社区日报 第177期 (2018-02-02)
http://t.cn/R8i2ws4
2、Elasticsearch聚合性能优化实战
http://t.cn/R8xdCra
3、Python福音|Elasticsearch 6.1 DSL 核心知识点(可下载)
http://t.cn/R8xuJC1
编辑:铭毅天下
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/publish/article/480
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
http://t.cn/R8i2ws4
2、Elasticsearch聚合性能优化实战
http://t.cn/R8xdCra
3、Python福音|Elasticsearch 6.1 DSL 核心知识点(可下载)
http://t.cn/R8xuJC1
编辑:铭毅天下
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/publish/article/480
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
收起阅读 »
Elastic 中文社区运维监控实战 (2) - 总体方案
接上一篇:Elastic 中文社区运维监控实战 (1) - 序
本文为系列文章第二篇,主要介绍如何把 Elastic 中文社区的网站服务器监控起来,对有同样想了解如何使用 Elastic Stack 来做运维监控的同学,可以作为一个很好的参考和入门资料,学习门槛定义为入门级。
本节内容
在深入到具体的监控指标收集的细节之前,今天先主要介绍一下 Elastic 中文社区的总体方案。这样我们在动手之前会有一个总体的思路和对所用工具有一个大致的了解。
技术选型
工欲善其事必先利其器
前面已经提到我们要对服务器进行各项性能指标的监控以及日志的监控。
看起来很复杂,因为有很多信息需要收集。 好在我们有 Elastic Stack,使用它们来作为我们的监控工具,整个工作就变得简单了,我们结合我们社区监控的这个场景,具体来看的话,需要的工具主要是如下几个:
- 监控数据存储:Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch 是一个分布式的 RESTful 风格的搜索和数据分析引擎。简单易用,用户众多,性能优良,久经考验,支持单节点部署到虚拟机,并可随着业务增长无缝伸缩扩容至上千个节点规模的集群,PB 级别数据也不在话下。
日志数据和指标监控数据都能放,通过集中式存储所有的这些时序型数据,可以快速方便的对这些数据进行分析和关联,实在是排障运维和性能调优的不二选择,你如果还不知道 Elasticsearch,那我只能说你真的是 out 了。
- 日志数据收集:Filebeat
Elastic Beats 家族的一员,Go 语言编写,轻量级,无依赖,这样就可以很方便的完成收集端的部署,所以如果你的场景和我一样, 可以优先使用 Filebeat 代替 Logstash 来收集日志,当然如果有日志的进一步加工,可以让 Filebeat 把数据发送给 Logstash,然后 Logstash 处理完之后再发送给 Elasticsearch。
Filebeat 使用很灵活,可以指定你的日志路径来进行收集,还可以对数据进行预过滤,对于一些常见的监控需求,Filebeat 以模块的方式替你打包好了一切,如:日志路径配置、解析规则、机器学习的任务,甚至还自带 Dashboard,简单几个操作,就可以完成从数据收集到最终可视化分析的所有工作。
- 指标数据收集:Metricbeat
我们这次需要监控的服务器都是一些常规的指标,而 Metricbeat 刚好都支持这些指标的收集,你说这不巧了不是。
Metricbeat 同样也是 Elastic Beats 家族的一员,同样也是开源的。定位是一个轻量级的监控指标采集器,采用 Go 语言编写,同样提供的是一个很小的无依赖的二进制文件包,能够收集服务器(Linux、Windows、Mac)本身的运行指标,如: CPU 使用率、内存、文件系统、磁盘 IO 和网络 IO 统计数据等,还能获取服务器上面的各项服务的运行指标,常见的如: Apache、NGINX、MongoDB、MySQL、PostgreSQL、Prometheus、Redis 等都有直接支持,并且内置了 Elasticsearch 索引和 mapping 设置,以及 Ingest pipeline 设置,还提前预置了不少 Kibana 的 Dashboard,开箱即用、即分析。
- 数据分析展现:Kibana
