es查询报错
Elasticsearch • rochy 回复了问题 • 2 人关注 • 1 个回复 • 2039 次浏览 • 2018-12-28 09:48
elasticsearch 宕机1台 会有20分钟不可访问
Elasticsearch • zqc0512 回复了问题 • 6 人关注 • 4 个回复 • 8010 次浏览 • 2019-01-07 08:53
为什么我们集群大量写入的时候,load负载及其不均匀呀?
Elasticsearch • rockybean 回复了问题 • 6 人关注 • 2 个回复 • 2939 次浏览 • 2018-12-27 23:53
es 进程占用的内存会越来越大
Elasticsearch • kennywu76 回复了问题 • 6 人关注 • 3 个回复 • 9324 次浏览 • 2018-12-28 17:57
社区日报 第491期 (2018-12-27)
社区日报 • 白衬衣 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 1819 次浏览 • 2018-12-27 13:52
http://t.cn/EyX3TRu
2.彻底解决es的unassigned shards症状
http://t.cn/EbP4B07
3.链家全链路跟踪平台设计实践
http://t.cn/EyI5qWI
编辑:金桥
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/6309
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
社区日报 第494期 (2018-12-31)
社区日报 • elk123 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 2750 次浏览 • 2018-12-27 13:49
http://t.cn/EApHfmI
2.es存储详解。
http://t.cn/Eb8LFXD
3.es集群部署的一些配置项。
http://t.cn/Eb8yNc1
编辑:wt
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/6308
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
为何要通过Kibana展示promethues的数据以及如何去做
Kibana • 点火三周 发表了文章 • 1 个评论 • 9577 次浏览 • 2018-12-27 10:59
Elastic stack不停的迭代中狂奔。在最新的V6.5版本发布后,我们可以发现,其路线图已经越来越倾向于成为一个全栈的,全链路的,从下至上,从底层硬件资源数据一直到上层用户数据,从资源监控,到性能监控,直至安全审计的智能化运维系统了。这其中解决的一个痛点是:企业中存在各种各样的业务系统,每个系统又存在不同的数据源和存储数据的数据库;同时在运维管理层面上,又各种不同的监控系统(资源监控,性能监控,安全和审计)以及上层的可视化系统。这样,导致运维人员需要面对繁多的系统、入口和数据维度,在处理问题时,需要登录不同的平台,并且无法对数据进行有效的关联分析,因此,是迫切需要一个强大的平台,能够快速便捷的处理这些问题的。
我们可以看到,从不停发布的beats,以及beats里面不停添加的modules:
以及支持的各种数据指标模版:
elastic stack在加速将越来越多的数据需要汇聚到一起,并且提供一个统一的接口进入,这就是Kibana。这里,我不打算深入的比较Kibana和Grafana,简单说一句,就是grafana的主要场景只是dashboard,并不适合将其用作一个将所有数据集中到一起,需要做各种维度的查询,分析,安全检查等功能的portal。所以,这里我们讨论的是Kibana上如何展示其他数据源的数据。
为什么是prometheus而不是beats
在这个人人上云的时代,无论是open stack还是K8S,最流行的资源监控软件我看到的是prometheus,特别是以node_exporter为基础的一系列metric采集工具,为prometheus提供了各种维度的监控数据。而对应的,elastic stack也提供了类似filebeat, metricbeat, packatbeat等一系列工具和对应的数据template。
我没有深入使用过prometheus,但作为一个beats的资深用户,我还是感觉到beats还存在诸多的问题,特别是filebeat上幽灵般存在的内存占用过多的问题,导致大规模在所有的节点上安装beats成为一种风险。并且,最主要的一个点,我觉得是beats采集的数据,是依赖于整个elastic stack进行展示的,而作为云的运维人员,其关心的重点是每个虚拟机,容器的资源监控情况,metric和alart是其重心,而非query,search,security等功能。并且安装一个prometheus,比安装整个elastic stack简便得多,消耗的资源也小的多。所以,普遍的,从主机运维人员的角度,肯定首选安装prometheus的exporter来作资源的监控,而非安装beats。
为什么Kibana上需要集成prometheus的数据
