字序列切分成一" +
"一个单独的词。分词就是将连续的字序列按照一定的规范重新组合成词序列的过程。";
/**
* 得到IKAnalyzer分词器
* @return
*/
public static Analyzer getIKAnalyzer(){
return new IKAnalyzer();
}
/**
* 得到Paoding分词器
* @return
*/
public static Analyzer getPaoding(){
return new PaodingAnalyzer();
}
/**
* 测试IKAnalyzer
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void TestIKAnalyzer()throws Exception{
Analyzer analyzer =getIKAnalyzer();
TokenStream tokenStream = analyzer.tokenStream("", new StringReader(testData));
tokenStream.addAttribute(TermAttribute.class);
System.out.println("分词数据:"+testData);
System.out.println("=====IKAnalyzer的分词结果====");
while (tokenStream.incrementToken()) {
TermAttribute termAttribute = tokenStream.getAttribute(TermAttribute.class);
System.out.println(new String(termAttribute.term()));
termAttribute.termLength();
}
}
/**
* 测试Paoding
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void TestPaoding()throws Exception{
Analyzer analyzer =getPaoding();
TokenStream ts = analyzer.tokenStream("", new StringReader(testData));
System.out.println("分词数据:"+testData);
System.out.println("=====Paoding的分词结果====");
Token t;
// while ((t = ts.next()) != null) {
// System.out.println(t.termText());
// }
}
}
测试数据:中文分词(Chinese Word Segmentation) 指的是将一个汉字序列切分成一个单独的词。分词就是将连续的字序列按照一定的规范重新组合成词序列的过程。
测试结果如下:
从结果上看,IKAnalyzer和paoding的分词相差无几,IKAnlyzer比paoding的分词粒度更细,这个可以查看他们的分词字典文件去分析
后记:除了上面介绍的两种分词,常用的还有中日韩二元分词器CJKAnalyzer,以及lucene基于中科院分词实现的SmartChineseAnalyzer,其中cjk在lucene-common的jar包里了,SmartChineseAnalyzer需要另外引入jar,如下pom依赖
<!--公共的分词器,包含大多数的语言分词-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId>
<artifactId>lucene-analyzers-common</artifactId>
<version>5.5.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--基于中科院的中文分词-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId>
<artifactId>lucene-analyzers-smartcn</artifactId>
<version>5.5.0</version>
</dependency>
原文地址:http://www.kailing.pub/article/index/arcid/76.html