和 Elasticsearch 工作的最佳拍档,结合 Elasticsearch 的实时分析能力,可以非常方便的对各种数据进行搜索和分析,你可以灵活的自定义的各种图形展现和 Dashboard,不用编写一行代码,即可进行数据分析,除了分析,还整合了 Elastic Stack 的各个产品的管理功能,作为 Elastic Stack 的图形交互终端。
除了上面这些工具,后续我们还可以考虑使用 Auditbeat 来收集服务器的安全行为日志,使用 Heartbeat 来监控各个服务的端口是否正常,我们先完成基本的监控之后,再慢慢将这些加上。
可以看到,我们没有用到 Logstash,是的,这个规模的监控,可以不考虑 Logstash,这样我们可以做到架构简单和足够的轻量级。
上面列的这些软件都是 Elastic 家族的产品,并且都是开源的,所有的源码都在:https://github.com/elastic/ 。
部署方案
在收集数据之前,我们需要明确我们数据放在哪里,毫无疑问,所有的数据都将放在 Elasticsearch 里面,不过 Elasticsearch 不能部署在 Elastic 中文社区的这台服务器上面,一个是资源的限制,另外一个是基于安全的考虑,如果 Elastic 社区的服务器挂了,数据不光收不到,连什么时候挂的都不知道。所以我们需要把 Elasticsearch 服务搭建在别的地方,有多种选择:
- 使用 Elastic Cloud,很方便就能开通,缺点国内访问速度慢,暂时还没开放机器学习的功能。
- 使用阿里云的 Elasticsearch,Elastic 官方合作伙伴,国内唯一包含 X-Pack 的完整功能的 Elasticsearch 云服务,国内访问速度快。
- 自己搭建的 Elasticsearch 集群。
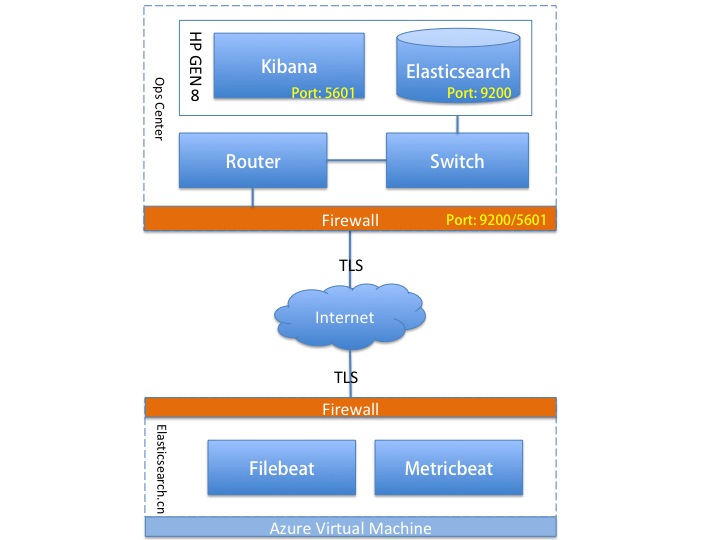
使用阿里云的 Elasticsearch 无疑很方便,不过我家里刚好有一台服务器,型号 HP Gen8,16GB 内存,上面运行了 SmartOS,跑几个 zone 很轻松,每天用来备份社区的数据库,再来起一个 Elasticsearch 服务也很方便,通过路由器将内网 IP 映射出去,让社区服务器将监控数据发送到这台服务器上面来,安全上面,需要保证这台服务器不被黑客攻击,需要做一些必要的访问控制,可以使用 X-Pack 的身份验证,结合 IP 白名单功能,只允许内网和 Elastic 中文社区服务器的 IP 访问。
我们将之命名为:Ops Center,方便后面招呼。
可以看到,Elastic 社区服务器除了启动 Filebeat 和 Metricbeat 之外,不需要额外做什么服务器本身的设置。
这里画一个简单的部署拓扑图,方便理解:
今天主要写到这里,后面将具体介绍它们的安装部署过程。
接上一篇:Elastic 中文社区运维监控实战 (1) - 序
本文为系列文章第二篇,主要介绍如何把 Elastic 中文社区的网站服务器监控起来,对有同样想了解如何使用 Elastic Stack 来做运维监控的同学,可以作为一个很好的参考和入门资料,学习门槛定义为入门级。
本节内容
在深入到具体的监控指标收集的细节之前,今天先主要介绍一下 Elastic 中文社区的总体方案。这样我们在动手之前会有一个总体的思路和对所用工具有一个大致的了解。
技术选型
工欲善其事必先利其器
前面已经提到我们要对服务器进行各项性能指标的监控以及日志的监控。
看起来很复杂,因为有很多信息需要收集。 好在我们有 Elastic Stack,使用它们来作为我们的监控工具,整个工作就变得简单了,我们结合我们社区监控的这个场景,具体来看的话,需要的工具主要是如下几个:
- 监控数据存储:Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch 是一个分布式的 RESTful 风格的搜索和数据分析引擎。简单易用,用户众多,性能优良,久经考验,支持单节点部署到虚拟机,并可随着业务增长无缝伸缩扩容至上千个节点规模的集群,PB 级别数据也不在话下。
日志数据和指标监控数据都能放,通过集中式存储所有的这些时序型数据,可以快速方便的对这些数据进行分析和关联,实在是排障运维和性能调优的不二选择,你如果还不知道 Elasticsearch,那我只能说你真的是 out 了。
- 日志数据收集:Filebeat
Elastic Beats 家族的一员,Go 语言编写,轻量级,无依赖,这样就可以很方便的完成收集端的部署,所以如果你的场景和我一样, 可以优先使用 Filebeat 代替 Logstash 来收集日志,当然如果有日志的进一步加工,可以让 Filebeat 把数据发送给 Logstash,然后 Logstash 处理完之后再发送给 Elasticsearch。