正因为之前所讲的,我们试图使用elastic stack作为一个多维度的统一的数据入口和展示工具,要求我们必须能在Kibana看到硬件资源监控级别的指标,而elastic stack提供的beats等工具,却并不为云运维人员所待见(因为他们更喜欢prometheus,而非elastic stack,原因见以上)。因此,如果我们需要将elastic stack打造为一套全栈的智能运维系统,大多数情况下,prometheus成为必须跨越的一个槛。
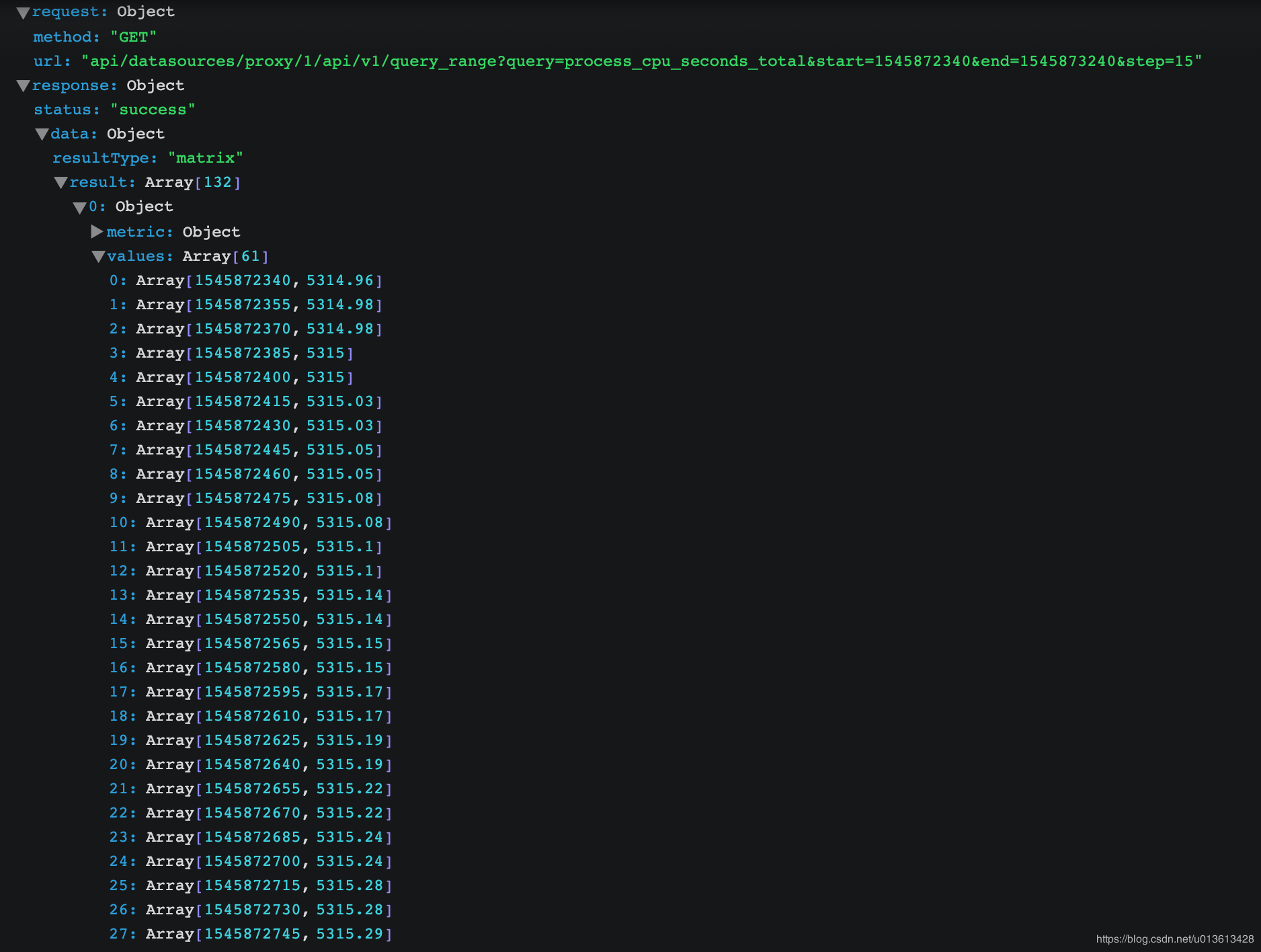
将prometheus上的数据转移到elasticsearch
这是我想到的第一个解决方案。可惜logstash上没有prometheus的input plugins。所以,我们还是需要beats。注意,在metricbeat上有一个prometheus的module,号称可以 fetch metric from prometheus exporter,但实际上只是一个乌龙,这个module的并不能从成千上万的云主机或者容器中拉取数据,它能做的只是获取prometheus服务器节点prometheus这个进程的基本数据,然并卵。
这里给大家介绍的是两个社区提供prometheus相关的beats:
但建议大家还是自己写一个beat吧,代码可以参考prombeat。
不过如果你仔细观看prometheus里面的数据,都是num type的,将其转存到elasticsearch绝对不是一个经济的选择:
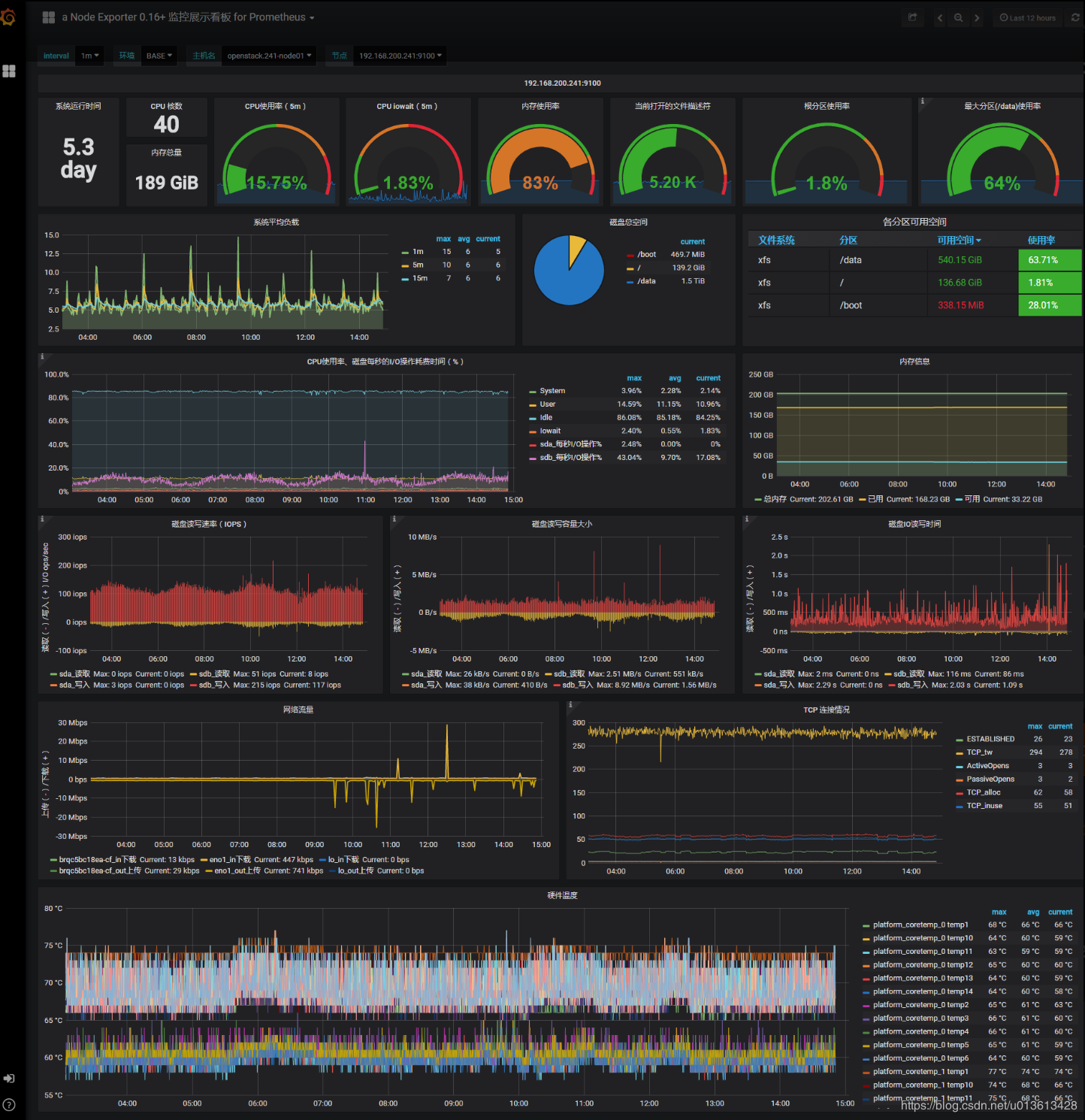
将grafana集成到kibana中
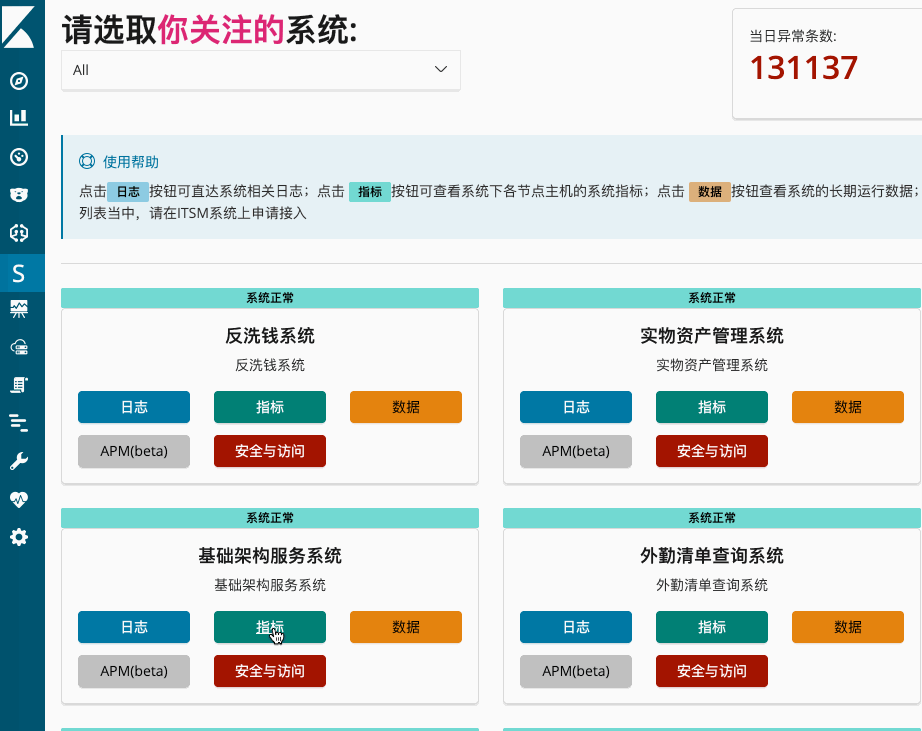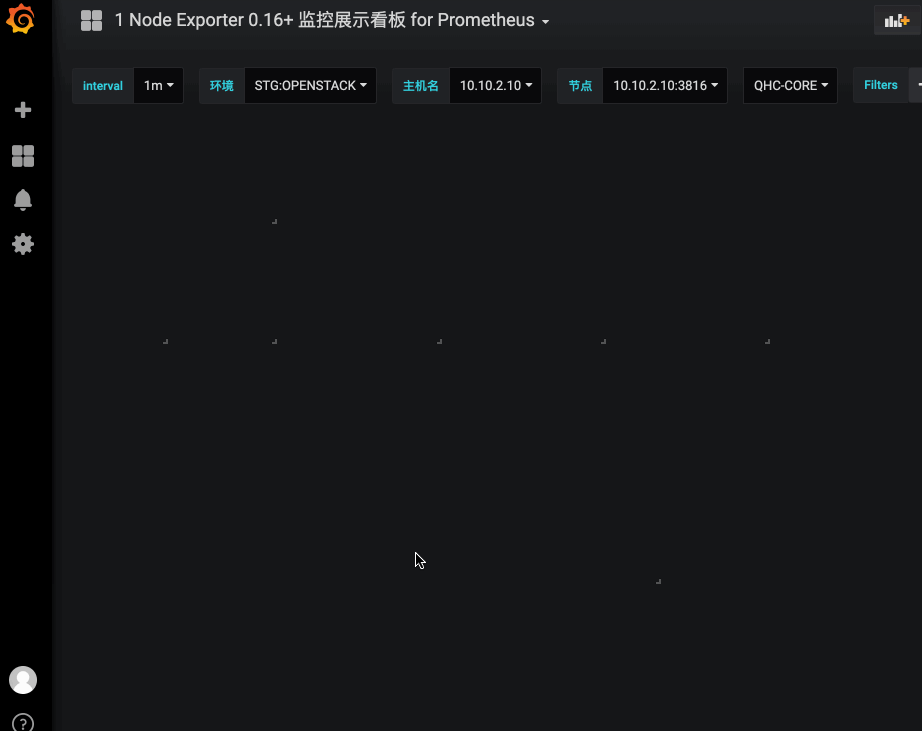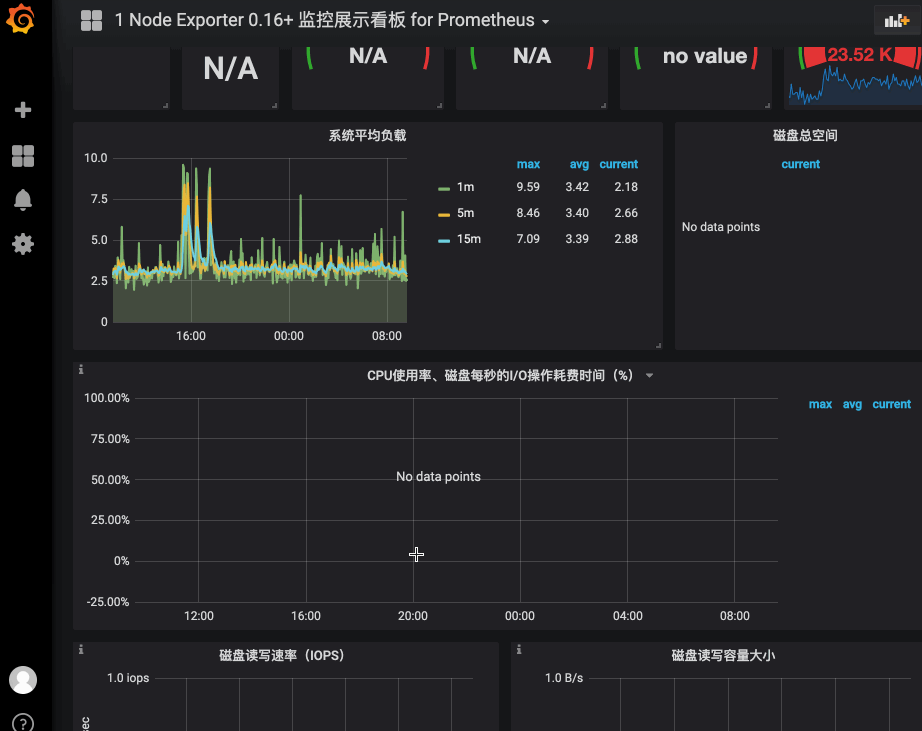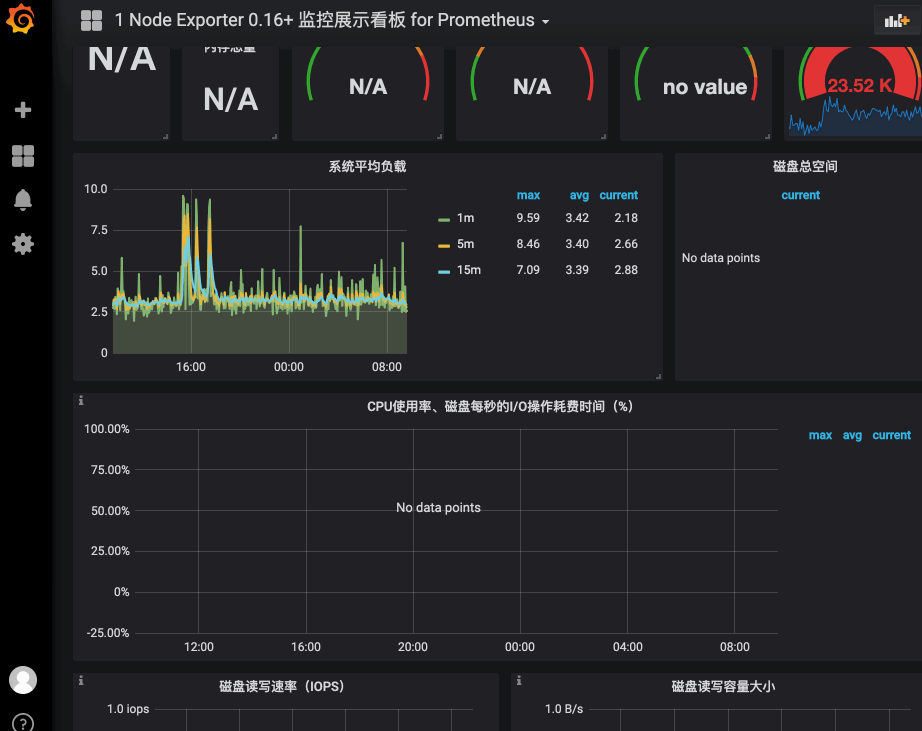
这是为什么我在一开始提到了grafana,虽然它不适合做portal,但是极其适合做dashboard,而kibana又是如此的开放,随便做个插件,可以轻松的跳转到grafana的dashboard上。而grafana与prometheus又是如此的登对,看看grafana上的各种专业而美丽的prometheus的dashboard吧:
我们要做的是做一个kibana的插件,然后将关键参数传递给grafana,并跳转:
虽然kibana和grafana是两个不同的工具,但并不妨碍我们将它们放在一起工作。而Kibana的开放性和基于插件的独立开发模式,让我们可以更方便的将各种好用的开源工具集成到一起,这里展示的Kibana与grafana和promethues的集成,希望能给到你一些微光。
关于elasticsearch缓存命中机制的奇怪问题。
Elasticsearch • medcl 回复了问题 • 4 人关注 • 2 个回复 • 2418 次浏览 • 2018-12-27 11:25
如何提高bulk写入速度
Elasticsearch • code4j 回复了问题 • 6 人关注 • 3 个回复 • 5349 次浏览 • 2018-12-27 14:49
如何建立parent/child父子关系
Elasticsearch • zz_hello 回复了问题 • 2 人关注 • 1 个回复 • 4449 次浏览 • 2018-12-26 18:49
对于日志场景,字段里面中英文混合,应该使用中文分词器吗?效率如何?