Filebeat 使用很灵活,可以指定你的日志路径来进行收集,还可以对数据进行预过滤,对于一些常见的监控需求,Filebeat 以模块的方式替你打包好了一切,如:日志路径配置、解析规则、机器学习的任务,甚至还自带 Dashboard,简单几个操作,就可以完成从数据收集到最终可视化分析的所有工作。
- 指标数据收集:Metricbeat
我们这次需要监控的服务器都是一些常规的指标,而 Metricbeat 刚好都支持这些指标的收集,你说这不巧了不是。
Metricbeat 同样也是 Elastic Beats 家族的一员,同样也是开源的。定位是一个轻量级的监控指标采集器,采用 Go 语言编写,同样提供的是一个很小的无依赖的二进制文件包,能够收集服务器(Linux、Windows、Mac)本身的运行指标,如: CPU 使用率、内存、文件系统、磁盘 IO 和网络 IO 统计数据等,还能获取服务器上面的各项服务的运行指标,常见的如: Apache、NGINX、MongoDB、MySQL、PostgreSQL、Prometheus、Redis 等都有直接支持,并且内置了 Elasticsearch 索引和 mapping 设置,以及 Ingest pipeline 设置,还提前预置了不少 Kibana 的 Dashboard,开箱即用、即分析。
- 数据分析展现:Kibana
和 Elasticsearch 工作的最佳拍档,结合 Elasticsearch 的实时分析能力,可以非常方便的对各种数据进行搜索和分析,你可以灵活的自定义的各种图形展现和 Dashboard,不用编写一行代码,即可进行数据分析,除了分析,还整合了 Elastic Stack 的各个产品的管理功能,作为 Elastic Stack 的图形交互终端。
除了上面这些工具,后续我们还可以考虑使用 Auditbeat 来收集服务器的安全行为日志,使用 Heartbeat 来监控各个服务的端口是否正常,我们先完成基本的监控之后,再慢慢将这些加上。
可以看到,我们没有用到 Logstash,是的,这个规模的监控,可以不考虑 Logstash,这样我们可以做到架构简单和足够的轻量级。
上面列的这些软件都是 Elastic 家族的产品,并且都是开源的,所有的源码都在:https://github.com/elastic/ 。
部署方案
在收集数据之前,我们需要明确我们数据放在哪里,毫无疑问,所有的数据都将放在 Elasticsearch 里面,不过 Elasticsearch 不能部署在 Elastic 中文社区的这台服务器上面,一个是资源的限制,另外一个是基于安全的考虑,如果 Elastic 社区的服务器挂了,数据不光收不到,连什么时候挂的都不知道。所以我们需要把 Elasticsearch 服务搭建在别的地方,有多种选择:
- 使用 Elastic Cloud,很方便就能开通,缺点国内访问速度慢,暂时还没开放机器学习的功能。
- 使用阿里云的 Elasticsearch,Elastic 官方合作伙伴,国内唯一包含 X-Pack 的完整功能的 Elasticsearch 云服务,国内访问速度快。
- 自己搭建的 Elasticsearch 集群。
使用阿里云的 Elasticsearch 无疑很方便,不过我家里刚好有一台服务器,型号 HP Gen8,16GB 内存,上面运行了 SmartOS,跑几个 zone 很轻松,每天用来备份社区的数据库,再来起一个 Elasticsearch 服务也很方便,通过路由器将内网 IP 映射出去,让社区服务器将监控数据发送到这台服务器上面来,安全上面,需要保证这台服务器不被黑客攻击,需要做一些必要的访问控制,可以使用 X-Pack 的身份验证,结合 IP 白名单功能,只允许内网和 Elastic 中文社区服务器的 IP 访问。
我们将之命名为:Ops Center,方便后面招呼。
可以看到,Elastic 社区服务器除了启动 Filebeat 和 Metricbeat 之外,不需要额外做什么服务器本身的设置。
这里画一个简单的部署拓扑图,方便理解:
今天主要写到这里,后面将具体介绍它们的安装部署过程。
收起阅读 »索引映射与分析整理
一、映射与分析
Elasticsearch 中的数据可以概括的分为两类:精确值和全文。
为了促进在全文域中的匹配查询,Elasticsearch 首先 分析 文档,之后根据结果创建 倒排索引;
倒排索引:倒排索引源于实际应用中需要根据属性的值来查找记录。这种索引表中的每一项都包
括一个属性值和具有该属性值的各记录的地址。由于不是由记录来确定属性值,而是由属性值来
确定记录的位置,因而称为倒排索引(inverted index)。带有倒排索引的文件我们称为倒排索引文
件,简称倒排文件(inverted file)。
分析器:字符过滤器
首先,字符串按顺序通过每个 字符过滤器 。他们的任务是在分词前整理字符串。
一个字符过滤器可以用来去掉HTML,或者将 & 转化成 `and`。
分词器:
其次,字符串被 分词器 分为单个的词条。一个简单的分词器遇到空格和标点的时
候,可能会将文本拆分成词条。
Token 过滤器:
最后,词条按顺序通过每个 token 过滤器 。这个过程可能会改变词条(例如,小
写化 Quick ),删除词条(例如, 像 a`, `and`, `the 等无用词),或者增加
词条(例如,像 jump 和 leap 这种同义词)
当我们 索引 一个文档时使用分析器,它的全文域被分析成词条以用来创建倒排索引当你查询一个 全文 域时, 会对查询字符串应用相同的分析器,以产生正确的搜索词条列表。
当你查询一个 精确值 域时,不会分析查询字符串, 而是搜索你指定的精确值。
elastic内置的分析器:standard,whitespace,simple,english
创建一个自定义分析器编辑:
PUT /my_index
{
"settings": {
//配置自定义的分析器
"analysis": { "char_filter": {
"&_to_and": {
"type": "mapping",
"mappings": [ "&=> and "]
}
},
"filter": {
"my_stopwords": {
"type": "stop",
"stopwords": [ "the", "a" ]
}
},
"analyzer": {
//自定义的分析器
"my_analyzer": { "type": "custom",
//字符过滤器
"char_filter": [ "html_strip", "&_to_and" ],
//分词器
"tokenizer": "standard",
//Token过滤器
"filter": [ "lowercase", "my_stopwords" ] }}
}
}
}
应用分析器:
PUT /my_index/_mapping/my_type
{ "properties": { "title": { "type": "string", "analyzer": "my_analyzer" } } }
映射:让elasticsearch知道索引的据类型
基本类型:
字符串: string
整数 : byte, short, integer, long
浮点数: float, double
布尔型: boolean
日期: date
查看映射:GET /gb/_mapping/tweet
取得索引 gb 中类型 tweet 的映射
域最重要的属性是 type 。对于不是 string 的域,你一般只需要设置 type;
string 域映射的两个最重要 属性是 index 和 analyzer
index:
analyzed
首先分析字符串,然后索引它。换句话说,以全文索引这个域。
not_analyzed
索引这个域,所以它能够被搜索,但索引的是精确值。不会对它进行分析。
no
不索引这个域。这个域不会被搜索到
analyzer:指定在搜索和索引时使用的分析器,可以使用内置的分析器或者自定义的分析器
自定义映射:
PUT /gb
{ "mappings": {
"tweet" : {
"properties" : {
"tweet" : { "type" : "string", "analyzer": "english" },
"date" : { "type" : "date" },
"name" : { "type" : "string" },
"user_id" : { "type" : "long" }
}
}
}
}
二、索引别名和零宕机
A.PUT /my_index_v1
B.PUT /my_index_v1/_alias/my_index
A创建索引,B建立别名
修改索引字段时,可以新建索引,然后将就索引数据导入新建索引,将别名指向新建索引即可实现
0宕机变更索引了
参考官方文档:https://www.elastic.co/guide/c ... iases
一、映射与分析
Elasticsearch 中的数据可以概括的分为两类:精确值和全文。
为了促进在全文域中的匹配查询,Elasticsearch 首先 分析 文档,之后根据结果创建 倒排索引;
倒排索引:倒排索引源于实际应用中需要根据属性的值来查找记录。这种索引表中的每一项都包
括一个属性值和具有该属性值的各记录的地址。由于不是由记录来确定属性值,而是由属性值来
确定记录的位置,因而称为倒排索引(inverted index)。带有倒排索引的文件我们称为倒排索引文
件,简称倒排文件(inverted file)。
分析器:字符过滤器
首先,字符串按顺序通过每个 字符过滤器 。他们的任务是在分词前整理字符串。
一个字符过滤器可以用来去掉HTML,或者将 & 转化成 `and`。
分词器:
其次,字符串被 分词器 分为单个的词条。一个简单的分词器遇到空格和标点的时
候,可能会将文本拆分成词条。
Token 过滤器:
最后,词条按顺序通过每个 token 过滤器 。这个过程可能会改变词条(例如,小
写化 Quick ),删除词条(例如, 像 a`, `and`, `the 等无用词),或者增加
词条(例如,像 jump 和 leap 这种同义词)
当我们 索引 一个文档时使用分析器,它的全文域被分析成词条以用来创建倒排索引当你查询一个 全文 域时, 会对查询字符串应用相同的分析器,以产生正确的搜索词条列表。
当你查询一个 精确值 域时,不会分析查询字符串, 而是搜索你指定的精确值。
elastic内置的分析器:standard,whitespace,simple,english
创建一个自定义分析器编辑:
PUT /my_index
{
"settings": {
//配置自定义的分析器
"analysis": { "char_filter": {
"&_to_and": {
"type": "mapping",
"mappings": [ "&=> and "]
}
},
"filter": {
"my_stopwords": {
"type": "stop",
"stopwords": [ "the", "a" ]
}
},
"analyzer": {
//自定义的分析器
"my_analyzer": { "type": "custom",
//字符过滤器
"char_filter": [ "html_strip", "&_to_and" ],
//分词器
"tokenizer": "standard",
//Token过滤器
"filter": [ "lowercase", "my_stopwords" ] }}
}
}
}
应用分析器:
PUT /my_index/_mapping/my_type
{ "properties": { "title": { "type": "string", "analyzer": "my_analyzer" } } }
映射:让elasticsearch知道索引的据类型
基本类型:
字符串: string
整数 : byte, short, integer, long
浮点数: float, double
布尔型: boolean
日期: date
查看映射:GET /gb/_mapping/tweet
取得索引 gb 中类型 tweet 的映射
域最重要的属性是 type 。对于不是 string 的域,你一般只需要设置 type;
string 域映射的两个最重要 属性是 index 和 analyzer
index:
analyzed
首先分析字符串,然后索引它。换句话说,以全文索引这个域。
not_analyzed
索引这个域,所以它能够被搜索,但索引的是精确值。不会对它进行分析。
no
不索引这个域。这个域不会被搜索到
analyzer:指定在搜索和索引时使用的分析器,可以使用内置的分析器或者自定义的分析器
自定义映射:
PUT /gb
{ "mappings": {
"tweet" : {
"properties" : {
"tweet" : { "type" : "string", "analyzer": "english" },
"date" : { "type" : "date" },
"name" : { "type" : "string" },
"user_id" : { "type" : "long" }
}
}
}
}
二、索引别名和零宕机
A.PUT /my_index_v1
B.PUT /my_index_v1/_alias/my_index
A创建索引,B建立别名
修改索引字段时,可以新建索引,然后将就索引数据导入新建索引,将别名指向新建索引即可实现
0宕机变更索引了
参考官方文档:https://www.elastic.co/guide/c ... iases
收起阅读 »
社区日报 第176期 (2018-02-01)
-
卫星系统——酒店后端全链路日志收集工具介绍。 http://t.cn/RQxFzOF
-
搜索,分析数据库和分布式计算引擎的融合介绍。 http://t.cn/R65inbR
- 使用Apache Spark将数据写入ElasticSearch。 http://t.cn/R8flF70
-
卫星系统——酒店后端全链路日志收集工具介绍。 http://t.cn/RQxFzOF
-
搜索,分析数据库和分布式计算引擎的融合介绍。 http://t.cn/R65inbR
- 使用Apache Spark将数据写入ElasticSearch。 http://t.cn/R8flF70
社区日报 第175期 (2018-01-31)
-
macos上安装elk详细教程 http://t.cn/R8bevN3
-
自己动手用ELK分析你的支出 http://t.cn/R8bko7m
- 利用es对地理坐标进行索引和搜索 http://t.cn/R8bFHB2
-
macos上安装elk详细教程 http://t.cn/R8bevN3
-
自己动手用ELK分析你的支出 http://t.cn/R8bko7m
- 利用es对地理坐标进行索引和搜索 http://t.cn/R8bFHB2
社区日报 第174期 (2018-01-30)
http://t.cn/R8yg6ob
2.Elasticsearch和Redis的多种整合方式实战。
http://t.cn/R8LK0Oe
3.使用Apache JMeter对Elasticsearch进行性能测试。
http://t.cn/R8LKlw8
编辑:叮咚光军
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/475
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
http://t.cn/R8yg6ob
2.Elasticsearch和Redis的多种整合方式实战。
http://t.cn/R8LK0Oe
3.使用Apache JMeter对Elasticsearch进行性能测试。
http://t.cn/R8LKlw8
编辑:叮咚光军
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/475
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
收起阅读 »
社区日报 第173期 (2018-01-29)
http://t.cn/R8wsVhO
2.使用elastic site search替代即将被关闭的google site search
http://t.cn/R8wsHvl
3.elastic stack APM 线上演示教程,快来预约吧。
http://t.cn/R8APlEN
编辑:cybrdak
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/474
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
http://t.cn/R8wsVhO
2.使用elastic site search替代即将被关闭的google site search
http://t.cn/R8wsHvl
3.elastic stack APM 线上演示教程,快来预约吧。
http://t.cn/R8APlEN
编辑:cybrdak
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/474
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
收起阅读 »
社区日报 第172期 (2018-01-28)
1. Puppet使用ELK堆栈进行日志记录--Part 2。 http://t.cn/R878jnu
2. Kubernetes监测:最佳实践,方法和现有解决方案。 http://t.cn/R87HYZE
3. (自备梯子)你职业生涯中的三个问题。 http://t.cn/R87YMvk
1. Puppet使用ELK堆栈进行日志记录--Part 2。 http://t.cn/R878jnu
2. Kubernetes监测:最佳实践,方法和现有解决方案。 http://t.cn/R87HYZE
3. (自备梯子)你职业生涯中的三个问题。 http://t.cn/R87YMvk
收起阅读 »社区日报 第171期 (2018-01-27)
1、社区文章:利用es获取词频的方法 https://elasticsearch.cn/article/461
2、关于es搜索客户端的源码分析,该博客的一系列es源码分析都值得一看。 http://t.cn/RtLXZol
3、一周热点:你是怎么抢火车票的呢? http://t.cn/R8vJ9Rf
1、社区文章:利用es获取词频的方法 https://elasticsearch.cn/article/461
2、关于es搜索客户端的源码分析,该博客的一系列es源码分析都值得一看。 http://t.cn/RtLXZol
3、一周热点:你是怎么抢火车票的呢? http://t.cn/R8vJ9Rf
收起阅读 »社区日报 第170期 (2018-01-26)
http://t.cn/RQkbVhv
2、ElasticSearch Aggregations 进行统计分析实战
http://t.cn/RQD5n3F
3、注意,这6种方式能搞死Elasticsearch!
http://t.cn/RQxkfQH
编辑:铭毅天下
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/471
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
http://t.cn/RQkbVhv
2、ElasticSearch Aggregations 进行统计分析实战
http://t.cn/RQD5n3F
3、注意,这6种方式能搞死Elasticsearch!
http://t.cn/RQxkfQH
编辑:铭毅天下
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/471
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily 收起阅读 »
Elastic 中文社区运维监控实战 (1) - 序
序
本文为系列文章第一篇,主要介绍如何把 Elastic 中文社区的网站服务器监控起来,对有同样想了解如何使用 Elastic Stack 来做运维监控的同学,可以作为一个很好的参考和入门资料,学习门槛定义为入门级。
首先,我们要监控的网站,也就是大家现在正在访问的 Elastic 官方中文社区,网址:elasticsearch.cn,这个网站基于开源的 WeCenter 搭建,开发语言是 PHP,后端数据库是 MySQL,目前只有一台服务器,由 ConvertLab 友情无偿赞助,大写的赞!再次感谢!
服务器部署环境是 Ubuntu 16.04.2,部署了以下服务及软件:
- Nginx - Http 反向代理,不要介绍了吧
- PHP-FPM - 一个常用的 PHP FastCGI 管理
- Elasticsearch - Elasticsearch 服务,用于社区的垂直搜索服务 Elastic 情报局 服务
- GOPA - 可以说是为社区而写的,一个轻量级的爬虫,用于爬取 Elatic 周边相关相关资料,创建索引存放到 Elasticsearch 里面,提供垂直搜索服务,代码地址
- Grok Debugger - 一个 Java 的 Grok pattern 调试服务,方便大家调试 Grok 日志解析规则,访问地址:grok.elasticsearch.cn
服务器上所有的财产就这些了,一个平淡无奇的网站,基本上所有的东西都能公开访问到,这个网站的目的就是为所有 Elastic 爱好者服务的,供大家交流和沟通的专属平台,所以请各位黑客大侠不要再扫描和攻击啦,画一个简单的拓扑图如下所示:
作为一个合格的网管,除了重启服务器之外,还必须要保证网站的正常运行,所以了解网站的运行情况就变成了一个需要解决的首要问题,我们可以先把任务具体列一下:
- 网站是否正常访问,各项服务有没有挂
- 网站访问情况如何,用户访问速度如何
- 网站访客统计分析,访客相关数据分析
- 服务器的各项指标,详细指标监控分析
- 服务器的各项服务,日志集中分析处理
- 服务器是否很安全,有没有黑客来造访
- 数据是否安全备份,有没有定期测试过
实在编不下去了(话说对的还蛮齐),说人话就是监控起服务器的各项指标和收集服务的日志,然后出几个分析的 Dashboard,监控报警整起来。
我们这次需要用到的工具主要就是 Elastic Stack 啦,Elastic Stack 包括 Elasticsearch、Logstash、Beats 和 Kibana,版本都用最新的 6.x,再结合我们实际的数据和实际的需求,在后面的文章里面,我会具体介绍它们是什么以及如何使用。
今天先写到这里,明天写监控指标的收集,此系列文章暂且定为需要 100 期完成。(开个玩笑,哈哈)。
序
本文为系列文章第一篇,主要介绍如何把 Elastic 中文社区的网站服务器监控起来,对有同样想了解如何使用 Elastic Stack 来做运维监控的同学,可以作为一个很好的参考和入门资料,学习门槛定义为入门级。
首先,我们要监控的网站,也就是大家现在正在访问的 Elastic 官方中文社区,网址:elasticsearch.cn,这个网站基于开源的 WeCenter 搭建,开发语言是 PHP,后端数据库是 MySQL,目前只有一台服务器,由 ConvertLab 友情无偿赞助,大写的赞!再次感谢!
服务器部署环境是 Ubuntu 16.04.2,部署了以下服务及软件:
- Nginx - Http 反向代理,不要介绍了吧
- PHP-FPM - 一个常用的 PHP FastCGI 管理
- Elasticsearch - Elasticsearch 服务,用于社区的垂直搜索服务 Elastic 情报局 服务
- GOPA - 可以说是为社区而写的,一个轻量级的爬虫,用于爬取 Elatic 周边相关相关资料,创建索引存放到 Elasticsearch 里面,提供垂直搜索服务,代码地址
- Grok Debugger - 一个 Java 的 Grok pattern 调试服务,方便大家调试 Grok 日志解析规则,访问地址:grok.elasticsearch.cn
服务器上所有的财产就这些了,一个平淡无奇的网站,基本上所有的东西都能公开访问到,这个网站的目的就是为所有 Elastic 爱好者服务的,供大家交流和沟通的专属平台,所以请各位黑客大侠不要再扫描和攻击啦,画一个简单的拓扑图如下所示:
作为一个合格的网管,除了重启服务器之外,还必须要保证网站的正常运行,所以了解网站的运行情况就变成了一个需要解决的首要问题,我们可以先把任务具体列一下:
- 网站是否正常访问,各项服务有没有挂
- 网站访问情况如何,用户访问速度如何
- 网站访客统计分析,访客相关数据分析
- 服务器的各项指标,详细指标监控分析
- 服务器的各项服务,日志集中分析处理
- 服务器是否很安全,有没有黑客来造访
- 数据是否安全备份,有没有定期测试过
实在编不下去了(话说对的还蛮齐),说人话就是监控起服务器的各项指标和收集服务的日志,然后出几个分析的 Dashboard,监控报警整起来。
我们这次需要用到的工具主要就是 Elastic Stack 啦,Elastic Stack 包括 Elasticsearch、Logstash、Beats 和 Kibana,版本都用最新的 6.x,再结合我们实际的数据和实际的需求,在后面的文章里面,我会具体介绍它们是什么以及如何使用。
今天先写到这里,明天写监控指标的收集,此系列文章暂且定为需要 100 期完成。(开个玩笑,哈哈)。
收起阅读 »社区日报 第169期 (2018-01-25)
-
如何运行一个elasticsearch集群。 https://elasticsearch.cn/article/465
-
Elasticsearch自定义过滤插件实现复杂逻辑过滤。 http://t.cn/RQ10N3J
- Elasticsearch refresh 和flush 操作指南。 http://t.cn/RQ10Ttw
-
如何运行一个elasticsearch集群。 https://elasticsearch.cn/article/465
-
Elasticsearch自定义过滤插件实现复杂逻辑过滤。 http://t.cn/RQ10N3J
- Elasticsearch refresh 和flush 操作指南。 http://t.cn/RQ10Ttw
社区日报 第168期 (2018-01-24)
http://t.cn/RQncDxy
2. AIOps 时代下的利器:ELK
http://t.cn/RQnVo4r
3. Elasticsearch 使用 optimize 强制合并 segment 测试
http://t.cn/RQnfz71
编辑:江水
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/468
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
http://t.cn/RQncDxy
2. AIOps 时代下的利器:ELK
http://t.cn/RQnVo4r
3. Elasticsearch 使用 optimize 强制合并 segment 测试
http://t.cn/RQnfz71
编辑:江水
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/468
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
收起阅读 »
社区日报 第167期 (2018-01-23)
http://t.cn/RQTbVuA
2.eBay Elasticsearch 性能优化实战之中文篇。
http://t.cn/RQTbKQn
3.Elastic Filebeat 快速入门。
http://t.cn/RQTbjQy
编辑:叮咚光军
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/466
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
http://t.cn/RQTbVuA
2.eBay Elasticsearch 性能优化实战之中文篇。
http://t.cn/RQTbKQn
3.Elastic Filebeat 快速入门。
http://t.cn/RQTbjQy
编辑:叮咚光军
归档:https://elasticsearch.cn/article/466
订阅:https://tinyletter.com/elastic-daily
收起阅读 »