Elasticsearch • 点火三周 回复了问题 • 3 人关注 • 3 个回复 • 4824 次浏览 • 2018-12-27 08:45
关于英文连词问题比如用户搜索iphonex怎么展示iphone x的结果
Elasticsearch • rochy 回复了问题 • 3 人关注 • 1 个回复 • 3556 次浏览 • 2018-12-26 17:43
官网的Logstash5.5.0版本的 Filter plugins 中的Ruby filter plugin用到的Event API介绍只有get,set不够用,请问还有更详细的资料吗
Logstash • rochy 回复了问题 • 2 人关注 • 1 个回复 • 3730 次浏览 • 2018-12-26 15:24
es中restHighLevelClient和Java Low Level REST Client性能上有什么区别
Elasticsearch • rochy 回复了问题 • 5 人关注 • 3 个回复 • 11873 次浏览 • 2018-12-26 17:46
社区日报 第490期 (2018-12-26)
社区日报 • 千夜 发表了文章 • 0 个评论 • 1875 次浏览 • 2018-12-26 12:08
http://t.cn/EbPvOva
2. 新浪是如何分析处理32亿条实时日志的
http://t.cn/RUuylp6
3. 苏宁大数据离线任务开发调度平台实践
http://t.cn/EbP7Kav
编辑:江水
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/6224
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily